(Press-News.org) DURHAM N.C. – An international team of scientists has uncovered toxic metals in mineral phosphate fertilizers worldwide by using a new tool to identify the spread and impact of such contaminants on soil, water resources, and food supply.
“While mineral phosphate fertilizers are critical to boost global sustainable agriculture and food security, we found high levels of toxic metals in many fertilizers worldwide,” said Avner Vengosh, chair of the Earth and Climate Sciences division at Duke University’s Nicholas School of the Environment. “Our study developed a new method to identify sources and impacts of these metals on the environment.” Those metals included cadmium, uranium, arsenic, vanadium, and chromium.
Use of mineral fertilizer – synthetic or naturally occurring substances with essential nutrients needed for plant growth – has helped boost sustainable crop yields worldwide. But until recently, its contamination with toxic metals has not been systematically evaluated. This new study analyzes global phosphate fertilizers from major phosphate-mining countries.
“We measured strontium isotopes in both phosphate rocks and fertilizers generated from those rocks to show how fertilizers’ isotope ‘fingerprint’ matches their original source,” said Robert Hill, the study’s lead author and a PhD student at Duke University.
Isotopes are variations of an element, in this case strontium. Chemical analysis of each fertilizer shows a unique isotope mix that matches phosphate rocks from where it was sourced.
“Given variations of strontium isotopes in global phosphate rocks, we have established a unique tool to detect fertilizers’ potential impact worldwide,” Hill said.
To learn whether strontium isotopes are a reliable indicator of trace elements in fertilizer worldwide, researchers analyzed 76 phosphate rocks, the main source of phosphate fertilizers, and 40 fertilizers from major phosphate rock-producing regions including the western United States, China, India, North Africa and the Middle East. Researchers collected samples from mines, commercial sources, and Tidewater Research Station, an experimental field in North Carolina. The research team published its findings on May 9, 2024 in Environmental Science & Technology Letters.
Metals found in soil and groundwater come from both naturally occurring and human-made sources.
“Strontium isotopes essentially are a ‘fingerprint’ that can reveal contamination in groundwater and soil worldwide,” said Vengosh. His research team has also used strontium isotopes to trace environmental contamination in landfill leaching, coal mining, coal ash, fracking fluids, and groundwater that is pulled to the surface with oil and natural gas extraction.
“The isotope is a proxy to identify the source of contamination,” Vengosh said. “Without this tool, it is difficult to identify, contain, and remediate contamination linked to fertilizer.”
Fertilizers in the study showed different concentrations of trace elements, with higher levels observed in fertilizers from the U.S. and the Middle East compared to those from China and India. As a result, the researchers conclude that phosphate fertilizers from the U.S. and the Middle East will have a greater impact on soil quality due to their higher concentrations of uranium, cadmium, chromium as compared to fertilizers from China and India, which have higher concentrations of arsenic.
The National Science Foundation funded this study. (EAR-2305946)
CITATION: “Tracing the Environmental Effects of Mineral Fertilizer Application with Trace Elements and Strontium Isotope Variations,” Robert C. Hill, Gordon D. Z. Williams, Zhen Wang, Jun Hu, Tayel El-Hasan, Owen W. Duckworth, Ewald Schnug, Roland Bol, Anjali Singh, and Avner Vengosh. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, May 9, 2024. DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.4c00170
Online: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.4c00170
END
Scientists develop new geochemical ‘fingerprint’ to trace contaminants in fertilizer
Heavy metals pollution traced back to mineral-based fertilizers
2024-05-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
From the road to the cloud: leveraging vehicle GNSS raw data for spatial high-resolution atmospheric mapping and user positioning
2024-05-17
Innovative Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) positioning technologies harness massive vehicle-generated data to create high-resolution atmospheric delay correction maps, significantly enhancing Global Positioning System (GPS) accuracy across varied spatial scales. This new method exploits real-time, crowd-sourced vehicle GNSS raw data, refining traditional GPS applications and presenting a cost-effective solution for precise positioning.
The quest for enhanced Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) accuracy has been hindered ...
Study suggests that air pollution promotes inflammation in the brain, accelerating cognitive decline and increasing risk of dementia
2024-05-17
Results from new study suggests that long-term exposure to air pollution leads to increased risk in dementia in Denmark.
"We also find association with noise, but this seems to be explained by air pollution primarily. Our study is in line with growing international knowledge on this topic." says Professor at Section of Environmental Health Zorana Jovanovic Andersen.
This is an important finding which adds that air pollution, beyond well-known effects on respiratory and cardiovascular system, also has major impacts on our brain, promoting inflammation in the brain, accelerating cognitive decline, and increasing ...
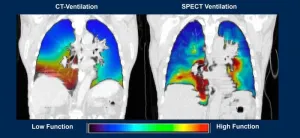
New imaging software improves lung diagnosis for 30% of patients who can't tolerate contrast dye; has added diagnostic benefits for all patients
2024-05-17
Southfield, Mich., May 17, 2024 – For up to 30% of patients who are allergic to medical contrast dye or have a dye restriction because of other health conditions, they might find that it takes longer to get a diagnosis when it comes to life-threatening lung issues such as pulmonary embolism. That's because imaging methods that detect lung problems but don't use contrast dye aren't as accurate and can be more time-consuming to administer.
Now, new imaging software, developed by pulmonologist Girish Nair, M.D., with Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in Royal Oak, Michigan, and biomedical ...
A trial HIV vaccine triggered elusive and essential antibodies in humans
2024-05-17
DURHAM, N.C. – An HIV vaccine candidate developed at the Duke Human Vaccine Institute triggered low levels of an elusive type of broadly neutralizing HIV antibodies among a small group of people enrolled in a 2019 clinical trial.
The finding, reported May 17 in the journal Cell, not only provides proof that a vaccine can elicit these antibodies to fight diverse strains of HIV, but that it can also initiate the process within weeks, setting in motion an essential immune response.
The vaccine candidate targets an area on the HIV-1 outer envelope called the membrane proximal external region (MPER), which ...
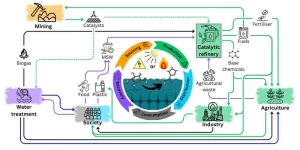
Can we revolutionise the chemical industry and create a circular economy? Yes, with the help of catalysts
2024-05-17
The chemical industry is a cornerstone of global development, driving innovation, and providing essential products that support our modern way of life.
However, its reliance on unsustainable fossil resources has posed significant threats to global ecosystems through climate change and chemical pollution.
A new commentary published in Cell Press’ OneEarth co-authored by Griffith University researchers puts forth a transformative solution: catalysis to leverage sustainable waste resources, ushering the industry from a linear to a circular economy.
“If ...
Rutgers researchers identify impacts of Russia-Ukraine war on hospitals
2024-05-17
Rutgers researchers, aided by international collaborators, have tracked the devastation war has made on Ukraine’s hospital system.
Hundreds of hospitals in Ukraine have been forced to close or operate at a reduced capacity since Russia’s invasion of the Eastern European country in February 2022. Damage, destruction and supply shortages caused by the war have impaired the nation’s hospital system and taken a serious toll on human health.
In a study published in JAMA, Rutgers researchers and collaborators from the United States, Pakistan and Ukraine collected and compared data on hospital services provided both during ...
Differing values of nature can still lead to joined up goals for sustainability
2024-05-17
Recognising and respecting the different ways nature is valued can enable better environmental decision-making, according to new research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
International agreements such as the Sustainable Development Goals represent wide support for a sustainable future, living within planetary boundaries and ensuring a safer future for current and next generations.
However, there remain huge disagreements about how to advance such goals, often resulting in marginalisation, conflict and inaction.
The paper, published in the journal One Earth, ...
Ultraprocessed food consumption and cardiometabolic risk factors in children
2024-05-17
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that high ultraprocessed food (UPF) consumption in young children is associated with adiposity and other cardiometabolic risk factors, highlighting the need for public health initiatives to promote the replacement of UPFs with unprocessed or minimally processed foods.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nancy Babio, Ph.D., email nancy.babio@urv.cat.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.11852)
Editor’s ...
Link between e-cigarette use and early age of asthma onset in US adults found through UTHealth Houston research
2024-05-17
A significant link between the use of electronic cigarettes and earlier age of asthma onset in U.S. adults was reported by UTHealth Houston researchers May 17, 2024 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Network Open.
Led by first author Adriana Pérez, PhD, MS, professor of biostatistics and data science at UTHealth Houston School of Public Health, the research found that adults who were asthma-free at the beginning of the study and reported e-cigarette use in the past 30 days increased their risk of developing earlier age of asthma onset by 252%.
“While previous studies have reported that e-cigarette use increases ...
UNC Greensboro researcher approved for NCInnovation grant funding for lithium refining research
2024-05-17
UNC Greensboro researcher Hemali Rathnayake, Ph.D., has been approved for grant funding from NCInnovation to continue her work in developing a cost-effective and efficient lithium refining process for converting lithium into battery-grade lithium carbonate.
The grant approval is conditioned on standard next steps, including executed grant agreements and formal notification to government partners. This funding is part of NCInnovation’s larger mission to unlock the innovative potential of North Carolina’s world-class universities.
“From ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Scientists develop new geochemical ‘fingerprint’ to trace contaminants in fertilizerHeavy metals pollution traced back to mineral-based fertilizers