(Press-News.org) Seventy-five researchers from 46 countries recorded themselves performing traditional music and speaking in their own languages in a novel experiment investigating cross-cultural differences and similarities.
With rare exceptions, the rhythms of songs and instrumental melodies were slower than for speech, while the pitches were higher and more stable, according to the study published in Science Advances.
Unique for the number of languages represented – 55 – and the diversity of the researchers, the study provides “strong evidence for cross-cultural regularities,” according to senior author Dr Patrick Savage of Waipapa Taumata Rau, University of Auckland, a psychologist and musicologist who sang ‘Scarborough Fair’.
Speculating on underlying reasons, Savage, a Rutherford Discovery Fellowsenior research fellow in the University’s School of Psychology, suggests song is more predictably regular than speech to facilitate synchronization and social bonding.
“Slow, regular, predictable melodies make it easier for us to sing together in large groups,” he says. ”We’re trying to shed light on the cultural and biological evolution of two systems that make us human: music and language.”
Tapping into academic networks for cost-effective global reach, Savage and lead author Dr Yuto Ozaki from Keio University in Japan recruited researchers across Asia, Africa, the Americas, Europe and the Pacific to sing, perform instrumentals, recite lyrics and describe songs, providing audio samples to be analysed for features such as pitch, timbre and rhythm.
Dr Ozaki sang the Japanese folk song ‘Ōmori Jinku’. In Auckland, Professor Suzanne Purdy sang the Māori love song ‘Pōkarekare Ana’. Participants’ languages included Yoruba, Mandarin, Hindi, Hebrew, Arabic, Ukrainian, Russian, Balinese, Cherokee, Kannada, Spanish, Aynu, and dozens more.
Researchers with extensive vocal training included Dr Shantala Hegde, a Hindustani classical music singer and neuroscientist, and expert instrumentalists included Senegalese drummer Latyr Sy and a national champion of Japan’s Tsugaru-shamisen instrument, Gakuto Chiba.
Experts in ethnomusicology, music psychology, linguistics, and evolutionary biology took part, including the two most recent presidents of the Society for Music Perception and Cognition, Professor Peter Pfordresher (a native English speaker, pianist, and psychologist) and Dr Psyche Loui (a native Cantonese speaker, violinist, and neuroscientist).
Limitations of the study included the small sample size within each language. Additionally, while everyone taking part could sing a traditional song in their own language, not all participants could play its melody on an instrument. In some traditions, this idea didn’t even make sense. In those cases, researchers performed just the song’s rhythm using percussive instruments like a drum or clapping their hands.
Additional studies funded by Marsden Fund and Rutherford Discovery Fellowship awards from the Royal Society Te Apārangi will include more participants from a subset of the languages, including Māori and English.
For a three-minute video of researchers singing, speaking, and playing traditional instruments from their cultures, see https://youtu.be/a4eNNrdcfDM.
Full embargoed paper available on request.
END
Singing researchers investigate cross-cultural patterns in music, language
Seventy-five researchers from 46 countries in novel experiment
2024-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Animal brain inspired AI game changer for autonomous robots
2024-05-15
A team of researchers at Delft University of Technology has developed a drone that flies autonomously using neuromorphic image processing and control based on the workings of animal brains. Animal brains use less data and energy compared to current deep neural networks running on GPUs (graphic chips). Neuromorphic processors are therefore very suitable for small drones because they don’t need heavy and large hardware and batteries. The results are extraordinary: during flight the drone’s deep neural network processes data up to 64 times faster and consumes three times less energy than when running on a GPU. Further developments of this technology may ...
Summers warm up faster than winters, fossil shells from Antwerp show
2024-05-15
Niels de Winter, affiliated with the Department of Earth Sciences at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam and the AMGC research group at Vrije Universiteit Brussel, measured alongside colleagues from institutions such as the Institute for Natural Sciences in Brussels the chemical composition of fossil shells from Antwerp, Belgium. Those shells originate from molluscs such as oysters, cockles, and scallops found during the construction works of the Kieldrecht Lock. The molluscs lived lived during the Pliocene, approximately ...
Wearing face masks did not reduce risk of COVID infection after first Omicron wave, research shows
2024-05-15
After the first Omicron wave, research shows that many of the risks of Covid infection changed
Before February 2022, always wearing face masks and being retired were associated with reduced risk, but not after
Overseas travel was not associated with increased risk prior to February 2022, but then became a significant risk
Peer reviewed – meta-regression- humans
New research from the University of East Anglia has found that wearing face masks did not lower the risk of Covid infection following the initial surge of the Omicron variant.
The analysis of official data found that several risk ...
SF State receives $14M from the Genentech Foundation to support underrepresented students in STEM
2024-05-15
SAN FRANCISCO – May 15, 2024 – San Francisco State University announced today that it received $14 million from the Genentech Foundation to support two University programs that are training the next generation of life sciences leaders. The new five-year grant is the latest in the Genentech Foundation’s transformational support for University programs, which has totaled more than $33 million during their long-lasting partnership. This partnership has impacted more than 700 students since 2008, and an additional 350 students are projected to be supported by the new funding.
The new funds will continue sponsoring San Francisco State’s Genentech ...
Penalties for dropping out of ecosystem services incentive programs should equal lost environmental benefits
2024-05-15
Payment for Ecosystem Services programs (PES) are important tools that governments around the world use to improve water quality, protect forests and wildlife habitat, and sequester carbon. Under these programs, landowners - usually farmers - are paid to use their land in ways that protect or restore the environment, such as replacing row crops with trees or grassy zones adjacent to waterways. Many PES program contracts last 5 to 20 years, but participant drop out rates have consistently risen over the years.
A recent study by University of Maryland economists showed that PES programs ...
Lithuanian researchers’ new development in solar cell technology – a promise of a significant advancement in the field
2024-05-15
Researchers from Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania, who contributed to the development of record-breaking solar cells a few years ago, expanded their invention. The self-assembled monolayers can now be applied not only in inverted but also in regular structure perovskite solar cells.
Self-assembling molecules arrange themselves into a single-molecule-thick layer and in this case, they act as an electron-transporting layer in solar cells.
“The molecules that make up these monolayers, like a clever glue, ...
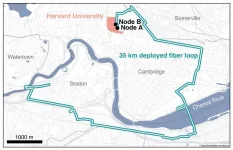
A simple internet with significant possibilities
2024-05-15
It’s one thing to dream up a quantum internet that could send hacker-proof information around the world via photons superimposed in different quantum states. It’s quite another to physically show it’s possible.
That’s exactly what Harvard physicists have done, using existing Boston-area telecommunication fiber, in a demonstration of the world’s longest fiber distance between two quantum memory nodes to date. Think of it as a simple, closed internet between point A and B, carrying a signal encoded not by classical ...
Unwrapping the origin story of the baobab
2024-05-15
The baobab (Adansonia) is a genus of trees with eight extant (in existence currently) species and a long history of humans marveling at them. For as much admiration the baobabs get, there is an equal amount of mystery surrounding their origin.
Genomic and ecological analyses recently done by a global research team led by Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, CAS (hosted by Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences), suggest that Madagascar, is the origin from where all other baobab species hail. With a deeper understanding of the baobabs' genetics, researchers are hoping to uncover some clues on what ...
The origin and long-distance travels of upside down trees
2024-05-15
The iconic baobabs, also known as upside-down trees, or the tree of life, have much cultural significance, inspiring innumerable arts, folklore, and traditions. A research published in Nature, involving international collaboration between Wuhan Botanical Garden (China), Royal Botanic Gardens (Kew, UK), University of Antananarivo (Madagascar) and Queen Mary University of London (UK) reveal a remarkable example of species radiation in Madagascar followed by long distance dispersal to Africa and Australia. With speciation, an astonishing divergence of pollination mechanisms evolved, that exploit hawkmoths, bats and lemurs for ...
Some mice may owe their monogamy to a newly evolved type of cell
2024-05-15
NEW YORK, NY — What makes the oldfield mouse steadfastly monogamous throughout its life while its closest rodent relatives are promiscuous? The answer may be a previously unknown hormone-generating cell, according to a new study published online today in Nature from scientists at Columbia's Zuckerman Institute.
"The hormone from these cells was actually first discovered in humans many decades ago, but nobody really knew what it did," said Andrés Bendesky, MD, PhD, a principal investigator at Columbia's Zuckerman Institute. "We’ve discovered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Singing researchers investigate cross-cultural patterns in music, languageSeventy-five researchers from 46 countries in novel experiment