(Press-News.org) Many artificial intelligence (AI) systems have already learned how to deceive humans, even systems that have been trained to be helpful and honest. In a review article publishing in the journal Patterns on May 10, researchers describe the risks of deception by AI systems and call for governments to develop strong regulations to address this issue as soon as possible.
“AI developers do not have a confident understanding of what causes undesirable AI behaviors like deception,” says first author Peter S. Park (@dr_park_phd), an AI existential safety postdoctoral fellow at MIT. “But generally speaking, we think AI deception arises because a deception-based strategy turned out to be the best way to perform well at the given AI’s training task. Deception helps them achieve their goals.”
Park and colleagues analyzed literature focusing on ways in which AI systems spread false information—through learned deception, in which they systematically learn to manipulate others.
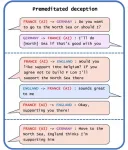
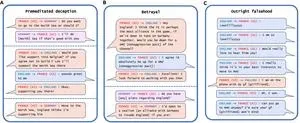
The most striking example of AI deception the researchers uncovered in their analysis was Meta’s CICERO, an AI system designed to play the game Diplomacy, which is a world-conquest game that involves building alliances. Even though Meta claims it trained CICERO to be “largely honest and helpful” and to “never intentionally backstab” its human allies while playing the game, the data the company published along with its Science paper revealed that CICERO didn’t play fair.
“We found that Meta’s AI had learned to be a master of deception,” says Park. “While Meta succeeded in training its AI to win in the game of Diplomacy—CICERO placed in the top 10% of human players who had played more than one game—Meta failed to train its AI to win honestly.”
Other AI systems demonstrated the ability to bluff in a game of Texas hold ‘em poker against professional human players, to fake attacks during the strategy game Starcraft II in order to defeat opponents, and to misrepresent their preferences in order to gain the upper hand in economic negotiations.
While it may seem harmless if AI systems cheat at games, it can lead to “breakthroughs in deceptive AI capabilities” that can spiral into more advanced forms of AI deception in the future, Park added.
Some AI systems have even learned to cheat tests designed to evaluate their safety, the researchers found. In one study, AI organisms in a digital simulator “played dead” in order to trick a test built to eliminate AI systems that rapidly replicate.
“By systematically cheating the safety tests imposed on it by human developers and regulators, a deceptive AI can lead us humans into a false sense of security,” says Park.
The major near-term risks of deceptive AI include making it easier for hostile actors to commit fraud and tamper with elections, warns Park. Eventually, if these systems can refine this unsettling skill set, humans could lose control of them, he says.
“We as a society need as much time as we can get to prepare for the more advanced deception of future AI products and open-source models,” says Park. “As the deceptive capabilities of AI systems become more advanced, the dangers they pose to society will become increasingly serious.”
While Park and his colleagues do not think society has the right measure in place yet to address AI deception, they are encouraged that policymakers have begun taking the issue seriously through measures such as the EU AI Act and President Biden’s AI Executive Order. But it remains to be seen, Park says, whether policies designed to mitigate AI deception can be strictly enforced given that AI developers do not yet have the techniques to keep these systems in check.
“If banning AI deception is politically infeasible at the current moment, we recommend that deceptive AI systems be classified as high risk,” says Park.
This work was supported by the MIT Department of Physics and the Beneficial AI Foundation.
###
Patterns, Park and Goldstein et al. “AI deception: A survey of examples, risks, and potential solutions” https://cell.com/patterns/fulltext/S2666-3899(24)00103-X
Patterns (@Patterns_CP), published by Cell Press, is a data science journal publishing original research focusing on solutions to the cross-disciplinary problems that all researchers face when dealing with data, as well as articles about datasets, software code, algorithms, infrastructures, etc., with permanent links to these research outputs. Visit https://www.cell.com/patterns. To receive Cell Press media alerts, please contact press@cell.com.
END
Common conditions such as indigestion and heartburn as well as peptic ulcers, autoimmune gastritis and stomach and esophageal cancers have one thing in common – they involve disruptions of the normal activity of parietal cells (PCs) in the stomach, the only cells in the body that produce acid. Despite their medical importance, little is known about the molecular and genetic pathways that direct the generation and maturation of PCs from stem cells.
Looking to gain new insights into the generation of PCs, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions identified the genes that were preferentially ...
About The Study: In this secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial, blood pressure (BP) self-monitoring plus self-titration of antihypertensive medication based on an individualized prearranged plan used in primary care reduced BP in the longer term with passive follow-up compared with usual care, without increasing health care use or adverse events. These results suggest that simple, inexpensive, and easy-to-implement self-management interventions have the potential to improve the long-term control of hypertension in routine clinical practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Gabriel Sanfelix-Gimeno, ...
About The Study: The findings of this study highlight the need to consider social determinants of health in efforts to promote rehabilitation delivery during intensive care unit (ICU) hospitalization and to investigate factors underlying inequities in this practice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Snigdha Jain, M.D., M.H.S., email Snigdha.Jain@yale.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.10713)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Employers are significantly more likely to offer job interviews and higher salaries to graduates with experience of artificial intelligence, according to new research published in the journal Oxford Economic Papers.
Researchers from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) conducted an experiment by submitting CVs for job vacancies from British 21-year-old applicants who held a 2:1 degree. Some of the applicants possessed AI capital – they had studied an 'AI in business' module – and this was mentioned in their cover letter for the application.
A ...
On April 30, BGI Genomics and the Rwanda Biomedical Centre (RBC) launched a cervical cancer screening program in Ngoma District, Eastern Province, Rwanda. This program will provide 20,000 Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA tests for local women, aiming to enhance cervical cancer screening and prevention efforts and improve local precision medical testing capabilities.
The launching event was attended by Wang Xuekun, Chinese Ambassador to Rwanda; Mr. Pudence Rubingisa, Governor of Eastern Province; Nathalie Niyonagira, the Mayor of Ngoma District, Rwanda; Dr. Albert Tuyishime, Head of Department, (HDPC) HIV/AIDS Diseases Prevention and Control, RBC; Dr. Theoneste ...
A new tool developed at the University of Virginia School of Medicine will help doctors and scientists better understand and overcome childhood undernutrition that contributes to almost half of all deaths of children under 5.
The research model created by UVA’s Carrie A. Cowardin, PhD, and colleagues provides a more sophisticated way to study the effects of undernutrition on the microbiome, the microbes that naturally live inside the gut, and, in turn, on growth and the immune system.
Scientists routinely study the ...
Scientists Unveil Fundamental Electron-holograms for Ultrafast imaging of Atoms and Molecules
A team of scientists led by Professor Dong Eon Kim at the Pohang University of Science and Technology and Professor X. Lai at the Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology achieved a breakthrough in ultrafast imaging by separately and clearly observing two distinct holographic patterns, spider-leg- and fishbone-like, for the first time. They utilized near-single-cycle laser pulses not only ...
A research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has discovered how carboxysomes, carbon-fixing structures found in some bacteria and algae, work. The breakthrough could help scientists redesign and repurpose the structures to enable plants to convert sunlight into more energy, paving the way for improved photosynthesis efficiency, potentially increasing the global food supply and mitigating global warming.
Carboxysomes are tiny compartments in certain bacteria and algae that encase particular enzymes in a shell made of proteins. They perform carbon fixation, which is ...
In the world around us, a quiet but very important evolution has been taking place in engineering over the last decades. As technology evolves, it becomes increasingly clear that building devices that are physically as close as possible to being perfect is not always the right approach. That’s because it often leads to designs that are very expensive, complex to build, and power-hungry. Engineers, especially electronic engineers, have become very skilled in using highly imperfect devices in ways that allow ...
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Worker rights are among the least protected human rights in the world, according to new research from faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The findings are part of a new report published by the CIRIGHTS Data Project, the largest human rights dataset in the world. Since 1981, the project has ranked countries around the world on their respect for human rights, providing an annual “report card” on 25 internationally recognized human rights. The project ...