(Press-News.org) (WASHINGTON, April 25, 2024) – The volume of hematopoietic cell transplants rose among all racial/ethnic groups, but grew faster among African Americans and Hispanics compared with Non-Hispanic white individuals, mirroring changes in population growth rates. Survival after both autologous hematopoietic cell transplant (autoHCT) and allogeneic hematopoietic transplant (alloHCT) improved over time across racial/ethnic groups, though non-Hispanic African Americans still have worse outcomes, according to results published in Blood Advances.
AutoHCT uses a patient’s own stem cells to help restore the body's ability to make normal blood cells after high doses of chemotherapy and is a common treatment modality for patients with multiple myeloma and lymphoma. AlloHCT is a potentially curative treatment for people with life-threatening blood cancers such as acute leukemias and myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative syndromes and involves the use of stem cells from a suitable donor.
Although previous studies have shown improvements in outcomes post-transplant, researchers said they have been relatively small or have not included robust data to examine trends by racial/ethnic background. For this study, researchers used data from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research, which collects patient data for 90% of autoHCT and nearly all alloHCT recipients in the United States. The analysis included 79,904 autologous transplants and 65,662 allogeneic transplants for non-Hispanic whites, non-Hispanic African Americans, and Hispanics across five two-year cohorts from 2009 to 2018.
“This is certainly the largest study to look at the state of the science in terms of use of transplants by racial/ethnic minorities, involving over 145,000 transplants over a 10-year period. We wanted to see if improvements translated proportionally for all patients,” said Nandita Khera, MD, MPH, professor of medicine in the Division of Hematology/Oncology at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, AZ and the study’s lead author. “Overall, we saw that the volume of transplants and survival increased for everyone, but not at the same rate.”
While survival improved after both autoHCT and alloHCT over time for all racial/ethnic groups, Non-Hispanic African American adults and children undergoing alloHCT had a 13% and 62% higher risk of death, respectively, compared to non-Hispanic whites, even after adjusting for known risk factors for mortality such as age, treatments received, disease status, and donor type.
“This suggests the need to better understand the reasons for these disparities through qualitative studies exploring the impact of social determinants of health on outcomes,” Dr. Khera said.
A positive trend, she added, is that based on adjusted analyses, survival outcomes for Hispanic patients are now on par with those of non-Hispanic whites, which is an “indicator of progress in the field.”
While outside the scope of the study, she says improvements in transplant volume could be due to greater awareness of transplantation, better access to donors for alloHCT, and policy changes stemming from Medicaid expansion and the Affordable Care Act.
The study is limited in that it didn’t include enough patients of Asian descent or mixed race/ethnicity, and only captures people who are coming to transplant, not those who never gained access. The study’s senior author, Theresa Hahn, PhD of the Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, has a separate ongoing study that is examining true use. “We are using data from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program and the U.S. Census to estimate the pool of people who need a transplant and using the registry data to calculate those who actually get a transplant.”
“This study helps justify efforts for continued investments in research, training, practice, and community engagement to address the disparities in access and outcomes of these highly expensive and complex medical technologies so that everyone can enjoy the benefits of scientific progress equally,” Dr. Khera said. Fortunately, she explained there is increasing awareness of these issues and societal efforts such as ACCESS initiative: a collaboration between American Society of Transplantation and Cellular Therapy and NMDP to help expand access to HCT and improve outcomes for all.
# # #
Blood Advances (bloodadvances.org) is an online, open access journal publishing more peer-reviewed hematology research than any other academic journal worldwide. Blood Advances is part of the Blood journals portfolio (bloodjournals.org) from the American Society of Hematology (ASH) (hematology.org).
END
INDIANAPOLIS – Chlamydia and gonorrhea are the two most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the United States, impacting 2.4 million in 2021, and the number is rising. A recent study of individuals ages 15 to 60 measuring and comparing treatment rates for these STIs has found that nearly one-in-five patients with chlamydia and one-in-four patients with gonorrhea did not receive Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended treatment for their infection.
Individuals seen by clinicians in a private healthcare setting were less likely to receive CDC recommended treatment than those seen ...
Plastic is a very complex material that can contain many different chemicals, some of which can be harmful. This is also true for plastic food packaging.
“We found as many as 9936 different chemicals in a single plastic product used as food packaging,” said Martin Wagner, a professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU’s) Department of Biology.
Wagner has been working with chemicals in plastic products for several years. He is part of a research group at NTNU that ...
One might think that snow, of all things, is easy to describe: it is cold, white and covers the landscape like a blanket. What else is there to say about it?
A lot, according to Mathieu Nguyen. He has just defended his doctoral thesis on the optical properties of snow at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) in Gjøvik.
“Snow reflects all wavelengths of light and can have very different colours depending on the conditions and the angle at which light hits it. The age and density ...
HOUSTON – (April 25, 2024) – Diagnosing rare Mendelian disorders is a labor-intensive task, even for experienced geneticists. Investigators at Baylor College of Medicine are trying to make the process more efficient using artificial intelligence. The team developed a machine learning system called AI-MARRVEL (AIM) to help prioritize potentially causative variants for Mendelian disorders. The study is published today in NEJM AI.
Researchers from the Baylor Genetics clinical diagnostic laboratory noted that AIM's module can contribute to predictions ...
Cross Country Healthcare, Inc. (NASDAQ: CCRN), a pioneering force in tech-driven workforce solutions and advisory services, in collaboration with Florida Atlantic University's Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing, released its latest research findings in the fourth annual installment of the Future of Nursing Survey: “Embracing Technology While Preserving Humanity.” Drawing insights from more than 1,100 nursing professionals and students, the study illuminates the intricate interplay between cutting-edge health care technologies and the enduring essence of compassionate care.
Survey results reveal a nuanced perspective among nurses toward the integration of Artificial ...
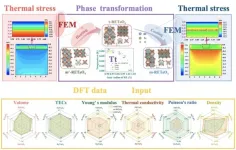
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) are widely used in gas turbine engines to obtain elevated working temperatures and improve engine efficiency. The phase transition of the ceramic layer is accompanied by a large volume difference, causing the concentration of thermal stress, eventually leading to TBCs to fall off and fail. Therefore, it is necessary to quantitatively evaluate the magnitude and distribution of thermal stress induced by phase transition in the ceramic layer.
A team of material scientists led ...
A new study published in the journal Animal-Human Interactions reveals that emotional turmoil experienced by dog owners after their pet has been stolen is like that of losing a loved one such as a caregiver losing their child.
The findings empirically support the notions that the ‘owner’ or guardian roles and relationships equate to familial relationships and, when faced with the theft of their pet, owners feel a similar sense of disenfranchised grief and ambiguous loss.
In the study, some participants felt the loss was more intense ...
The PhRMA Foundation (PhF) awarded $500,000 grants to David G. Armstrong, DPM, MD, PhD, of the University of Southern California and Nino Isakadze, MD, MHS, of Johns Hopkins University to conduct research using digital health technologies (DHTs) to improve health equity and health outcomes for patients.
Armstrong and Isakadze were selected out of a group of seven researchers awarded $25,000 planning grants in 2023 by the Foundation to develop comprehensive research proposals to study the use of DHTs for advancing patient health, especially in underserved populations.
“Digital ...
Athens, Greece – 25 April 2024: Women with heart disease are less often treated with cholesterol-lowering drugs than men, according to research presented today at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2024, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“Cholesterol-lowering drugs save lives and prevent heart attacks, and should be prescribed to all patients with coronary artery disease,” said study author Dr. Nina Johnston of Uppsala University, Sweden. “Unfortunately, our study shows that women are missing out on these essential medications.”
Patients with ...
Two of the biggest challenges faced by new and potential electric vehicle (EV) drivers are range anxiety and speed of charging, but these shouldn’t have to be challenges at all. That is according to a study by Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, and the University of Delaware, USA. Researchers discovered that a change in refuelling mindset, rather than improving the size or performance of the battery, could be the answer to these concerns.
The transition from filling up at a petrol station to recharging your electric vehicle in the most convenient location for you, requires a whole new way ...