(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered 17 additional genes that drive the abnormal overgrowth of mutated blood cells as we age. The findings, published today (14 May) in Nature Genetics, provide a more complete view of the genetic factors behind clonal haematopoiesis – a process associated with ageing and linked to increased risks of blood cancers1.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Calico Life Sciences, California, and the University of Cambridge analysed sequencing data from over 200,000 individuals in the UK Biobank cohort. They searched for genes showing signals of "positive selection" – where mutations allow mutant cell populations to greatly expand over time.
The 17 newly discovered genes were found to have similar disease associations as previously known clonal haematopoiesis mutations, highlighting their clinical significance in driving the accumulation of mutant blood cell clones.
By uncovering these previously unrecognised genetic drivers, the research opens new avenues for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying clonal haematopoiesis and its role in disease development, leading to new ways to promote healthier ageing. Additionally, it could lead to better genetic tests that help identify the risks of blood cancers and cardiovascular diseases.
As we age, our cells accumulate random genetic mutations. Some of these mutations can provide a competitive growth advantage, allowing mutant cells to multiply and outnumber the healthy cells, forming large ‘clones’ or populations of identical mutant cells. When this positive selection happens in blood stem cells, it is called clonal haematopoiesis. This process is associated with blood cancers, cardiovascular disease and other age-related diseases.
While previous studies have identified around 70 genes linked to clonal haematopoiesis2, most cases observed recently have not involved mutations in any of these known driver genes. This suggests the involvement of additional genetic factors.
Researchers set out to map characteristic patterns of positive selection in the ageing blood system, leveraging whole exome sequencing data from over 200,000 individuals in the UK Biobank cohort. They identified 17 genes driving the accumulation of mutant cell clones in our blood, beyond the known set of drivers.
Incorporating mutations in these newly identified genes increased the prevalence of clonal haematopoiesis by 18 per cent in the UK Biobank cohort, underscoring their impact on ageing3.
Dr Michael Spencer Chapman, co-first author of the study at the Wellcome Sanger Institute, said: “While existing genetic tests have been valuable for early disease detection, our findings suggest there are opportunities to improve them further. By incorporating these 17 additional genes linked to clonal haematopoiesis, we can enhance genetic testing methods to better identify risks of associated blood cancers and cardiovascular diseases.”
Nick Bernstein, co-first author of the study, formerly at Calico Life Sciences, California and now based at NewLimit, said: “With our newly identified genes, we now have a more complete picture to explore strategies for delaying or reversing abnormal mutant cell overgrowths in blood to promote healthier ageing. These genes seem to affect inflammation and immunity, important factors in conditions like heart disease and strokes. While interventions based on this research are still a long way off, it opens up possibilities for future treatments across a wide range of diseases.”
Dr Jyoti Nangalia, senior author of the study from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute at the University of Cambridge, said: “Our study reveals a much broader set of genes fuelling mutant blood cell clone accumulation with age, but this is only the beginning. Larger studies across diverse populations are needed to identify remaining driver genes and provide further insights into this process and disease links.”
END
Genes driving age-related blood cell mutations uncovered
New research identifies a larger pool of genes involved in clonal haematopoiesis than previously thought, and their implications for disease and diagnostic tests.
2024-05-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
WASP-193b, a giant planet with a density similar to that of cotton candy
2024-05-14
An international team led by researchers from the EXOTIC Laboratory of the University of Liège, in collaboration with MIT and the Astrophysics Institute in Andalusia, has just discovered WASP-193b, an extraordinarily low-density giant planet orbiting a distant Sun-like star.
This new planet, located 1,200 light-years from Earth, is 50% larger than Jupiter but seven times less massive, giving it an extremely low density comparable to that of cotton candy. "WASP-193b is the second least dense planet discovered to date, after Kepler-51d, which is much smaller," explains ...
IOP Publishing report reveals peer review capacity not used to its full potential
2024-05-14
A new global study from IOP Publishing (IOPP) has found that certain peer review communities continue to feel overburdened by reviewer requests, while others remain underrepresented.
The survey, which generated over 3,000 responses from peer reviewers from across the globe, revealed regional and career-stage disparities:
30% of reviewers from high-income countries indicated that they receive too many peer review requests, compared with just 10% from low and middle-income countries*
Just 6% of respondents from China and 7% from India indicated that they ...
Eco-friendly and affordable battery for low-income countries
2024-05-14
A battery made from zinc and lignin that can be used over 8000 times. This has been developed by researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, with a vision to provide a cheap and sustainable battery solution for countries where access to electricity is limited. The study has been published in the journal Energy & Environmental Materials.
“Solar panels have become relatively inexpensive, and many people in low-income countries have adopted them. However, near the equator, the sun sets at around 6 PM, leaving households and businesses without electricity. The hope is that ...
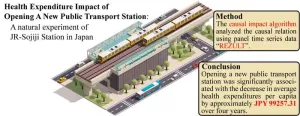
New transit station in Japan significantly reduced cumulative health expenditures
2024-05-14
The declining population in Osaka is related to an aging society that is driving up health expenditures. Dr. Haruka Kato, a junior associate professor at Osaka Metropolitan University, teamed up with the Future Co-creation Laboratory at Japan System Techniques Co., Ltd. to conduct natural experiments on how a new train station might impact healthcare expenditures.
JR-Sojiji Station opened in March 2018 in a suburban city on the West Japan Railway line connecting Osaka and Kyoto. The researchers used a causal impact algorithm to analyze the medical expenditure data gathered from the time series medical ...
USC study reveals racial disparities in diagnosis and drug use for dementia symptoms
2024-05-14
Compared to Black and Asian people, white and Hispanic people with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias were most likely to be diagnosed with symptoms like depression and agitation, according to a new study from the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics.
White and Hispanic people with these diagnoses were also most likely to be prescribed central nervous system (CNS) active drugs, including antidepressants, antipsychotics and anticonvulsants. Yet, these drugs have been associated with higher risk of falls, cardiovascular events, hospitalization and death, according to the study published today in the Journal of Alzheimer’s ...
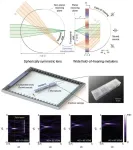
Metalens expands Its reach from light to sound
2024-05-14
Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Department of Chemical Engineering, and the Department of Electrical Engineering, Dr. Dongwoo Lee from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Beomseok Oh, a PhD student, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) have achieved a breakthrough in surpassing the limitations of traditional acoustic metalenses. They have successfully developed the first wide field-of-hearing metalens. This research has been recently published in the international journal, Nature Communications.
Sound ...
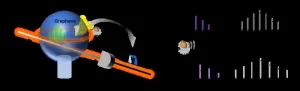
Ultrasensitive gas detection empowered by synergy of graphene and sub-comb dynamics
2024-05-14
Since the inception of microcomb, whose generation relies on Kerr nonlinearity in microresonator, the coherent soliton state has attracted intense researches. Although the operation of sub-comb outputs is straightforward, as noncoherent comb state, it was often overlooked in previous techniques. With graphene sensitization, this sub-comb heterodyne sensing device exhibits an exceptional response to gas molecular adsorption, achieving detect limits of 1.2 ppb for H2S gas and 1.4 ppb for SO2 gas, respectively. In summary, our research synergizes flexible ...
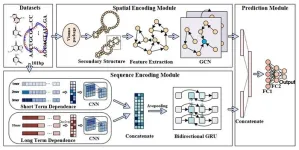
DeepCRBP: Improved predicting function of circRNA-RBP binding sites with deep feature learning
2024-05-14
There is growing evidence that it is essential to predict the interactions between circRNAs and RBP binding sites for diagnosing diseases and providing a potential target to treat diseases. Many studies have predicted the binding sites of circRNA-RBPs by using deep learning methods based on the sequence information of circRNAs for each RBP. However, the most of previous works only extract sequence feature, with a lack of exploiting the essential topological information from the secondary structure which contains rich spatial information.
To ...
Concussion, CTE experts warn term used to describe head impacts – “subconcussion” – is misleading and dangerous
2024-05-14
BOSTON (May 14, 2024) – A new editorial published this May in the British Journal of Sports Medicine by experts from Spaulding Rehabilitation, Boston University, Mayo Clinic, and the Concussion Legacy Foundation, argues that the term “subconcussion” is a dangerous misnomer that should be retired. The authors are appealing to the medical community and media to substitute the term with more specific terms so the public can better understand the risks of brain injuries and advance effective efforts to prevent chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).
“The public has been led to believe through media coverage ...
High genetic diversity discovered in South African leopards
2024-05-14
Researchers say the discovery of very high genetic diversity in leopards found in the Highveld region of South Africa has increased the need for conservation efforts to protect leopards in the country.
Declan Morris, a PhD candidate with the University of Adelaide’s School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, led the research project, which discovered that the two maternal lineages of leopards found in Africa overlap in the Highveld, leading to the high genetic diversity.
One lineage can be found across most of the African continent, while the other is confined ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
[Press-News.org] Genes driving age-related blood cell mutations uncoveredNew research identifies a larger pool of genes involved in clonal haematopoiesis than previously thought, and their implications for disease and diagnostic tests.