EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MAY 8, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Neuropathy, the nerve damage that causes pain and numbness in the feet and hands and can eventually lead to falls, infection and even amputation, is very common and underdiagnosed, according to a study published in the May 8, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“More than one-third of people with neuropathy experience sharp, prickling or shock-like pain, which increases their rates of depression and decreases quality of life,” said study author Melissa A. Elafros, MD, PhD, of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor and a member of the American Academy of Neurology. “People with neuropathy also have an increased risk of earlier death, even when you take into account other conditions they have, so identifying and treating people with or at risk for neuropathy is essential.”
The study involved 169 people from an outpatient internal medicine clinic serving mainly Medicaid patients in Flint, Michigan. The participants had an average age of 58 years and 69% were Black people. One-half of the people had diabetes, which can cause neuropathy. A total of 67% had metabolic syndrome, which is defined as having excess belly fat plus two or more of the following risk factors: high blood pressure, higher than normal triglycerides (a type of fat found in the blood), high blood sugar and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, or “good” cholesterol. These risk factors are also associated with neuropathy.
All participants were tested for distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Information about other health conditions was also collected.
A total of 73% of the people had neuropathy. Of those, 75% had not been previously diagnosed with the condition. Nearly 60% of those with neuropathy were experiencing pain.
Of those with neuropathy, 74% had metabolic syndrome, compared to 54% of those who did not have neuropathy.
After adjusting for other factors that could affect the risk of neuropathy, researchers found that people with metabolic syndrome were more than four times more likely to have neuropathy than people who did not have the syndrome.
Researchers were also looking for any relationship between race and income and neuropathy, as few studies have been done on those topics. There was no relationship between low income and neuropathy. For race, Black people had a decreased risk of neuropathy. Black people made up 60% of those with neuropathy and 91% of those without neuropathy.
“The amount of people with neuropathy in this study, particularly undiagnosed neuropathy, was extraordinarily high with almost three fourths of the study population,” Elafros said. “This highlights the urgent need for interventions that improve diagnosis and management of this condition, as well as the need for managing risk factors that can lead to this condition.”
A limitation of the study is that it is a snapshot in time; it did not follow people to see who developed neuropathy over time. It also did not look at reasons why people were not able to manage risk factors that can lead to neuropathy.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
Learn more about neuropathy at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, X and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world's largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN’s mission is to enhance member career fulfillment and promote brain health for all. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, concussion, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, headache and migraine.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, X, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
Study: Neuropathy very common, underdiagnosed
2024-05-08
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute announces Reid Wiseman as Bicentennial Commencement Speaker and will award its first posthumous honorary degree to Emily Warren Roebling
2024-05-08
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) today announced two special honorands for its Bicentennial Commencement celebrations. Astronaut and Artemis II Commander Reid Wiseman ’97 will return to RPI as the Bicentennial Commencement Speaker, and Emily Warren Roebling, who led the construction of the Brooklyn Bridge to completion, will receive a posthumous honorary degree, the first to be awarded in the history of RPI.
Reid Wiseman ’97
Reid Wiseman ’97, decorated naval aviator, test pilot, and commander of the Artemis II mission — which will ...
Diabetes in youth may increase risk for neurodegenerative disease, like Alzheimer’s disease later in life
2024-05-08
AURORA, Colo. (May 8, 2024) – Young people with diabetes may have a significantly higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease later in life, according to a new study by researchers in the Lifecourse Epidemiology of Adiposity and Diabetes (LEAD) Center at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
In the study, published this week in the journal Endocrines, scientists showed the presence of specific blood biomarkers indicating early signs of neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s ...
Teens who view their homes as more chaotic than their siblings have poorer mental health in adulthood
2024-05-08
Many parents ponder why one of their children seems more emotionally troubled than the others. A new study in the United Kingdom reveals a possible basis for those differences.
Adolescents who view their households as more unstructured, disorganized, or hectic than their siblings develop more mental health and behavioral problems in early adulthood, according to the study. The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
In research tracking ...
New insight into genesis of spina bifida
2024-05-08
A group of researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine led an investigation that offers new insight into the causes of spina bifida, the most common structural disorder of the human nervous system.
Work of the group, led by Keng Ioi Vong, Ph.D., and Sangmoon Lee, M.D. Ph.D., both from the laboratory of Joseph G. Gleeson, M.D., at the UC San Diego School of Medicine Department of Neurosciences and the Rady Children’s Institute for Genomic Medicine, reveals the first link between spina bifida and a common chromosomal microdeletion ...
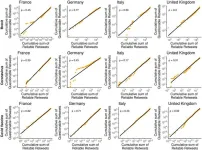
The spread of misinformation varies by topic and by country in Europe
2024-05-08
The eventual prevalence of a piece of misinformation may depend on its topic and the country in which it spreads, with notable differences between the UK, Germany, France and Italy, according to a study published May 8, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Fabiana Zollo from the Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Italy, and colleagues. This finding suggests that policies to combat misinformation and polarization may need to be context-specific in order to be effective, the authors say.
Researchers analyzed ...
Pacific Oyster density has increased up to 32-fold across a decade in some California waters, and coincides with summer seawater temperature increases of 2-4°C
2024-05-08
Pacific Oyster density has increased up to 32-fold across a decade in some California waters, and coincides with summer seawater temperature increases of 2-4°C
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302935
Article Title: Intra-decadal increase in globally-spread Magallana gigas in southern California estuaries
Author Countries: USA
Funding: “Funding was provided by CSU Fullerton and via subcontracts with Merkel & Associates, Inc. and Port of San Diego to DCZ. Funders had no involvement in the study design or data collection process.” The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
The EU could mitigate climate change equivalent to 13% of its agricultural greenhouse gas emissions by planting cover crops on bare soil before maize
2024-05-08
The EU could mitigate climate change equivalent to 13% of its agricultural greenhouse gas emissions by planting cover crops on bare soil before maize
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302139
Article Title: Cover crops support the climate change mitigation potential of agroecosystems
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The research was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research within the Project "CATCHY", project number: 031B1060C. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
Strengthening CAR-T therapy to work against solid tumors
2024-05-08
May 8, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Researchers at the National Cancer Institute-designated Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center (MECCC) have shown that a breakthrough therapy for treating blood cancers can be adapted to treat solid tumors—an advance that could transform cancer treatment. The promising findings, reported today in Science Advances, involve CAR-T cell therapy, which supercharges the immune system to identify and attack cancer cells.
“CAR-T cell therapy has revolutionized ...
Exercise, new drug class recommended for management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
2024-05-08
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) today released a new clinical guideline for effectively managing individuals diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). The guideline reiterates the importance of collaborative decision-making with patients who have HCM and provides updated recommendations for the most effective treatment pathways for adult and pediatric patients.
HCM is an inherited cardiac condition most often caused by a gene mutation that makes the heart muscle too thick (hypertrophy), which impairs its ability to adequately pump blood throughout ...
Study: Heavy snowfall and rain may contribute to some earthquakes
2024-05-08
When scientists look for an earthquake’s cause, their search often starts underground. As centuries of seismic studies have made clear, it’s the collision of tectonic plates and the movement of subsurface faults and fissures that primarily trigger a temblor.
But MIT scientists have now found that certain weather events may also play a role in setting off some quakes.
In a study appearing today in Science Advances, the researchers report that episodes of heavy snowfall and rain likely contributed to ...