(Press-News.org) Consumers are drawn to authenticity when it comes to craft-based firms, and a new study published in the Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal explores what factors can help give credence to such a quality.
The study, authored by Stanislav D. Dobrev of the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee and J. Cameron Verhaal of Tulane University, looked at how managers in identity-driven markets are challenged to maintain their authenticity as their company’s scale of operations expands. In such craft industries, the authors note, overt claims of authenticity by producers are ineffective. By studying the craft beer market, Dobrev and Verhaal found that managers can leverage three strategic assets to credibly and visibly communicate their firm’s identity: organizational resources, capabilities, and position.
“While authenticity used to be predominantly assessed as a quality of a person or an object, increasingly, it is being evaluated at the level of organizations,” Dobrev says. “So we need a theory that explains whether organizations can legitimately claim to be authentic and be perceived as such.”
The authors established that authenticity matters and is beneficial to producers, but it was less clear how to project an authentic identity that the audience would believe. The modern consumer is jaded, skeptical, and even cynical about brands — and this is especially true with authenticity claims because, the authors say, authenticity belies self-promotion by nature. So the central research question became: How do organizations succeed in presenting themselves as authentic?
One market where craft and authenticity are inextricably intertwined is the microbrewery and brewpub industry. Here, the driving motivation is to make beer “for beer’s sake” and not for the primary purpose of making money.
The research team collected data from the website beeradvocate.com, a respected source that posts reviews of beers by craft beer enthusiasts. They coded the individual reviews using definitions of authenticity and created a score for each review of each beer. They aggregated reviews of beers by the same brewery to produce an authenticity score for each producer for each year from 1996 to 2012, which allowed them to look at authenticity perceptions for the brewers over time and to statistically test what predicts the perceived levels of authenticity among consumers. They also coded many other features of the beers (e.g., style, awards won, naming strategy, perceived quality, ingredients) and of the producers (e.g., whether independently owned, range of beer styles, popularity). Finally, they coded the average appeal of each producer based on the combined rankings of its beers across all website reviews.
The authors found three main factors that play a role in credible claims of authenticity. The first, organizational resources, refers to a company’s independence as an ownership structure: Many successful craft producers enter production alliances with mass producers to increase volume, which tends to suggest to its audience that it’s shifted to placing profits first. Second is capabilities, or learning how to make different styles of beers: A focus on a single capability suggests a profit-driven operation because it’s more profitable to just make one beer style. Lastly, position refers to third-party endorsements, where others make the authenticity claim for the company. For example, winning an award by an independent third party can be thought of as an authenticity endorsement because that organization is charged with upholding and promoting the status of independent craft beer.
“Our theory emphasizes three pillars that help organizations to appear authentic even as they grow and become successful — a development that may erode perceptions of authenticity,” Dobrev says. “First, they have to convey a message to their target audience that they are what the audience considers authentic. … Second, the facets that make a company authentic have to be visible. This is needed because, again, if a company just says ‘we’re authentic,’ that will likely backfire. ... And third, for the same reason, the expressions or claims of authenticity have to be credible. Credibility comes with costly, often irreversible commitments — like investment in technology.”
To read the full context of the study and its methods, access the full paper available in the Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal.
About the Strategic Management Society
The Strategic Management Society (SMS) is the leading global member organization fostering and supporting rigorous and practice-engaged strategic management research. SMS enjoys the support of 3,000 members, representing more than 1,100 institutions and companies in more than 70 countries. SMS publishes three leading academic journals in partnership with Wiley: Strategic Management Journal, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, and Global Strategy Journal. These journals publish top-quality work applicable to researchers and practitioners with complementary access for all SMS Members. The SMS Explorer offers the latest insights and takeaways from the SMS Journals for business practitioners, consultants, and academics.
Click here to subscribe to the monthly SMS Explorer newsletter.
Click here to learn more about the programs and opportunities SMS has to offer.
END
Craft-based firms can project authenticity through credibly and visibly communicating their identity — but not through overt means
2024-05-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Size of a person’s fat cells may hold clues to their future weight
2024-05-11
New research being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May) suggests that it is possible to predict if someone is going to gain weight based on their size of their fat cells.
Individuals with large fat cells tend to lose weight over time, while those with small fat cells gain weight, the Swedish study found.
The size and number of fat cells are known to determine fat mass – how much body fat someone has. But their impact on long-term changes in body weight are unknown.
To explore this further, Professor Peter ...
Do sex differences in how adipose tissue responds to insulin explain why type 2 diabetes is more common in men?
2024-05-11
New research being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), and published in the International Journal of Obesity, could help explain why type 2 diabetes is more common in men than in women.
“Previous studies have shown that men develop type 2 diabetes (TD2) at a younger age and at a lower weight than women and, overall, men appear to be at higher risk of the condition,” says lead researcher Dr Daniel P Andersson, at the Department of Endocrinology, Karolinska University Hospital Huddinge, Stockholm, Sweden. “One reason for ...
Poor muscle health is common in people living with obesity – and increases the risk of an early death, Swedish study of people in UK finds
2024-05-11
New research being presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May) has found that poor muscle health is associated with a higher risk of an early death in people living with obesity.
Individuals with adverse muscle composition were up to three times more likely to die during the course of the study than those with healthy muscles, a Swedish study of people in the UK concluded.
“We found that just by looking at muscle composition we can predict which individuals with obesity are most likely to die during the next few years,” says lead researcher Dr Jennifer Linge, of AMRA Medical, ...
The American Journal of Health Economics releases a special issue on health equity
2024-05-10
The May 2024 issue of the American Journal of Health Economics collects articles on the topic of health equity. The edition was inspired in part by the COVID-19 pandemic, writes guest editor Mónica García-Pérez, and the ways in which that “health crisis exposed the sources of disparities among different US populations that affect access to health care, quality of care, and final health outcomes.”
Consisting of five papers, the issue devotes particular attention to the topics of “race/ethnicity, ...
Optical power evolution in fiber-optic networks: New framework for better modeling and control
2024-05-10
With the emergence of internet services such as AI-generated content and virtual reality, the demand for global capacity has surged, significantly intensifying pressures on fiber-optic communication systems. To address this surge and reduce operational costs, efforts are underway to develop autonomous driving optical networks (ADONs) with highly-efficient network operations. One of the most important tasks for an ADON is to accurately model and control the optical power evolution (OPE) over fiber links, since it ...
Therapeutic opportunities for hypermutated urothelial carcinomas beyond immunotherapy
2024-05-10
“These results argue that combinations based on immunotherapy may also provide an opportunity for targeting urothelial cancers with low TMB, and provide efficacy superior to classic chemotherapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 10, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on April 25, 2024, entitled, “Therapeutic opportunities for hypermutated urothelial carcinomas beyond immunotherapy.”
In this new editorial, researcher Ioannis A. Voutsadakis from Sault Area Hospital and Northern Ontario School of Medicine discusses tumor mutation burden (TMB)—a ...
UC Santa Cruz study discovers cellular activity that hints recycling is in our DNA
2024-05-10
By Rose Miyatsu, UC Santa Cruz Genomics Institute
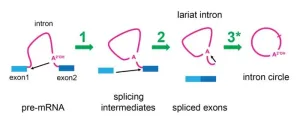
Although you may not appreciate them, or have even heard of them, throughout your body, countless microscopic machines called spliceosomes are hard at work. As you sit and read, they are faithfully and rapidly putting back together the broken information in your genes by removing sequences called “introns” so that your messenger RNAs can make the correct proteins needed by your cells.
Introns are perhaps one of our genome’s biggest mysteries. They are DNA sequences that interrupt the sensible protein-coding information ...
A retrospective look at Human Computer Interaction - free public lecture by Professor Manolya Kavakli
2024-05-10
Professor Manolya Kavakli is an expert in gamification
Her talk will examine the complex relationship between humans, computers and tech
She will examine how digital developments have the potential to improve lives and modernise industry.
The latest inaugural lecture at Aston University will look at the complex relationship between humans, computers and technology.
Professor Manolya Kavakli will discuss progress so far and offer insights into how to ease into digital transformation for the challenges that lie ahead.
The professor is an expert in gamification, the process of using elements of gaming in non-gaming situations such as learning and training.
She ...
Reducing prejudice in war zones proves challenging
2024-05-10
There are 62.5 million internally displaced persons worldwide, according to 2022 data by the UNHCR, the United Nations Refugee Agency. These individuals were forced to leave their homes but remain in the same country.
Prior research has shown that internally displaced persons often experience prejudice and discrimination, as residents in their new locale fear that the migrants may be insurgents or criminals, or compete for jobs.
Now, a new Dartmouth study involving Afghanistan indicates that changing such attitudes is an uphill battle. Given the decades of fighting there, Afghanistan has had one of the largest populations ...
Chapman professor contributes to breakthrough hemostasis and wound healing research
2024-05-10
A breakthrough study, published in Science Translational Medicine, features a biomedical engineering innovation with the potential to transform trauma care and surgical practices. Chapman University’s Fowler School of Engineering Founding Dean and Professor, Andrew Lyon, is a member of this multidisciplinary, multi-university scientific research team developing platelet-like particles that integrate into the body’s clotting pathways to stop hemorrhage. Sanika Pandit, an alumna of Chapman University, is also among the 15 authors in this research.
Addressing a longstanding gap in surgical and trauma care, this advancement holds potential for patient implementation. Patients ...