(Press-News.org) A new study has confirmed a long-held assumption: that orcas take just one breath between dives.
The researchers used drone footage and biological data from tags suction-cupped to 11 northern and southern resident killer whales off the coast of B.C. to gather information on the animals’ habits.
Whaley fun facts
Published in PLOS ONE, the study found that residents spend most of their time making shallow dives, with the majority of dives less than one minute. The longest dive recorded was 8.5 minutes, for an adult male. “Killer whales are like sprinters who don’t have the marathon endurance of blue and humpback whales to make deep and prolonged dives,” said co-author Dr. Andrew Trites, professor in the UBC Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries (IOF).
For how many fish could an orca wish?
Confirming orcas take only one breath between dives allowed the researchers to calculate how many litres of oxygen adults and juveniles consume per minute. This provides another piece of the puzzle in estimating orca energy expenditure, and eventually, how many fish the animals need to eat per day. “Researchers can then work out if the orcas are getting enough food, including the endangered southern residents, a key factor in their conservation,” said first author Tess McRae, IOF masters student.
Breathe like an orca
Killer whales in the study took 1.2 to 1.3 breaths per minute while resting and 1.5 to 1.8 while travelling or hunting. Comparatively, humans tend to take about 15 breaths per minute when resting and from 40 to 60 while exercising. “It’s the equivalent of holding your breath and running to the grocery store, shopping, and coming back before breathing again,” said co-author Dr. Beth Volpov, IOF postdoctoral fellow.
END
Killer whales breathe just once between dives, study confirms
2024-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bees and butterflies on the decline in western and southern North America
2024-05-15
Bee and butterfly populations are in decline in major regions of North America due to ongoing environmental change, and significant gaps in pollinator research limit our ability to protect these species, according to a study published May 15, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Sara Souther of Northern Arizona University, US, and colleagues.
Recent research has detected declines in populations of pollinator species, sparking alarm from scientists and policymakers concerned about negative impacts on ecosystems and agriculture. These declines have been linked to various factors including climate change, habitat loss, and invasive species, but ...
Singing researchers investigate cross-cultural patterns in music, language
2024-05-15
Seventy-five researchers from 46 countries recorded themselves performing traditional music and speaking in their own languages in a novel experiment investigating cross-cultural differences and similarities.
With rare exceptions, the rhythms of songs and instrumental melodies were slower than for speech, while the pitches were higher and more stable, according to the study published in Science Advances.
Unique for the number of languages represented – 55 – and the diversity of the researchers, the study provides “strong evidence for cross-cultural regularities,” according to senior author Dr Patrick ...
Animal brain inspired AI game changer for autonomous robots
2024-05-15
A team of researchers at Delft University of Technology has developed a drone that flies autonomously using neuromorphic image processing and control based on the workings of animal brains. Animal brains use less data and energy compared to current deep neural networks running on GPUs (graphic chips). Neuromorphic processors are therefore very suitable for small drones because they don’t need heavy and large hardware and batteries. The results are extraordinary: during flight the drone’s deep neural network processes data up to 64 times faster and consumes three times less energy than when running on a GPU. Further developments of this technology may ...
Summers warm up faster than winters, fossil shells from Antwerp show
2024-05-15
Niels de Winter, affiliated with the Department of Earth Sciences at Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam and the AMGC research group at Vrije Universiteit Brussel, measured alongside colleagues from institutions such as the Institute for Natural Sciences in Brussels the chemical composition of fossil shells from Antwerp, Belgium. Those shells originate from molluscs such as oysters, cockles, and scallops found during the construction works of the Kieldrecht Lock. The molluscs lived lived during the Pliocene, approximately ...
Wearing face masks did not reduce risk of COVID infection after first Omicron wave, research shows
2024-05-15
After the first Omicron wave, research shows that many of the risks of Covid infection changed
Before February 2022, always wearing face masks and being retired were associated with reduced risk, but not after
Overseas travel was not associated with increased risk prior to February 2022, but then became a significant risk
Peer reviewed – meta-regression- humans
New research from the University of East Anglia has found that wearing face masks did not lower the risk of Covid infection following the initial surge of the Omicron variant.
The analysis of official data found that several risk ...
SF State receives $14M from the Genentech Foundation to support underrepresented students in STEM
2024-05-15
SAN FRANCISCO – May 15, 2024 – San Francisco State University announced today that it received $14 million from the Genentech Foundation to support two University programs that are training the next generation of life sciences leaders. The new five-year grant is the latest in the Genentech Foundation’s transformational support for University programs, which has totaled more than $33 million during their long-lasting partnership. This partnership has impacted more than 700 students since 2008, and an additional 350 students are projected to be supported by the new funding.
The new funds will continue sponsoring San Francisco State’s Genentech ...
Penalties for dropping out of ecosystem services incentive programs should equal lost environmental benefits
2024-05-15
Payment for Ecosystem Services programs (PES) are important tools that governments around the world use to improve water quality, protect forests and wildlife habitat, and sequester carbon. Under these programs, landowners - usually farmers - are paid to use their land in ways that protect or restore the environment, such as replacing row crops with trees or grassy zones adjacent to waterways. Many PES program contracts last 5 to 20 years, but participant drop out rates have consistently risen over the years.
A recent study by University of Maryland economists showed that PES programs ...
Lithuanian researchers’ new development in solar cell technology – a promise of a significant advancement in the field
2024-05-15
Researchers from Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania, who contributed to the development of record-breaking solar cells a few years ago, expanded their invention. The self-assembled monolayers can now be applied not only in inverted but also in regular structure perovskite solar cells.
Self-assembling molecules arrange themselves into a single-molecule-thick layer and in this case, they act as an electron-transporting layer in solar cells.
“The molecules that make up these monolayers, like a clever glue, ...
A simple internet with significant possibilities
2024-05-15
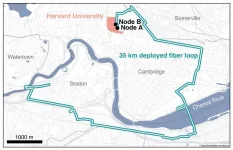
It’s one thing to dream up a quantum internet that could send hacker-proof information around the world via photons superimposed in different quantum states. It’s quite another to physically show it’s possible.
That’s exactly what Harvard physicists have done, using existing Boston-area telecommunication fiber, in a demonstration of the world’s longest fiber distance between two quantum memory nodes to date. Think of it as a simple, closed internet between point A and B, carrying a signal encoded not by classical ...
Unwrapping the origin story of the baobab
2024-05-15
The baobab (Adansonia) is a genus of trees with eight extant (in existence currently) species and a long history of humans marveling at them. For as much admiration the baobabs get, there is an equal amount of mystery surrounding their origin.
Genomic and ecological analyses recently done by a global research team led by Sino-Africa Joint Research Center, CAS (hosted by Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences), suggest that Madagascar, is the origin from where all other baobab species hail. With a deeper understanding of the baobabs' genetics, researchers are hoping to uncover some clues on what ...