(Press-News.org) The British Journal of Sports Medicine has retracted six further articles authored by former editor, Dr Paul McCrory, and corrected another two, following an extensive investigation of his sole authored content in the journal.*
The retractions comprise four ‘warm up’ editorials and one book review due to plagiarism. A letter has also been retracted because of duplicate publication. And a research article and a review article have been corrected due to inappropriate reuse of content.
This latest tranche of retractions and corrections completes BMJ’s 2-year investigation of McCrory’s single-authored articles published in BMJ journals. Several other articles in the journals portfolio were also investigated at the request of Dr McCrory’s former employer, the University of Melbourne.
It follows the retraction in 2022 of 10 articles—’warm up’ editorials, opinion pieces, and commentaries—due to plagiarism, redundant publication, and in one case, misrepresentation of a quote.
Expressions of concern have been applied to articles published in BMJ journals in which McCrory is the single author. Most were published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, with the remainder in The BMJ and Injury Prevention.
A rapid response posted online in the journal fully updates this latest evolution of the investigation, following the editorial which set out the initial concerns raised in 2022.
Dr McCrory, who edited the British Journal of Sports Medicine between 2001 and 2008, has approved these latest retractions and corrections.
Commenting on the conclusion of the investigation into Dr McCrory’s authorship, Dr Helen Macdonald, Publication Ethics & Content Integrity Editor for BMJ, said: “As no further concerns have been raised with BMJ about Dr McCrory’s authorship in BMJ journals, no further action will be taken.
“But should any further allegations be made about Dr McCrory’s work published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine or in any of the other titles in BMJ’s journal portfolio, these will be investigated.”
Professor Jonathan Drezner, editor in chief of the British Journal of Sports Medicine, added: “Upholding the scientific integrity of our published content is a top priority for the British Journal of Sports Medicine and all BMJ journals. This requires time and commitment, and I want to thank BMJ’s research integrity team and the University of Melbourne for their collaboration throughout this investigation.”
Editorial: Macdonald H, Ragavooloo S, Abbasi K, Drezner J. Update on the investigation into the publication record of former BJSM editor-in-chief Paul McCrory https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2022-106408
Retracted content
McCrory P, Davis G. Paediatric sport related concussion pilot study. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2005;39:116.
McCrory P. “Elementary, my dear Watson”. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2006;40:283-4.
McCrory P. Cheap solutions for big problems? British Journal of Sports Medicine 2007;41:545.
McCrory P. Is it all too much? British Journal of Sports Medicine 2007;41:405-6.
McCrory P. You are a better man than I am, Gunga Din. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2006;40:737.
McCrory P. Boxing: medical aspects. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2006;40:561.
Corrected content
McCrory P, Meeuwisse WH, Echemendia RJ, et al. What is the lowest threshold to make a diagnosis of concussion? British Journal of Sports Medicine 2013;47:268-71.
McCrory P. Prevalence of headache in Australian footballers. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2001;35:286-7.
END
Journal retracts 6 further articles and corrects 2 others authored by former editor
These conclude BMJ’s investigation into research integrity issues concerning Paul McCrory
2024-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Running under a four-minute mile could be the key to a long and healthy life
2024-05-10
A new study released to mark the 70th anniversary of Sir Roger Bannister’s sub-four-minute mile record has revealed the first 200 runners to follow in his footsteps also share another remarkable trait.
The study from investigators in Australia and Canada found the 200 elite runners live on average almost five years longer than the general population.
Professor Mark Haykowsky, the Research Chair in Aging and Quality of Life in the Faculty of Nursing at the University of Alberta, says the findings published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine demonstrate the vital importance of aerobic fitness.
Professor Haykowsky says: “Breaking ...
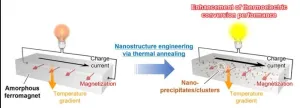
Transforming common soft magnets into a next-generation thermoelectric conversion materials by 3 minutes heat treatment
2024-05-10
1. A research team from NIMS and Nagoya University has demonstrated that an iron-based amorphous alloy, widely used as a soft magnetic material in transformers and motors, can be transformed into a "transverse" thermoelectric conversion material that converts electric and thermal currents in orthogonal directions, with just a short period of heat treatment. This is the first example that highlights the importance of microstructure engineering in the development of transverse thermoelectric conversion materials, and provides new design guidelines for materials development to realize environmentally friendly power generation and thermal management technologies ...
Good vibrations: New tech may lead to smaller, more powerful wireless devices
2024-05-09
What if your earbuds could do everything your smartphone can do already, except better? What sounds a bit like science fiction may actually not be so far off. A new class of synthetic materials could herald the next revolution of wireless technologies, enabling devices to be smaller, require less signal strength and use less power.
The key to these advances lies in what experts call phononics, which is similar to photonics. Both take advantage of similar physical laws and offer new ways to advance technology. While photonics takes advantage of photons – or light – phononics does the same with phonons, which are the physical particles that transmit mechanical vibrations ...
Revolutionizing nurse work environment research
2024-05-09
PHILADELPHIA (May 9, 2024) – New research from Penn Nursing’s Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research (CHOPR) – recently published online in the journal Research in Nursing & Health – has successfully validated a new, streamlined version of the Practice Environment Scale of the Nursing Work Index (PES-NWI), originally authored in 2002 by Eileen T. Lake, PhD, RN, FAAN, Professor of Nursing, the Edith Clemmer Steinbright Professor in Gerontology, and Associate Director of CHOPR, who is also lead author on this publication. This innovative tool, known as the PES-5, is designed to revolutionize how nurse work environments are measured across ...
New ‘forever chemical’ cleanup strategy discovered
2024-05-09
As the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency cracks down on insidious “forever chemical” pollution in the environment, military and commercial aviation officials are seeking ways to clean up such pollution from decades of use of fire suppressant foams at military air bases and commercial airports.
Fire-suppression foams contain hundreds unhealthful forever chemicals, known by chemists as PFAS or poly- and per-fluoroalkyl substances. These compounds have stubbornly strong fluorine-to-carbon bonds, which allow them to persist indefinitely in the environment, hence the moniker “forever chemicals.” ...
Squeezed by neighbors, planet glows with molten lava
2024-05-09
UC Riverside astrophysicist Stephen Kane had to double check his calculations. He wasn’t sure the planet he was studying could be as extreme as it seemed.
Kane never expected to learn that a planet in this faraway star system is covered with so many active volcanoes that seen from a distance it would take on a fiery, glowing-red hue.
“It was one of those discovery moments that you think, ‘wow, it’s amazing this can actually exist,” Kane said. A paper detailing the discovery has been published in The Astronomical Journal.
Launched in 2018, NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey ...
GPS-like system shows promise as HIV vaccine strategy to elicit critical antibodies
2024-05-09
DURHAM, N.C. – A team led by the Duke Human Vaccine Institute (DHVI) has developed a vaccine approach that works like a GPS, guiding the immune system through the specific steps to make broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV.
Publishing in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, the study describes an approach that provides step-by-step directions for the immune system to generate the elusive, yet necessary antibodies for a successful HIV vaccine.
“HIV is the fastest-evolving virus known. So it’s been a long-standing goal in HIV research to create ...
NSF awards $630,000 to study teeth of non-human primates
2024-05-09
The National Science Foundation awarded $630,444 to Kathleen Paul, an assistant professor of anthropology at the U of A, to provide a comprehensive outline of dental genetic architecture for two primate species of tamarins and macaques.
Paul's research team’s ultimate goal is to harness this information to advance bioanthropological practice, including the use of teeth for reconstructing evolutionary processes and experiences of stress and illness.
No live animals will be used in the research. Instead, skeletonized individuals from collections ...
Discrimination may accelerate aging
2024-05-09
Discrimination may speed up the biological processes of aging, according to a new study led by researchers at the NYU School of Global Public Health.
The research links interpersonal discrimination to changes at the molecular level, revealing a potential root cause of disparities in aging-related illness and death.
“Experiencing discrimination appears to hasten the process of aging, which may be contributing to disease and early mortality and fueling health disparities,” said Adolfo Cuevas, assistant professor in the Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences at NYU’s ...
New machine learning algorithm promises advances in computing
2024-05-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Systems controlled by next-generation computing algorithms could give rise to better and more efficient machine learning products, a new study suggests.
Using machine learning tools to create a digital twin, or a virtual copy, of an electronic circuit that exhibits chaotic behavior, researchers found that they were successful at predicting how it would behave and using that information to control it.
Many everyday devices, like thermostats and cruise control, utilize linear controllers – which use ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain cells drive endurance gains after exercise
Same-day hospital discharge is safe in selected patients after TAVI
Why do people living at high altitudes have better glucose control? The answer was in plain sight
Red blood cells soak up sugar at high altitude, protecting against diabetes
A new electrolyte points to stronger, safer batteries
Environment: Atmospheric pollution directly linked to rocket re-entry
Targeted radiation therapy improves quality of life outcomes for patients with multiple brain metastases
Cardiovascular events in women with prior cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
Transplantation and employment earnings in kidney transplant recipients
Brain organoids can be trained to solve a goal-directed task
Treatment can protect extremely premature babies from lung disease
Roberto Morandotti wins prestigious Max Born Award for pioneering research in quantum photonics
Scientists map brain's blood pressure control center
Acute coronary events registry provides insights into sex-specific differences
Bar-Ilan University and NVIDIA researchers improve AI’s ability to understand spatial instructions
New single-cell transcriptomic clock reveals intrinsic and systemic T cell aging in COVID-19 and HIV
Smaller fish and changing food webs – even where species numbers stay the same
Missed opportunity to protect pregnant women and newborns: Study shows low vaccination rates among expectant mothers in Norway against COVID-19 and influenza
Emotional memory region of aged brain is sensitive to processed foods
Neighborhood factors may lead to increased COPD-related emergency department visits, hospitalizations
Food insecurity impacts employees’ productivity
Prenatal infection increases risk of heavy drinking later in life
‘The munchies’ are real and could benefit those with no appetite
FAU researchers discover novel bacteria in Florida’s stranded pygmy sperm whales
DEGU debuts with better AI predictions and explanations
‘Giant superatoms’ unlock a new toolbox for quantum computers
Jeonbuk National University researchers explore metal oxide electrodes as a new frontier in electrochemical microplastic detection
Cannabis: What is the profile of adults at low risk of dependence?
Medical and materials innovations of two women engineers recognized by Sony and Nature
Blood test “clocks” predict when Alzheimer’s symptoms will start
[Press-News.org] Journal retracts 6 further articles and corrects 2 others authored by former editorThese conclude BMJ’s investigation into research integrity issues concerning Paul McCrory