(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, April 30, 2024 – Interactions with voice technology, such as Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and Google Assistant, can make life easier by increasing efficiency and productivity. However, errors in generating and understanding speech during interactions are common. When using these devices, speakers often style-shift their speech from their normal patterns into a louder and slower register, called technology-directed speech.
Research on technology-directed speech typically focuses on mainstream varieties of U.S. English without considering speaker groups that are more consistently misunderstood by technology. In JASA Express Letters, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, researchers from Google Research, the University of California, Davis, and Stanford University wanted to address this gap.
One group commonly misunderstood by voice technology are individuals who speak African American English, or AAE. Since the rate of automatic speech recognition errors can be higher for AAE speakers, downstream effects of linguistic discrimination in technology may result.
“Across all automatic speech recognition systems, four out of every ten words spoken by Black men were being transcribed incorrectly,” said co-author Zion Mengesha. “This affects fairness for African American English speakers in every institution using voice technology, including health care and employment.”
“We saw an opportunity to better understand this problem by talking to Black users and understanding their emotional, behavioral, and linguistic responses when engaging with voice technology,” said co-author Courtney Heldreth.
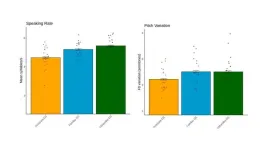
The team designed an experiment to test how AAE speakers adapt their speech when imagining talking to a voice assistant, compared to talking to a friend, family member, or stranger. The study tested familiar human, unfamiliar human, and voice assistant-directed speech conditions by comparing speech rate and pitch variation. Study participants included 19 adults identifying as Black or African American who had experienced issues with voice technology. Each participant asked a series of questions to a voice assistant. The same questions were repeated as if speaking to a familiar person and, again, to a stranger. Each question was recorded for a total of 153 recordings.
Analysis of the recordings showed that the speakers exhibited two consistent adjustments when they were talking to voice technology compared to talking to another person: a slower rate of speech with less pitch variation (more monotone speech).
“These findings suggest that people have mental models of how to talk to technology,” said co-author Michelle Cohn. “A set ‘mode’ that they engage to be better understood, in light of disparities in speech recognition systems.”
There are other groups misunderstood by voice technology, such as second-language speakers. The researchers hope to expand the language varieties explored in human-computer interaction experiments and address barriers in technology so that it can support everyone who wants to use it.
###
The article “African American English speakers’ pitch variation and rate adjustments for imagined technological and human addressees” is authored by Michelle Cohn, Zion Mengesha, Michal Lahav, and Courtney Heldreth. The article will appear in JASA Express Letters on April 30, 2024 (DOI: 10.1121/10.0025484). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1121/10.0025484.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
JASA Express Letters is a gold open-access journal devoted to the rapid and open dissemination of important new research results and technical discussion in all fields of acoustics. It serves physical scientists, life scientists, engineers, psychologists, physiologists, architects, musicians, and speech communication specialists who wish to quickly report the results of their acoustical research in letter-sized contributions. See https://asa.scitation.org/journal/jel.
ABOUT ACOUSTICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA
The Acoustical Society of America (ASA) is the premier international scientific society in acoustics devoted to the science and technology of sound. Its 7,000 members worldwide represent a broad spectrum of the study of acoustics. ASA publications include The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America (the world’s leading journal on acoustics), JASA Express Letters, Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics, Acoustics Today magazine, books, and standards on acoustics. The society also holds two major scientific meetings each year. See https://acousticalsociety.org/.
###
END
Machine listening: Making speech recognition systems more inclusive
Study explores how African American English speakers adapt their speech to be understood by voice technology.
2024-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Biodegradable ‘living plastic’ houses bacterial spores that help it break down
2024-04-30
A new type of bioplastic could help reduce the plastic industry’s environmental footprint. Researchers led by the University of California San Diego have developed a biodegradable form of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), a soft yet durable commercial plastic used in footwear, floor mats, cushions and memory foam. It is filled with bacterial spores that, when exposed to nutrients present in compost, germinate and break down the material at the end of its life cycle.
The work is detailed in a paper published on April 30 in Nature Communications.
The biodegradable TPU was made with ...
Loneliness grows as we age
2024-04-30
Adults are lonelier in early and older adulthood, less lonely in middle adulthood
Consistent loneliness pattern found across nine longitudinal studies, all collected prior to COVID-19 pandemic
CHICAGO --- Loneliness in adulthood follows a U-shaped pattern: it’s higher in younger and older adulthood, and lowest during middle adulthood, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study that examined nine longitudinal studies from around the world.
The study also identified several risk factors for heightened loneliness across the whole lifespan, including ...
Listening to mindfulness audios during radiation improves physical, emotional side effects
2024-04-30
It’s a ‘twofer’: Helping men manage side effects, receive cancer treatment at same time
Men with cancer rarely participate in oncology supportive care: ‘You build it, and they don’t come’
First study to deliver mindfulness during radiation therapy while patients were ‘a captive audience’
CHICAGO --- Men with prostate cancer who are treated with radiation therapy experience significant side effects such as fatigue, sleep problems, anxiety and depressive symptoms. But listening to mindfulness audio recordings significantly eased those symptoms, a new Northwestern ...
INSEAD’s research on sustainable circular models among the most influential papers in last 30 years
2024-04-30
Studies by INSEAD Professors Atalay Atasu and Luk Van Wassenhove have been recognised by members of the Product Operations Management Society for their impact.
Their papers are named among the top 10 most influential papers published in the first 30 years of the Production and Operations Management (POM) journal. They were voted for by POM society members based on an original list of 150 of the most cited papers since the publications launch in 1992.
Emeritus Professor Van Wassenhove is a co-author of two papers that made the top 10. His 2005 paper, “Sustainable Operations Management” looked at ...
Quitting smoking during pregnancy may have a positive effect on placental weight
2024-04-30
The researchers in Bergen and Exeter used data from the Norwegian Mother, Father and Child Cohort Study (MoBa) and a similar study in the UK, the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC), to investigate the relationship between smoking and placental weight. The aim was to determine to what extent expectant mothers who quit smoking could impact the weight of the placenta at the time of birth.
The study was recently published in the journal BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.
Previous research has demonstrated ...
GPT-4, Google Gemini fall short in breast imaging classification
2024-04-30
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Use of publicly available large language models (LLMs) resulted in changes in breast imaging reports classification that could have a negative effect on patient management, according to a new international study published today in the journal Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The study findings underscore the need to regulate these LLMs in scenarios that require high-level medical reasoning, researchers said.
LLMs are a type of artificial intelligence (AI) widely used today for a variety of purposes. In radiology, LLMs have already been tested in ...
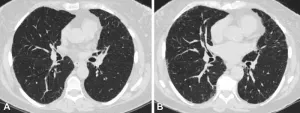
Lung abnormality progression linked to acute respiratory disease in smokers
2024-04-30
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Smokers who have small abnormalities on their CT scans that grow over time have a greater likelihood of experiencing acute respiratory disease events, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Quantitative interstitial abnormalities (QIA) are subtle abnormalities on chest CTs that do not meet the diagnostic criteria for advanced pulmonary diseases but are nonetheless associated with decreased ...
Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
2024-04-30
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts.
Pole-top fires pose significant challenges to power providers and communities worldwide. In March, pole-top fires cut power from 40,000 homes and businesses in Perth.
The 2020 Royal Commission into National Natural Disaster Arrangements found that power outages experienced by 280,000 customers from various energy providers during Black Summer fires were mainly triggered by events involving insulators ...
Citizen scientists help discover record-breaking exoplanet in binary star system
2024-04-30
A team of astronomers and citizen scientists has discovered a planet in the habitable zone of an unusual star system, including two stars and potentially another exoplanet.
The planet hunters spotted the Neptune-like planet as it crossed in front of its host star, temporarily dimming the star’s light in a way akin to a solar eclipse on Earth. This ‘transit method’ usually identifies planets with tight orbits, as they are more likely to follow paths that put them between Earth and their host star and, when following such paths, move into light-blocking positions more frequently. That’s why this newly discovered planet is ...
Tambourine Philanthropies commits over $5 million in new funding for research into ALS, in partnership with the Milken Institute
2024-04-30
WASHINGTON, DC (April 30, 2024)—Tambourine Philanthropies (Tambourine), in partnership with the Milken Institute Science Philanthropy Accelerator for Research and Collaboration (SPARC), is pleased to announce the recipients of its ALS Breakthrough Research Fund. Tambourine has committed over $5 million total to eight teams around the world for basic and discovery-focused research aiming to change how we understand and treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Tambourine launched the ALS Breakthrough Research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Machine listening: Making speech recognition systems more inclusiveStudy explores how African American English speakers adapt their speech to be understood by voice technology.