(Press-News.org) Europe's forests have already been severely affected by climate change. Thousands of hectares of trees have already died due to drought and bark beetles. Scientists from the University of Vienna and the Technical University of Munich TUM have now investigated which trees can be used for reforestation. Their findings: only a few tree species are fit for the future, such as English oak in the UK. However, mixed forests are important for the survival of forests, otherwise the forest ecosystem as a whole could be weakened. The results of the study were recently published in the renowned journal Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Although European forests are naturally home to a mix of trees, the number of tree species is lower than in climatically comparable areas of North America or East Asia. In the future, even fewer species will be available to the forestry industry, as scientists led by Johannes Wessely and Stefan Dullinger from the University of Vienna have shown in their new study. Depending on the region, between a third and a half of the tree species found there today will no longer be able to cope with future conditions. "This is an enormous decline," says lead author Johannes Wessely, "especially when you consider that only some of the species are of interest for forestry".
The scientists examined the 69 more common of the just over 100 European tree species with regard to the 21st century in Europe. On average, only nine of these 69 species per location are fit for the future in Europe, compared to four in the UK. "Trees that are planted now for reforestation must survive under both current and future conditions. This is difficult because they have to withstand the cold and frost of the next few years as well as a much warmer climate at the end of the 21st century. There is only a very small overlap," says Wessely. In the UK, these climate-fit species include, for example, the English oak. Which tree species will suit which region of Europe in the future varies greatly overall.
Forest ecosystem at risk due to restriction of species
However, even with the selected set of future-proof trees, a major problem remains: the average of nine species is not enough for a species-rich mixed forest. "Mixed forests consisting of many tree species are an important measure to make forests more robust against disturbances such as bark beetles. In some places in Europe, however, we could run out of tree species to establish such colorful mixed forests," explains last author Rupert Seidl from the Technical University of Munich TUM.
Not all trees offer important properties
Trees store carbon, provide a habitat or food source for animals or can be processed into timber – these are all important properties of forests. But not all trees fulfill these functions equally; only an average of three of the nine climate-fit tree species can do this.
"Our work clearly shows how severely the vitality of forests is affected by climate change. We cannot rely solely on a new mix of tree species; rapid measures to mitigate climate change are essential for the sustainable protection of our forests," says Wessely.
More information on current research at the University of Vienna can be found in the University of Vienna's science magazine Rudolphina in the section Nature, Climate and the Cosmos.
END
How can forests be reforested in a climate-friendly way?
Only a few tree species are flexible enough to survive a century of rapid climate change
2024-04-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
More plants on the menu of ancient hunter-gatherers
2024-04-29
Conducted by an international team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (Leipzig, Germany), Géoscience et Environnement Toulouse (Toulouse, France), and the Institut National des Sciences de l’Archéologie et du Patrimoine (Rabat, Morocco), the study examines the diet of individuals associated with the Iberomaurusian culture discovered in the cave of Taforalt, Morocco. Using a comprehensive multi-isotopic approach, including zinc and strontium isotope analysis in dental enamel, carbon, nitrogen, ...
The aspirin conundrum: navigating negative results, age, aging dynamics and equity
2024-04-29
WASHINGTON – A new study examining the role of aspirin in breast cancer treatment reveals critical issues related to health equity and aging that have broad implications for cancer and other disease intervention trials, say researchers from Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center. They outline their concerns in an editorial accompanying the study’s findings published April 29 in the JAMA (“The Aspirin Conundrum: Navigating Negative Results, Age, Aging Dynamics and Equity”).
The ...
Cancer screening rates are significantly lower in US federally qualified health centers
2024-04-29
HOUSTON and ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. ― A national study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and The University of New Mexico (UNM) Comprehensive Cancer Center found major gaps in breast, cervical and colorectal cancer screening use in Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) in the U.S., relative to overall screening rates in the country.
The findings, published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, revealed screening use in FQHCs was 45.4% for breast cancer, 51% for cervical cancer and 40.2% for colorectal cancer, compared to cancer screening rates in the general American population of 78.2%, 82.9% and 72.3%, respectively.
“FQHCs ...
Nature's nudge: Study shows green views lead to healthier food choices
2024-04-29
Natural scenery typically conjures up positive emotions and a sense of wellbeing for most individuals. A new study by INSEAD shows that verdant views can also nudge people to pick healthier food.
Published in Communications Psychology, a new journal by Nature, the study suggests that spending time in a natural setting, such as walking in a park (vs. on city streets), or simply viewing greenery outside the window (vs. an urban view), leads people to make healthier food choices afterward.
“Our ...
AI algorithms can determine how well newborns nurse, study shows
2024-04-29
A modified pacifier and AI algorithms to analyze the data it produces could determine if newborns are learning the proper mechanics of nursing, a recent study shows.
Specifically, the researchers from the University of California San Diego measured if babies are generating enough suckling strength to breastfeed and whether they are suckling in a regular pattern based on eight independent parameters.
The results, published in the April 18 online edition of IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering ...
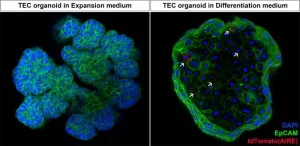
Scientists develop new organoid model to study thymus function
2024-04-29
Researchers from the Organoid group have developed a new organoid model that can be used to study the thymus. The organoids, derived from mouse thymus tissue, specifically model thymic epithelial cells (TECs). These cells are responsible for training the T cells of the immune system to properly respond to pathogens. It is the first laboratory model that enables long-term culture of TECs, which presents new opportunities to study their function. Ultimately, this could also bring new insights into the treatment ...
A revised classification of primary iron overload syndromes
2024-04-29
Background and Aims
The clinical introduction of hepcidin25 (Hep25) has led to a more detailed understanding of its relationship with ferroportin (FP) and divalent metal transporter1 in primary iron overload syndromes (PIOSs). In 2012, we proposed a classification of PIOSs based on the Hep25/FP system, which consists of prehepatic aceruloplasminemia, hepatic hemochromatosis (HC), and posthepatic FP disease (FP-D). However, in consideration of accumulated evidence on PIOSs, we aimed to renew the classification.
Methods
We ...
Expanding health equity by including nursing home residents in clinical trials
2024-04-29
INDIANAPOLIS – Clinical trials are constantly being designed and study participants enrolled to determine if medical treatments and therapies are safe and effective. Much has been written about the importance of including diverse populations in these trials.
However, the nearly 1.4 million individuals who live in the 15,600 nursing homes across the U.S. have been largely left out of clinical trials, despite the prevalence of such common conditions as hypertension, depression, diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease in this population.
A commentary by faculty of Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University, UCLA ...
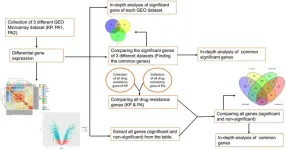
Identification and exploration of transcripts involved in antibiotic resistance mechanism of two critical superbugs
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic strains of bacteria are a global cause of morbidity and mortality. Hospital-acquired infections caused by Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were found vulnerable during the COVID-19 pandemic. They are also responsible for the onset of certain life-threatening infectious diseases such as cystic fibrosis, endocarditis, bacteremia, and sepsis. Looking into the importance of these two superbugs there is a strong need for extensive comparative differential gene expression analysis ...
Quantum fiber optics in the brain enhance processing, may protect against degenerative diseases
2024-04-29
WASHINGTON, DC – (April 26, 2024) The effects of quantum mechanics—the laws of physics that apply at exceedingly small scales—are extremely sensitive to disturbances. This is why quantum computers must be held at temperatures colder than outer space, and only very, very small objects, such as atoms and molecules, generally display quantum properties. By quantum standards, biological systems are quite hostile environments: they’re warm and chaotic, and even their fundamental components—such as cells—are considered very large.
But ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
New discovery of younger Ediacaran biota
Lymphovenous bypass: Potential surgical treatment for Alzheimer's disease?
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
[Press-News.org] How can forests be reforested in a climate-friendly way?Only a few tree species are flexible enough to survive a century of rapid climate change