(Press-News.org) A new global study from IOP Publishing (IOPP) has found that certain peer review communities continue to feel overburdened by reviewer requests, while others remain underrepresented.
The survey, which generated over 3,000 responses from peer reviewers from across the globe, revealed regional and career-stage disparities:
30% of reviewers from high-income countries indicated that they receive too many peer review requests, compared with just 10% from low and middle-income countries*
Just 6% of respondents from China and 7% from India indicated that they receive too many requests, compared with 23% of respondents globally
28% of senior researchers say they receive too many requests, compared to just 7% of PhD students and 9% of postdocs
Laura Feetham-Walker, Reviewer Engagement Manager at IOPP, said: “As research outputs increase globally, the demands on peer reviewers also increase. The pressures can be eased by tapping into the groups that are currently underused, which in turn brings different viewpoints and expertise. It’s also important to acknowledge that peer review can be a daunting task for those with little or no experience in the process, which is why we offer free peer review training and certification tailored for the physical sciences. Casting the net wider when looking for potential reviewers and helping to boost peer review confidence are just some of the ways we’re working to address the global imbalance.
“Quality peer review is essential to the integrity and validity of science and relies on reviewers who are engaged, motivated and competent at providing constructive feedback. The insights we gain from this survey helps us to ensure we can continue to evolve the support we provide to the global reviewer community to help with their important work.”
Other findings from the survey show that just over half of reviewers (52%) prefer to review double-anonymous manuscripts where the identity of both authors and reviewers are concealed. IOPP introduced this approach in 2021 to tackle the significant gender, racial and geographical under-representation in the scholarly publishing process. The predominant peer review approach in the physical sciences hitherto has been single-anonymous.
IOPP’s ‘The State of Peer Review’ report provides rich and practical insights that will help improve the efficiency and quality of the peer review process. To read the full report, click here.
ENDS
*As defined by the World Bank
END
IOP Publishing report reveals peer review capacity not used to its full potential
2024-05-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Eco-friendly and affordable battery for low-income countries
2024-05-14
A battery made from zinc and lignin that can be used over 8000 times. This has been developed by researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, with a vision to provide a cheap and sustainable battery solution for countries where access to electricity is limited. The study has been published in the journal Energy & Environmental Materials.
“Solar panels have become relatively inexpensive, and many people in low-income countries have adopted them. However, near the equator, the sun sets at around 6 PM, leaving households and businesses without electricity. The hope is that ...
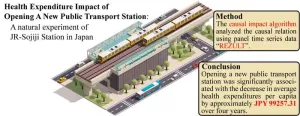
New transit station in Japan significantly reduced cumulative health expenditures
2024-05-14
The declining population in Osaka is related to an aging society that is driving up health expenditures. Dr. Haruka Kato, a junior associate professor at Osaka Metropolitan University, teamed up with the Future Co-creation Laboratory at Japan System Techniques Co., Ltd. to conduct natural experiments on how a new train station might impact healthcare expenditures.
JR-Sojiji Station opened in March 2018 in a suburban city on the West Japan Railway line connecting Osaka and Kyoto. The researchers used a causal impact algorithm to analyze the medical expenditure data gathered from the time series medical ...
USC study reveals racial disparities in diagnosis and drug use for dementia symptoms
2024-05-14
Compared to Black and Asian people, white and Hispanic people with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias were most likely to be diagnosed with symptoms like depression and agitation, according to a new study from the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics.
White and Hispanic people with these diagnoses were also most likely to be prescribed central nervous system (CNS) active drugs, including antidepressants, antipsychotics and anticonvulsants. Yet, these drugs have been associated with higher risk of falls, cardiovascular events, hospitalization and death, according to the study published today in the Journal of Alzheimer’s ...
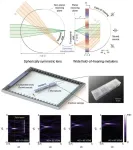
Metalens expands Its reach from light to sound
2024-05-14
Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Department of Chemical Engineering, and the Department of Electrical Engineering, Dr. Dongwoo Lee from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Beomseok Oh, a PhD student, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) have achieved a breakthrough in surpassing the limitations of traditional acoustic metalenses. They have successfully developed the first wide field-of-hearing metalens. This research has been recently published in the international journal, Nature Communications.
Sound ...
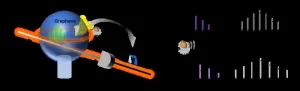
Ultrasensitive gas detection empowered by synergy of graphene and sub-comb dynamics
2024-05-14
Since the inception of microcomb, whose generation relies on Kerr nonlinearity in microresonator, the coherent soliton state has attracted intense researches. Although the operation of sub-comb outputs is straightforward, as noncoherent comb state, it was often overlooked in previous techniques. With graphene sensitization, this sub-comb heterodyne sensing device exhibits an exceptional response to gas molecular adsorption, achieving detect limits of 1.2 ppb for H2S gas and 1.4 ppb for SO2 gas, respectively. In summary, our research synergizes flexible ...
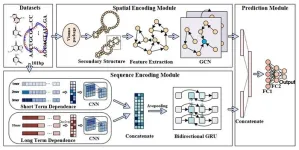
DeepCRBP: Improved predicting function of circRNA-RBP binding sites with deep feature learning
2024-05-14
There is growing evidence that it is essential to predict the interactions between circRNAs and RBP binding sites for diagnosing diseases and providing a potential target to treat diseases. Many studies have predicted the binding sites of circRNA-RBPs by using deep learning methods based on the sequence information of circRNAs for each RBP. However, the most of previous works only extract sequence feature, with a lack of exploiting the essential topological information from the secondary structure which contains rich spatial information.
To ...
Concussion, CTE experts warn term used to describe head impacts – “subconcussion” – is misleading and dangerous
2024-05-14
BOSTON (May 14, 2024) – A new editorial published this May in the British Journal of Sports Medicine by experts from Spaulding Rehabilitation, Boston University, Mayo Clinic, and the Concussion Legacy Foundation, argues that the term “subconcussion” is a dangerous misnomer that should be retired. The authors are appealing to the medical community and media to substitute the term with more specific terms so the public can better understand the risks of brain injuries and advance effective efforts to prevent chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).
“The public has been led to believe through media coverage ...
High genetic diversity discovered in South African leopards
2024-05-14
Researchers say the discovery of very high genetic diversity in leopards found in the Highveld region of South Africa has increased the need for conservation efforts to protect leopards in the country.
Declan Morris, a PhD candidate with the University of Adelaide’s School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, led the research project, which discovered that the two maternal lineages of leopards found in Africa overlap in the Highveld, leading to the high genetic diversity.
One lineage can be found across most of the African continent, while the other is confined ...
Facebook Marketplace is home to steals and deals—and serious trust issues
2024-05-14
Love it or hate it, Facebook Marketplace is the largest online resale site today with more than one billion monthly users. A new study conducted by UBC researchers sheds light on the intricate web of trust, privacy and safety factors shaping users’ experiences on this popular platform.
Researchers interviewed 42 Facebook Marketplace buyers and sellers in the U.S. and Canada to uncover the factors associated with trading decisions.
“Concerns for physical and financial safety, as well as well-being, were top ...
Mount Sinai study identifies genetic link between inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease
2024-05-14
[New York, NY, May 13, 2024] — Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have made a significant discovery, identifying genetic connections between inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD). Published in Genome Medicine (DOI 10.1186/s13073-024-01335-2) on May 13, their study highlights the potential for joint therapeutic strategies to target these two challenging disorders.
The team, led by Meltem Ece Kars, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at The Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine; Yuval Itan, PhD, Associate Professor of Genetics and Genomic ...