Strictly no dancing
2024-05-08
(Press-News.org)
Since the discovery of quantum mechanics more than a hundred years ago, it has been known that electrons in molecules can be coupled to the motion of the atoms that make up the molecules. Often referred to as molecular vibrations, the motion of atoms act like tiny springs, undergoing periodic motion. For electrons in these systems, being joined to the hip with these vibrations means they are constantly in motion too, dancing to the tune of the atoms, on timescales of a millionth of a billionth of a second. But all this dancing around leads to a loss of energy and limits the performance of organic molecules in applications like light emitting diodes (OLEDs), infrared sensors and fluorescent biomarkers used in the study of cells and for tagging diseases such as cancer cells.
Now, researchers using laser-based spectroscopic techniques have discovered ‘new molecular design rules’ capable of halting this molecular dance. Their results, reported in Nature, revealed crucial design principles that can stop the coupling of electrons to atomic vibrations, in effect shutting down their hectic dancing and propelling the molecules to achieve unparalleled performance.
“All organic molecules, such as those found in living cells or within the screen of your phone consist of carbon atoms connected to each other via a chemical bond,” said Cavendish PhD student Pratyush Ghosh, first author of the study and member of St John’s College.
“Those chemical bonds are like tiny vibrating springs, which are generally felt by electrons, impairing the performance of molecules and devices. However, we have now found that certain molecules can avoid these detrimental effects when we restrict the geometric and electronic structure of the molecule to some special configurations.”
To demonstrate these design principles, the scientists designed a series of efficient near-infrared emitting (680-800 nm) molecules. In these molecules, energy losses resulting from vibrations—essentially, electrons dancing to the tune of atoms —were more than 100 times lower than in previous organic molecules.
This understanding and development of new rules to design light emitting molecules has opened an extremely interesting trajectory for the future, where these fundamental observations can be applied to industries.
“These molecules also have a wide range of applications today. The task now is to translate our discovery to make better technologies, from enhanced displays to improved molecules for bio-medical imaging and disease detection,” concluded Professor Akshay Rao from Cavendish Laboratory, who led this research.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-08
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Ancient, expansive tracts of continental crust called cratons have helped keep Earth’s continents stable for billions of years, even as landmasses shift, mountains rise and oceans form. A new mechanism proposed by Penn State scientists may explain how the cratons formed some 3 billion years ago, an enduring question in the study of Earth’s history.
The scientists reported today (May 8) in the journal Nature that the continents may not have emerged from Earth’s ...
2024-05-08
The rapid advancement in photonic integrated circuits (PICs), whichcombine multiple optical devices and functionalities on a single chip, has revolutionized optical communications and computing systems.
For decades, silicon-based PICs have dominated the field due to their cost-effectiveness and through their integration with existing semiconductor manufacturing technologies, despite their limitations with regard to their electro-optical modulation bandwidth. Nevertheless, silicon-on-insulator optical transceiver chips were successfully commercialized, driving information traffic through millions of glass fibers in modern datacenters.
Recently, the lithium niobate-on-insulator ...
2024-05-08
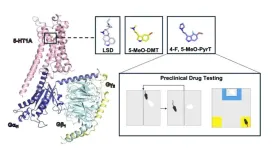
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have shed valuable light on the complex mechanisms by which a class of psychedelic drugs binds to and activates serotonin receptors to produce potential therapeutic effects in patients with neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety. In a study published May 8 in Nature, the team reported that certain psychedelic drugs interact with an underappreciated member of the serotonin receptor family in the brain known as 5-HT1A to produce therapeutic benefits in animal models.
“Psychedelics like LSD and psilocybin have entered clinical trials with promising early results, though we still don’t ...
2024-05-08
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC hospitals and USC Student Health, part of Keck Medicine, received the ‘LGBTQ+ Healthcare Equality Leader’ designation in the Human Rights Campaign Foundation’s 2024 Healthcare Equality Index (HEI).
HEI is the leading national benchmarking survey of health care facility policies and practices dedicated to the equitable treatment and inclusion of LGBTQ+ patients, visitors and employees. A record 1,065 health care facilities participated in the 2024 HEI survey; ...
2024-05-08
Psychiatrists and mental health professionals have a new standard for managing major depression, thanks to refreshed clinical guidelines published today by the Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT).
The CANMAT guidelines are the most widely used clinical guidelines for depression in the world. The new version integrates the latest scientific evidence and advances in depression care since the previous guidelines were published in 2016. The update was led by researchers at the University of B.C. and the University of Toronto, alongside ...
2024-05-08
Children who experience chronic lack of sleep from infancy may be at increased risk of developing psychosis in early adulthood, new research shows.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham examined information on nighttime sleep duration from a large cohort study of children aged between 6 months and 7 years old. They found that children who persistently slept fewer hours, throughout this time period, were more than twice as likely to develop a psychotic disorder in early adulthood, and nearly four times as likely to have a psychotic episode.
While ...
2024-05-08
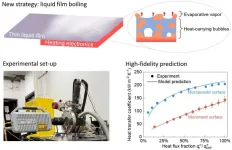
In the past decade, fires from electronic devices and batteries, from small smartphones to electrical vehicles and airplanes, have repeatedly made headlines. Enhanced computational power has led to a large amount of waste heat generation and undesirable temperature rise of electronics. Poor heat management is the cause of over half of electronic device failures. To tackle this issue, it is crucial to develop advanced cooling technologies to effectively manage heat and maintain temperatures in the working conditions.
Among various cooling technologies, liquid-vapor phase-change cooling, which utilizes the boiling or evaporation of ...
2024-05-08
This study is led by Prof. Xu (State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University), Prof. Yu (College of Information Science and Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University), Prof. Han (Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Technology, Tianjin University and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information Processing, School of Optoelectronic Engineering, Guilin University of Electronic Technology), and Prof. Sun ...
2024-05-08
Hypertension is among the leading cardiovascular diseases. Despite extensive research, evidence concerning the relationship between long-term exposure to ambient particulate matter and hypertension remains limited and inconsistent, particularly with regard to submicron particulate matter (PM1). While randomized controlled trials are considered the gold standard for causal inference, environmental epidemiological studies typically rely on observational data. Traditional approaches in observational studies are less effective than randomized controlled trials in fully controlling for confounding factors to achieve results with causal interpretability. With the advancement of causal ...
2024-05-08
Recently, Science Bulletin published a research conducted by Prof. Pingqing Fu and Dr. Libin Wu from Tianjin University, Peng Wang from Fudan University, and their Chinese and foreign collaborators. They explored the source of ammonium in PM2.5 at different heights of the atmospheric boundary layer in Beijing, and found that combustion-related ammonia is very important to ammonium in PM2.5 during haze pollution in winter.
Air pollution and treatment in Beijing have been widely concerned by both the scientific community and the public. Although its PM2.5 has decreased significantly in the past few years, there is still haze pollution in Beijing, especially in winter. The chemical compositions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Strictly no dancing