(Press-News.org) Employers are significantly more likely to offer job interviews and higher salaries to graduates with experience of artificial intelligence, according to new research published in the journal Oxford Economic Papers.
Researchers from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) conducted an experiment by submitting CVs for job vacancies from British 21-year-old applicants who held a 2:1 degree. Some of the applicants possessed AI capital – they had studied an 'AI in business' module – and this was mentioned in their cover letter for the application.
A matched pair of male applicants, one with AI capital and the other without, submitted applications, resulting in a total of 1,360 applications from male applicants to 680 UK companies. A total of 1,316 similarly matched applications from female applicants were sent to 658 firms.
Male applicants with AI capital received an interview invitation in 54% of cases, whereas male applicants without AI capital were invited to interview in 28% of cases.
Female applicants with AI capital received an interview invitation in 50% of cases, whereas female applicants without AI capital received one in 32% of cases.
In large firms, applicants with AI capital were 36 percentage points more likely to be invited to an interview than in small-medium sized firms.
Male applicants with AI qualifications were shortlisted for jobs offering wages that were, on average, 12% higher than those for male applicants without AI capital, while female applicants with AI qualifications were offered interviews for jobs offering wages that were, on average, 13% higher than without AI capital.
Lead author Professor Nick Drydakis, Professor of Economics at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), said: “In the UK, AI is causing dramatic shifts in the workforce, and firms need to respond to these demands by upgrading their workforces through enhancing their AI skill levels.
“Our study clearly indicates that employers value AI knowledge and skills among job applicants. Those applicants with AI capital were significantly more likely to be invited to interview and were also more likely to have access to better paid jobs.
“Job applicants with AI capital might possess the knowledge, skills and capabilities related to data analysis, data-driven decision-making, creativity, innovation, and effective communication, among other factors. These skills can enhance business operations, making them more efficient and potentially contributing to increased productivity within a firm.
“Larger firms particularly valued AI capital, possibly because they tend to undergo more AI-based structural technological transformations and have greater capacity for innovation.”
END
AI knowledge gets your foot in the door – new study
Firms more likely to offer interviews and higher wages to those who have studied AI
2024-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rwanda initiative: public health boost with cervical cancer screening for 20,000
2024-05-10
On April 30, BGI Genomics and the Rwanda Biomedical Centre (RBC) launched a cervical cancer screening program in Ngoma District, Eastern Province, Rwanda. This program will provide 20,000 Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA tests for local women, aiming to enhance cervical cancer screening and prevention efforts and improve local precision medical testing capabilities.
The launching event was attended by Wang Xuekun, Chinese Ambassador to Rwanda; Mr. Pudence Rubingisa, Governor of Eastern Province; Nathalie Niyonagira, the Mayor of Ngoma District, Rwanda; Dr. Albert Tuyishime, Head of Department, (HDPC) HIV/AIDS Diseases Prevention and Control, RBC; Dr. Theoneste ...
New tool to boost battle against childhood undernutrition
2024-05-10
A new tool developed at the University of Virginia School of Medicine will help doctors and scientists better understand and overcome childhood undernutrition that contributes to almost half of all deaths of children under 5.
The research model created by UVA’s Carrie A. Cowardin, PhD, and colleagues provides a more sophisticated way to study the effects of undernutrition on the microbiome, the microbes that naturally live inside the gut, and, in turn, on growth and the immune system.
Scientists routinely study the ...
Strong-field photoelectron holography in the subcycle limit
2024-05-10
Scientists Unveil Fundamental Electron-holograms for Ultrafast imaging of Atoms and Molecules
A team of scientists led by Professor Dong Eon Kim at the Pohang University of Science and Technology and Professor X. Lai at the Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology achieved a breakthrough in ultrafast imaging by separately and clearly observing two distinct holographic patterns, spider-leg- and fishbone-like, for the first time. They utilized near-single-cycle laser pulses not only ...
HKUST researchers throw new light on carboxysomes in key discovery that could boost photosynthesis
2024-05-10
A research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has discovered how carboxysomes, carbon-fixing structures found in some bacteria and algae, work. The breakthrough could help scientists redesign and repurpose the structures to enable plants to convert sunlight into more energy, paving the way for improved photosynthesis efficiency, potentially increasing the global food supply and mitigating global warming.
Carboxysomes are tiny compartments in certain bacteria and algae that encase particular enzymes in a shell made of proteins. They perform carbon fixation, which is ...
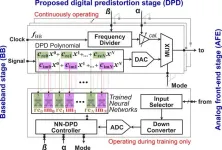
Learning the imperfections: a new approach to using neural networks for low-power digital pre-distortion (DPD) in mmWave systems
2024-05-10
In the world around us, a quiet but very important evolution has been taking place in engineering over the last decades. As technology evolves, it becomes increasingly clear that building devices that are physically as close as possible to being perfect is not always the right approach. That’s because it often leads to designs that are very expensive, complex to build, and power-hungry. Engineers, especially electronic engineers, have become very skilled in using highly imperfect devices in ways that allow ...
Worker rights are one of the least protected human rights, new research reveals
2024-05-10
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Worker rights are among the least protected human rights in the world, according to new research from faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The findings are part of a new report published by the CIRIGHTS Data Project, the largest human rights dataset in the world. Since 1981, the project has ranked countries around the world on their respect for human rights, providing an annual “report card” on 25 internationally recognized human rights. The project ...
Unveiling crucial virulent milRNAs implicated in the initial infection of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense
2024-05-10
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) is a typical soil-borne fungus that causes Fusarium wilt by infecting the roots and blocking the vascular tissues of host banana, and threatens the global banana production. Total four races have been reported in Foc, of which the tropical race 4 (TR4) is the most widespread race. In some severely affected banana plantations, the conventional ‘Cavendish’ variety had to be abandoned for other alternative crops due to the spread of TR4. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis of FWB and the development ...
Developing an efficient host-vector system for a model archaeon by solving CRISPR-based host-plasmid conflict
2024-05-10
This study is led by Prof. Qunxin She (Shandong University) and Dr. Guanhua Yuan (Shandong University). The research group has constructed versatile genetic tools for Saccharolobus islandicus REY15A, one of the very few archaeal models for archaea biology and CRISPR biology research, and these include efficient genome editing, robust protein expression systems, interference plasmid assay, gene silencing and CRISPR-based gene editing. Nevertheless, plasmid vectors constructed for this crenarchaeon thus far are based solely on the pRN2 cryptic plasmid. “A dual host-vector system is required to enrich the genetic toolbox for this model archaeon.” the ...
Development of technology for producing bioplastics from agricultural and food byproducts by the World Institute of Kimchi
2024-05-10
As kimchi has been drawing attention as a global healthy food trend, cabbage is one of the representative vegetables used as a main ingredient for manufacturing kimchi overseas.
The annual global production of cabbage and other Brassica crops is reported to be 72 million tons, and more than 30% of them are estimated to be discarded during the manufacturing and distribution processes, causing environmental pollution as well as considerable waste disposal costs in the industry.
In connection with this problem, Hae Choon Chang, President of the World Institute of Kimchi (WiKim), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, announced on April 22 that ...
How the brain is flexible enough for a complex world (without being thrown into chaos)
2024-05-10
Every day our brains strive to optimize a trade-off: With lots of things happening around us even as we also harbor many internal drives and memories, somehow our thoughts must be flexible yet focused enough to guide everything we have to do. In a new paper in Neuron, a team of neuroscientists describes how the brain achieves the cognitive capacity to incorporate all the information that’s relevant without becoming overwhelmed by what’s not.
The authors argue that the flexibility arises from a key property observed in many neurons: “mixed selectivity.” While many neuroscientists used to think each cell had just one dedicated function, more recent evidence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] AI knowledge gets your foot in the door – new studyFirms more likely to offer interviews and higher wages to those who have studied AI