Strong-field photoelectron holography in the subcycle limit
2024-05-10
(Press-News.org)
Scientists Unveil Fundamental Electron-holograms for Ultrafast imaging of Atoms and Molecules
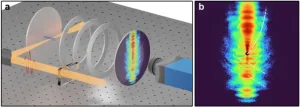
A team of scientists led by Professor Dong Eon Kim at the Pohang University of Science and Technology and Professor X. Lai at the Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology achieved a breakthrough in ultrafast imaging by separately and clearly observing two distinct holographic patterns, spider-leg- and fishbone-like, for the first time. They utilized near-single-cycle laser pulses not only to unveil and identify spider-leg-like and fishbone-like patterns, but also the Gouy phase effect on the electron hologram. This study opens an avenue for correctly extracting the internuclear separation of a target molecule from a holographic pattern.
Traditional imaging methods, such as X-ray diffraction, have limitations in capturing the rapid movement of electrons within molecules. This new approach, based on strong-field photoelectron holography (SFPH), promises to revolutionize our understanding of these fundamental building blocks with an unprecedented resolution. By using carrier-envelope-phase-controlled, near-single-cycle laser pulses, the team was able to clearly visualize and identify distinct holographic patterns, revealing details of electron dynamics within a target molecule because inter-cycle interference patterns that had previously hampered SFPH measurements were suppressed. "For the first time, these patterns have been directly observed," explained Professor Kim.
"Our approach allows us to control electron behavior on an attosecond timescale [an attosecond is a billionth of a billionth of a second]."
The researchers demonstrated the power of their method by extracting structural information about the target molecule. The results find applications in fields ranging from chemistry and biology to materials science.
Simplified Approach, Exciting Possibilities
Importantly, this new approach is simpler than previous methods that often require multiple measurements. This advancement is versatile, with the potential to be combined with other techniques to provide even more precise control and insights.
"Our work opens up exciting avenues for studying molecular dynamics and controlling chemical reactions," remarked Professor Kim.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-10
A research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has discovered how carboxysomes, carbon-fixing structures found in some bacteria and algae, work. The breakthrough could help scientists redesign and repurpose the structures to enable plants to convert sunlight into more energy, paving the way for improved photosynthesis efficiency, potentially increasing the global food supply and mitigating global warming.
Carboxysomes are tiny compartments in certain bacteria and algae that encase particular enzymes in a shell made of proteins. They perform carbon fixation, which is ...
2024-05-10
In the world around us, a quiet but very important evolution has been taking place in engineering over the last decades. As technology evolves, it becomes increasingly clear that building devices that are physically as close as possible to being perfect is not always the right approach. That’s because it often leads to designs that are very expensive, complex to build, and power-hungry. Engineers, especially electronic engineers, have become very skilled in using highly imperfect devices in ways that allow ...
2024-05-10
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Worker rights are among the least protected human rights in the world, according to new research from faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The findings are part of a new report published by the CIRIGHTS Data Project, the largest human rights dataset in the world. Since 1981, the project has ranked countries around the world on their respect for human rights, providing an annual “report card” on 25 internationally recognized human rights. The project ...
2024-05-10
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) is a typical soil-borne fungus that causes Fusarium wilt by infecting the roots and blocking the vascular tissues of host banana, and threatens the global banana production. Total four races have been reported in Foc, of which the tropical race 4 (TR4) is the most widespread race. In some severely affected banana plantations, the conventional ‘Cavendish’ variety had to be abandoned for other alternative crops due to the spread of TR4. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis of FWB and the development ...
2024-05-10
This study is led by Prof. Qunxin She (Shandong University) and Dr. Guanhua Yuan (Shandong University). The research group has constructed versatile genetic tools for Saccharolobus islandicus REY15A, one of the very few archaeal models for archaea biology and CRISPR biology research, and these include efficient genome editing, robust protein expression systems, interference plasmid assay, gene silencing and CRISPR-based gene editing. Nevertheless, plasmid vectors constructed for this crenarchaeon thus far are based solely on the pRN2 cryptic plasmid. “A dual host-vector system is required to enrich the genetic toolbox for this model archaeon.” the ...
2024-05-10
As kimchi has been drawing attention as a global healthy food trend, cabbage is one of the representative vegetables used as a main ingredient for manufacturing kimchi overseas.
The annual global production of cabbage and other Brassica crops is reported to be 72 million tons, and more than 30% of them are estimated to be discarded during the manufacturing and distribution processes, causing environmental pollution as well as considerable waste disposal costs in the industry.
In connection with this problem, Hae Choon Chang, President of the World Institute of Kimchi (WiKim), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, announced on April 22 that ...
2024-05-10
Every day our brains strive to optimize a trade-off: With lots of things happening around us even as we also harbor many internal drives and memories, somehow our thoughts must be flexible yet focused enough to guide everything we have to do. In a new paper in Neuron, a team of neuroscientists describes how the brain achieves the cognitive capacity to incorporate all the information that’s relevant without becoming overwhelmed by what’s not.
The authors argue that the flexibility arises from a key property observed in many neurons: “mixed selectivity.” While many neuroscientists used to think each cell had just one dedicated function, more recent evidence ...
2024-05-10
The HIV variant dominant in Indonesia was introduced from Thailand over multiple events. The Kobe University study traces where it came from and how it spread from there, offering insights of possible value to the development of treatments against the disease.
HIV is the virus causing AIDS, but one of the things that make it so difficult to treat is that there are many variants of it. Kobe University virologist KAMEOKA Masanori says, “The diversity is increasing every day and the prevalent virus strains differ from region to ...
2024-05-10
Researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine have shed new light on the changes in metabolism that occur between birth and the presentation of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) later in childhood. The researchers discovered that a small number of biochemical pathways are responsible for the majority of these changes, which could help inform new early detection and prevention strategies for autism.
“At birth, the physical appearance and behavior of a child who will develop autism over the next few years are indistinguishable from that of a neurotypical child. Indeed, in most cases the fate of the child with regard to autism is not ...
2024-05-10
Advancements in large language models, robotics, and software such as text-to-speech, have made it possible to develop robots that can understand language, interact physically, and communicate verbally. These breakthroughs have opened up possibilities for robots to be used for educational purposes. However, this raises the question of whether robots are as good as human tutors. While robots offer certain benefits, they cannot replicate the nuanced interactions and personalized feedback human tutors provide.
To determine the suitability of using ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Strong-field photoelectron holography in the subcycle limit