(Press-News.org) It is estimated that up to 85% of stars exist in binary star systems, some even in systems with three or more stars. These stellar pairs are born together out of the same molecular cloud from a shared abundance of chemical building blocks, so astronomers would expect to find that they have nearly identical compositions and planetary systems. However, for many binaries that isn’t the case. While some proposed explanations attribute these dissimilarities to events occurring after the stars evolved, a team of astronomers have confirmed for the first time that they can actually originate from before the stars even began to form.
Led by Carlos Saffe of the Institute of Astronomical, Earth and Space Sciences (ICATE-CONICET) in Argentina, the team used the Gemini South telescope in Chile, one half of the International Gemini Observatory, supported in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation and operated by NSF NOIRLab. With the new, precise Gemini High Resolution Optical SpecTrograph (GHOST) the team studied the different wavelengths of light, or spectra, given off by a pair of giant stars, which revealed significant differences in their chemical make-up. “GHOST’s extremely high-quality spectra offered unprecedented resolution,” said Saffe, “allowing us to measure the stars’ stellar parameters and chemical abundances with the highest possible precision.” These measurements revealed that one star had higher abundances of heavy elements than the other. To disentangle the origin of this discrepancy, the team used a unique approach.
Previous studies have proposed three possible explanations for observed chemical differences between binary stars. Two of them involve processes that would occur well into the stars’ evolution: atomic diffusion, or the settling of chemical elements into gradient layers depending on each star’s temperature and surface gravity; and the engulfment of a small, rocky planet, which would introduce chemical variations in a star’s composition.
The third possible explanation looks back at the beginning of the stars’ formation, suggesting that the differences originate from primordial, or pre-existing, areas of nonuniformity within the molecular cloud. In simpler terms, if the molecular cloud has an uneven distribution of chemical elements, then stars born within that cloud will have different compositions depending on which elements were available at the location where each formed.
So far, studies have concluded that all three explanations are probable; however, these studies focused solely on main-sequence binaries. The ‘main-sequence’ is the stage where a star spends most of its existence, and the majority of stars in the Universe are main-sequence stars, including our Sun. Instead, Saffe and his team observed a binary consisting of two giant stars. These stars possess extremely deep and strongly turbulent external layers, or convective zones. Owing to the properties of these thick convective zones, the team was able to rule out two of the three possible explanations.
The continuous swirling of fluid within the convective zone would make it difficult for material to settle into layers, meaning giant stars are less sensitive to the effects of atomic diffusion — ruling out the first explanation. The thick external layer also means that a planetary engulfment would not change a star’s composition much since the ingested material would rapidly be diluted — ruling out the second explanation. This leaves primordial inhomogeneities within the molecular cloud as the confirmed explanation. “This is the first time astronomers have been able to confirm that differences between binary stars begin at the earliest stages of their formation,” said Saffe.
“Using the precision-measurement capabilities provided by the GHOST instrument, Gemini South is now collecting observations of stars at the end of their lives to reveal the environment in which they were born,” says Martin Still, NSF program director for the International Gemini Observatory. “This gives us the ability to explore how the conditions in which stars form can influence their entire existence over millions or billions of years.”
Three consequences of this study are of particular significance. First, these results offer an explanation for why astronomers see binary stars with such different planetary systems. “Different planetary systems could mean very different planets — rocky, Earth-like, ice giants, gas giants — that orbit their host stars at different distances and where the potential to support life might be very different,” said Saffe.
Second, these results pose a crucial challenge to the concept of chemical tagging — using chemical composition to identify stars that came from the same environment or stellar nursery — by showing that stars with different chemical compositions can still have the same origin.
Finally, observed differences previously attributed to planetary impacts on a star’s surface will need to be reviewed, as they might now be seen as having been there from the very beginning of the star’s life.
“By showing for the first time that primordial differences really are present and responsible for differences between twin stars, we show that star and planet formation could be more complex than initially thought,” said Saffe. “The Universe loves diversity!”
More information
This research was presented in a paper accepted in Astronomy & Astrophysics Letters. DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202449263
The team is composed of C. Saffe (ICATE-CONICET/UNSJ, Argentina), P. Miquelarena (ICATE-CONICET/UNSJ, Argentina), J. Alacoria (ICATE-CONICET, Argentina), E. Martioli (LNA/MCTI, Brasil), M. Flores (ICATE-CONICET/UNSJ, Argentina), M. Jaque Arancibia (Universidad de La Serena, Chile), R. Angeloni (International Gemini Observatory/NSF NOIRLab, Chile), E. Jofré (OAC/CONICET, Argentina), J. Yana Galarza (Carnegie Institution for Science, CA), E. González (UNSJ, Argentina), and A. Collado (ICATE-CONICET/UNSJ, Argentina).
NSF NOIRLab (U.S. National Science Foundation National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory), the U.S. center for ground-based optical-infrared astronomy, operates the International Gemini Observatory (a facility of NSF, NRC–Canada, ANID–Chile, MCTIC–Brazil, MINCyT–Argentina, and KASI–Republic of Korea), Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO), Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO), the Community Science and Data Center (CSDC), and Vera C. Rubin Observatory (operated in cooperation with the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory). It is managed by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA) under a cooperative agreement with NSF and is headquartered in Tucson, Arizona. The astronomical community is honored to have the opportunity to conduct astronomical research on I’oligam Du’ag (Kitt Peak) in Arizona, on Maunakea in Hawai‘i, and on Cerro Tololo and Cerro Pachón in Chile. We recognize and acknowledge the very significant cultural role and reverence that these sites have to the Tohono O’odham Nation, to the Native Hawaiian community, and to the local communities in Chile, respectively.
Links
Read the paper: Disentangling the origin of chemical differences using GHOST
Photos of the Gemini South telescope
Videos of the Gemini South telescope
Other Gemini South news
Other discoveries made with GHOST
Check out other NOIRLab Science Releases END
Gemini south reveals origin of unexpected differences in giant binary stars
Astronomers confirm that differences in the chemical composition of binary stars can be traced back to the earliest stages of their formation
2024-04-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hornets found to be primary pollinators of two Angelica species
2024-04-29
Researcher Ko Mochizuki of the University of Tokyo discovered that two species in the genus Angelica are pollinated primarily by hornets. This overturns the conventional belief that Angelica species are “generalists,” meaning that there is not one primary pollinator but a variety of species. As hornets are rarely primary pollinators, the discovery also impacts future ecological research and conservation efforts. The findings were published in the journal Ecology.
White, small, open, secretes nectar and produces pollen: these are the kinds of flowers that many types of insects can reach ...
Aspirin vs placebo as adjuvant therapy for breast cancer
2024-04-29
About The Study: In this randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial that included 3,020 patients with high-risk nonmetastatic breast cancer, daily aspirin therapy did not improve risk of breast cancer recurrence or survival in early follow-up. Despite its promise and wide availability, aspirin should not be recommended as an adjuvant breast cancer treatment.
Authors: Wendy Y. Chen, M.D., of the Dana Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Association of new-onset seizures with SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
2024-04-29
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis showed that the incidence proportion of new-onset seizures after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination was not statistically different between vaccine recipients and placebo recipients or unvaccinated participants in the pooled analyses of more than 118,000 participants in randomized clinical trials.
Authors: Churl-Su Kwon, M.D., M.P.H., of Columbia University in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.0967)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
How can forests be reforested in a climate-friendly way?
2024-04-29
Europe's forests have already been severely affected by climate change. Thousands of hectares of trees have already died due to drought and bark beetles. Scientists from the University of Vienna and the Technical University of Munich TUM have now investigated which trees can be used for reforestation. Their findings: only a few tree species are fit for the future, such as English oak in the UK. However, mixed forests are important for the survival of forests, otherwise the forest ecosystem as a whole could be weakened. The results of the study were recently published in the renowned journal Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Although European forests are naturally home to a ...
More plants on the menu of ancient hunter-gatherers
2024-04-29
Conducted by an international team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (Leipzig, Germany), Géoscience et Environnement Toulouse (Toulouse, France), and the Institut National des Sciences de l’Archéologie et du Patrimoine (Rabat, Morocco), the study examines the diet of individuals associated with the Iberomaurusian culture discovered in the cave of Taforalt, Morocco. Using a comprehensive multi-isotopic approach, including zinc and strontium isotope analysis in dental enamel, carbon, nitrogen, ...
The aspirin conundrum: navigating negative results, age, aging dynamics and equity
2024-04-29
WASHINGTON – A new study examining the role of aspirin in breast cancer treatment reveals critical issues related to health equity and aging that have broad implications for cancer and other disease intervention trials, say researchers from Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center. They outline their concerns in an editorial accompanying the study’s findings published April 29 in the JAMA (“The Aspirin Conundrum: Navigating Negative Results, Age, Aging Dynamics and Equity”).
The ...
Cancer screening rates are significantly lower in US federally qualified health centers
2024-04-29
HOUSTON and ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. ― A national study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and The University of New Mexico (UNM) Comprehensive Cancer Center found major gaps in breast, cervical and colorectal cancer screening use in Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) in the U.S., relative to overall screening rates in the country.
The findings, published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, revealed screening use in FQHCs was 45.4% for breast cancer, 51% for cervical cancer and 40.2% for colorectal cancer, compared to cancer screening rates in the general American population of 78.2%, 82.9% and 72.3%, respectively.
“FQHCs ...
Nature's nudge: Study shows green views lead to healthier food choices
2024-04-29
Natural scenery typically conjures up positive emotions and a sense of wellbeing for most individuals. A new study by INSEAD shows that verdant views can also nudge people to pick healthier food.
Published in Communications Psychology, a new journal by Nature, the study suggests that spending time in a natural setting, such as walking in a park (vs. on city streets), or simply viewing greenery outside the window (vs. an urban view), leads people to make healthier food choices afterward.
“Our ...
AI algorithms can determine how well newborns nurse, study shows
2024-04-29
A modified pacifier and AI algorithms to analyze the data it produces could determine if newborns are learning the proper mechanics of nursing, a recent study shows.
Specifically, the researchers from the University of California San Diego measured if babies are generating enough suckling strength to breastfeed and whether they are suckling in a regular pattern based on eight independent parameters.
The results, published in the April 18 online edition of IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering ...
Scientists develop new organoid model to study thymus function
2024-04-29
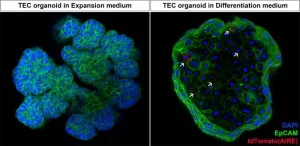
Researchers from the Organoid group have developed a new organoid model that can be used to study the thymus. The organoids, derived from mouse thymus tissue, specifically model thymic epithelial cells (TECs). These cells are responsible for training the T cells of the immune system to properly respond to pathogens. It is the first laboratory model that enables long-term culture of TECs, which presents new opportunities to study their function. Ultimately, this could also bring new insights into the treatment ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Gemini south reveals origin of unexpected differences in giant binary starsAstronomers confirm that differences in the chemical composition of binary stars can be traced back to the earliest stages of their formation