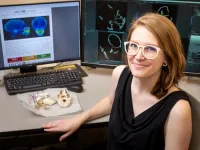
(Press-News.org) The National Science Foundation awarded $630,444 to Kathleen Paul, an assistant professor of anthropology at the U of A, to provide a comprehensive outline of dental genetic architecture for two primate species of tamarins and macaques.
Paul's research team’s ultimate goal is to harness this information to advance bioanthropological practice, including the use of teeth for reconstructing evolutionary processes and experiences of stress and illness.
No live animals will be used in the research. Instead, skeletonized individuals from collections of known lineage will be scanned and studied. These collections contain the teeth and skulls of two long-term monkey colonies, one captive and one free-ranging, enabling the researchers to study changes over generations.
Due to their high mineral content, teeth are relatively abundant in the fossil record. This makes them useful to paleoanthropologists, who can study quantifiable differences in external crown and root surfaces to answer questions about past environments, diets, growth, development and evolution.
But can they be sure they are answering their questions correctly? Not always. In some cases, dental characters have failed to reliably reconstruct evolutionary relationships among humans, their fossil ancestors and their close living primate relatives.
Using images generated at the U of A’s MICRO facility, Paul and her colleagues will take a deeper look into tooth variation. The powerful scanner at MICRO will allow the team to examine crown shape at both the outer enamel and inner dentin surfaces. Pairing these data with relatedness and environmental information from the primate colonies, Paul and her colleagues hope to gain insight into the driving mechanisms of dental variation and how genes are recruited throughout development to influence distinct tooth structures.
“In our teeth, the boundary between the hard enamel that we chew on and the underlying dentin is formed very early in development. Using this unique combination of datasets, we can now explore if and how subsequent developmental events diffuse the genetic signal initially encoded in that enamel-dentin boundary,” Paul explained.
Joining Paul as co-principal investigators are Susan Antón and Alejandra Ortiz, biological anthropology faculty at New York University.
The researchers expect to produce more than 1,000 microCT scans and 3D surface models of skulls and teeth for public access. The researchers will also work with K-12 students in Puerto Rico to teach them about evolution and bones during scheduled visits to the Caribbean Primate Research Center in Puerto Rico.
Paul directs the U of A’s Predental Studies Program, which helps position students for dental school acceptance. As such, the researchers will also use the grant to recruit aspiring dentists and underrepresented/first generation scholars for project roles with the goal of building a more diverse STEM community and the next generation of oral health professionals serving our state.
END
NSF awards $630,000 to study teeth of non-human primates
The award will be used to investigate the influence of genes and environment on morphology expressed across distinct tissues of the tooth crown.
2024-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Discrimination may accelerate aging
2024-05-09
Discrimination may speed up the biological processes of aging, according to a new study led by researchers at the NYU School of Global Public Health.
The research links interpersonal discrimination to changes at the molecular level, revealing a potential root cause of disparities in aging-related illness and death.
“Experiencing discrimination appears to hasten the process of aging, which may be contributing to disease and early mortality and fueling health disparities,” said Adolfo Cuevas, assistant professor in the Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences at NYU’s ...
New machine learning algorithm promises advances in computing
2024-05-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Systems controlled by next-generation computing algorithms could give rise to better and more efficient machine learning products, a new study suggests.
Using machine learning tools to create a digital twin, or a virtual copy, of an electronic circuit that exhibits chaotic behavior, researchers found that they were successful at predicting how it would behave and using that information to control it.
Many everyday devices, like thermostats and cruise control, utilize linear controllers – which use ...
How climate change will affect malaria transmission
2024-05-09
University of Leeds news release
Embargoed until 1900 BST, 9 May 2024
How climate change will affect malaria transmission
A new model for predicting the effects of climate change on malaria transmission in Africa could lead to more targeted interventions to control the disease according to a new study.
Previous methods have used rainfall totals to indicate the presence of surface water suitable for breeding mosquitoes, but the research led by the University of Leeds used several climatic and hydrological models to include real-world processes of evaporation, infiltration and flow through rivers.
This ...
Presenting a safer, low-cost, and low-energy whole-body magnetic resonance imaging device
2024-05-09
Machine learning enables cheaper and safer low-power magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without sacrificing accuracy, according to a new study. According to the authors, these advances pave the way for affordable, patient-centric, and deep learning-powered ultra-low-field (ULF) MRI scanners, addressing unmet clinical needs in diverse healthcare settings worldwide. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has revolutionized healthcare, offering noninvasive and radiation-free imaging. It holds immense promise for advancing medical diagnoses through artificial intelligence. However, despite its five decades of development, MRI remains largely inaccessible, particularly ...
Climate models predict larger than expected decline in African malaria transmission areas
2024-05-09
Areas at risk for malaria transmission in Africa may decline more than previously expected because of climate change in the 21st century, suggests an ensemble of environmental and hydrologic models. The combined models predicted that the total area of suitable malaria transmission will start to decline in Africa after 2025 through 2100, including in West Africa and as far east as South Sudan. The new study’s approach captures hydrologic features that are typically missed with standard predictive models of malaria transmission, offering a more nuanced view that could inform malaria control efforts in a warming world. Most of the burden of malaria falls on people living ...
Indian ocean temperature anomalies predict global dengue trends
2024-05-09
Sea surface temperature anomalies in the Indian Ocean predict the magnitude of global dengue epidemics, according to a new study. The findings suggest that the climate indicator could enhance the forecasting and planning for outbreak responses. Dengue – a mosquito-borne flavivirus disease – affects nearly half the world’s population. Currently, there are no specific drugs or vaccines for the disease, and outbreaks can have serious public health and economic impacts. As a result, the ability to predict the risk of outbreaks and prepare accordingly is crucial for many regions where ...
Cubic millimeter fragment of human brain reconstructed at nanoscale resolution
2024-05-09
Using more than 1.4 petabytes of electron microscopy (EM) imaging data, researchers have generated a nanoscale-resolution reconstruction of a millimeter-scale fragment of human cerebral cortex, providing an unprecedented view into the structural organization of brain tissue at the supracellular, cellular, and subcellular levels. The human brain is a vastly complex organ and, to date, little is known about its cellular microstructure, including the synaptic and neural circuits it supports. Disruption of these circuits is known to play a role in myriad brain disorders. Yet studying human brain ...
What makes a public health campaign successful?
2024-05-09
The highest performing countries across public health outcomes share many drivers that contribute to their success. That’s the conclusion of a new study published May 9 in the open-access journal PLOS Global Public Health by Dr. Nadia Akseer, an Epidemiologist-Biostatistician at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and co-author of the study and colleagues in the Exemplars in Global Health (EGH) program.
In recent years, the EGH program has begun to identify and study positive outliers when it comes to global health programs around the world, with an aim of uncovering not only which health interventions work, ...
Manganese sprinkled with iridium: a quantum leap in green hydrogen production
2024-05-09
As the world is transitioning from a fossil fuel-based energy economy, many are betting on hydrogen to become the dominant energy currency. But producing “green” hydrogen without using fossil fuels is not yet possible on the scale we need because it requires iridium, a metal that is extremely rare. In a study published May 10 in Science, researchers led by Ryuhei Nakamura at the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science (CSRS) in Japan report a new method that reduces the amount of iridium needed for the reaction by 95%, without altering the rate of hydrogen production. This breakthrough could revolutionize our ability to produce ecologically ...
Topological Phonos: Where vibrations find their twist
2024-05-09
An international team of researchers has discovered that the quantum particles responsible for the vibrations of materials—which influence their stability and various other properties—can be classified through topology. Phonons, the collective vibrational modes of atoms within a crystal lattice, generate disturbances that propagate like waves through neighboring atoms. These phonons are vital for many properties of solid-state systems, including thermal and electrical conductivity, neutron scattering, and quantum phases like charge density waves and superconductivity.
The spectrum of phonons—essentially ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
New study reveals differences between anime bamboo muzzle and actual bamboo
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
[Press-News.org] NSF awards $630,000 to study teeth of non-human primatesThe award will be used to investigate the influence of genes and environment on morphology expressed across distinct tissues of the tooth crown.