(Press-News.org) The HIV variant dominant in Indonesia was introduced from Thailand over multiple events. The Kobe University study traces where it came from and how it spread from there, offering insights of possible value to the development of treatments against the disease.
HIV is the virus causing AIDS, but one of the things that make it so difficult to treat is that there are many variants of it. Kobe University virologist KAMEOKA Masanori says, “The diversity is increasing every day and the prevalent virus strains differ from region to region around the world.” Knowing which variants of the virus are prevalent in a given region and how it spreads from one to another is relevant not only to better trace the epidemic, but also to ensure that treatments are deployed against those variants that are most likely to occur in any given region.
In Indonesia, the fourth-most populous country on Earth, only a third of the affected have access to anti-HIV drugs, and little is known about the circulating strains. “Indonesia is recognized as one of the countries where the HIV/AIDS pandemic is still expanding. Kobe University has established a joint research center for infectious diseases at the Institute of Tropical Diseases at the Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia, and so we decided to decode the viral genome from blood samples of individuals infected with HIV-1 (out of the two main HIV types, the one causing the vast majority of AIDS cases worldwide) around the country to clarify the viral transmission trends,” explains Kameoka.
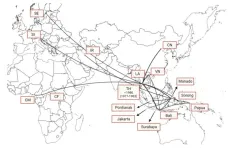
Their findings, now published in the journal Scientific Reports, show that all of the analyzed viruses belonged to a strain called “CRF01_AE” first identified in Thailand. But their detailed analysis shows that from there, the virus was brought to Indonesia at least three different times, sometimes via different countries such as Vietnam and Laos. And while it was Thai substrains that spread to most of Southeast Asia and also to other parts of the world, it was an Indonesian substrain that moved on to Iran. In the paper, the researchers write, “As a country with a high incidence of HIV-1 infection in Southeast Asia, Indonesia may contribute to the spread of HIV to other Asian countries.”
With their data, the Kobe University research team could trace the timeline of the spread of the CRF01_AE strain. Having originally emerged in Africa, it probably was brought to Thailand around 1977, from where it started to spread through Southeast Asia. It probably first entered Indonesia around 1980, then again via Laos around 1983 and via Vietnam around 1985. Only then, in 1985, it was recorded for the first time, in Thailand, and according to the WHO has been the dominant strain of HIV in Southeast Asia since 1990 and has become the dominant strain in East Asia, including also China and Japan, in the last decade.
Kameoka explains the importance of pursuing this line of research: “I personally believe that it is important to constantly monitor and accumulate information on viral genome genetic information in endemic areas, as viruses causing infectious diseases can change their properties due to genetic variation. Such information could also be useful for control and countermeasures against infectious diseases by estimating epidemic routes and transmission trends.”
This research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sport, Science and Technology Japan, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Research, and Technology, Indonesia, and Universitas Airlangga (grant 571/UN3.15/PT/2021). It was conducted in collaboration with researchers from Universitas Airlangga and Ritsumeikan University.
Kobe University is a national university with roots dating back to the Kobe Commercial School founded in 1902. It is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive research universities with nearly 16,000 students and nearly 1,700 faculty in 10 faculties and schools and 15 graduate schools. Combining the social and natural sciences to cultivate leaders with an interdisciplinary perspective, Kobe University creates knowledge and fosters innovation to address society’s challenges.
END
Tracing HIV in Indonesia
2024-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Metabolism of autism reveals developmental origins
2024-05-10
Researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine have shed new light on the changes in metabolism that occur between birth and the presentation of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) later in childhood. The researchers discovered that a small number of biochemical pathways are responsible for the majority of these changes, which could help inform new early detection and prevention strategies for autism.
“At birth, the physical appearance and behavior of a child who will develop autism over the next few years are indistinguishable from that of a neurotypical child. Indeed, in most cases the fate of the child with regard to autism is not ...
Comparative analysis of robot-assisted language learning systems and human tutors in English conversation lessons
2024-05-10
Advancements in large language models, robotics, and software such as text-to-speech, have made it possible to develop robots that can understand language, interact physically, and communicate verbally. These breakthroughs have opened up possibilities for robots to be used for educational purposes. However, this raises the question of whether robots are as good as human tutors. While robots offer certain benefits, they cannot replicate the nuanced interactions and personalized feedback human tutors provide.
To determine the suitability of using ...
Under 4-minute milers’ longevity shows that extreme exercise doesn’t seem to curb lifespan
2024-05-10
Extreme exercise doesn’t seem to shorten the lifespan as is widely believed, suggest the findings of a study on the longevity of the first 200 athletes to run a mile in under 4 minutes, and published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
They outlive the general population by several years, shows the study, which marks the 70th anniversary of the seminal achievement of Roger Bannister, who was the first person to run a mile in under 4 minutes in May 1954.
While regular moderate exercise is considered a pillar of healthy ageing, ...
Journal retracts 6 further articles and corrects 2 others authored by former editor
2024-05-10
The British Journal of Sports Medicine has retracted six further articles authored by former editor, Dr Paul McCrory, and corrected another two, following an extensive investigation of his sole authored content in the journal.*
The retractions comprise four ‘warm up’ editorials and one book review due to plagiarism. A letter has also been retracted because of duplicate publication. And a research article and a review article have been corrected due to inappropriate reuse of content.
This latest tranche of retractions and corrections completes BMJ’s 2-year investigation ...
Running under a four-minute mile could be the key to a long and healthy life
2024-05-10
A new study released to mark the 70th anniversary of Sir Roger Bannister’s sub-four-minute mile record has revealed the first 200 runners to follow in his footsteps also share another remarkable trait.
The study from investigators in Australia and Canada found the 200 elite runners live on average almost five years longer than the general population.
Professor Mark Haykowsky, the Research Chair in Aging and Quality of Life in the Faculty of Nursing at the University of Alberta, says the findings published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine demonstrate the vital importance of aerobic fitness.
Professor Haykowsky says: “Breaking ...
Transforming common soft magnets into a next-generation thermoelectric conversion materials by 3 minutes heat treatment
2024-05-10
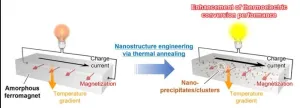
1. A research team from NIMS and Nagoya University has demonstrated that an iron-based amorphous alloy, widely used as a soft magnetic material in transformers and motors, can be transformed into a "transverse" thermoelectric conversion material that converts electric and thermal currents in orthogonal directions, with just a short period of heat treatment. This is the first example that highlights the importance of microstructure engineering in the development of transverse thermoelectric conversion materials, and provides new design guidelines for materials development to realize environmentally friendly power generation and thermal management technologies ...
Good vibrations: New tech may lead to smaller, more powerful wireless devices
2024-05-09
What if your earbuds could do everything your smartphone can do already, except better? What sounds a bit like science fiction may actually not be so far off. A new class of synthetic materials could herald the next revolution of wireless technologies, enabling devices to be smaller, require less signal strength and use less power.
The key to these advances lies in what experts call phononics, which is similar to photonics. Both take advantage of similar physical laws and offer new ways to advance technology. While photonics takes advantage of photons – or light – phononics does the same with phonons, which are the physical particles that transmit mechanical vibrations ...
Revolutionizing nurse work environment research
2024-05-09
PHILADELPHIA (May 9, 2024) – New research from Penn Nursing’s Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research (CHOPR) – recently published online in the journal Research in Nursing & Health – has successfully validated a new, streamlined version of the Practice Environment Scale of the Nursing Work Index (PES-NWI), originally authored in 2002 by Eileen T. Lake, PhD, RN, FAAN, Professor of Nursing, the Edith Clemmer Steinbright Professor in Gerontology, and Associate Director of CHOPR, who is also lead author on this publication. This innovative tool, known as the PES-5, is designed to revolutionize how nurse work environments are measured across ...
New ‘forever chemical’ cleanup strategy discovered
2024-05-09
As the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency cracks down on insidious “forever chemical” pollution in the environment, military and commercial aviation officials are seeking ways to clean up such pollution from decades of use of fire suppressant foams at military air bases and commercial airports.
Fire-suppression foams contain hundreds unhealthful forever chemicals, known by chemists as PFAS or poly- and per-fluoroalkyl substances. These compounds have stubbornly strong fluorine-to-carbon bonds, which allow them to persist indefinitely in the environment, hence the moniker “forever chemicals.” ...
Squeezed by neighbors, planet glows with molten lava
2024-05-09
UC Riverside astrophysicist Stephen Kane had to double check his calculations. He wasn’t sure the planet he was studying could be as extreme as it seemed.
Kane never expected to learn that a planet in this faraway star system is covered with so many active volcanoes that seen from a distance it would take on a fiery, glowing-red hue.
“It was one of those discovery moments that you think, ‘wow, it’s amazing this can actually exist,” Kane said. A paper detailing the discovery has been published in The Astronomical Journal.
Launched in 2018, NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey ...