(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – Upward social mobility may ward off dementia, according to a new study. Dementia, a collective term for conditions marked by memory loss and diminished cognitive functioning, strains healthcare systems and devastates quality of life for patients and their families. Research thus far has found correlations between socioeconomic status (SES) – Parent’s asset, education level, income, and work status – and susceptibility to dementia, and SES changes throughout a person’s life, known as social mobility, seem to influence this risk; however, scientific evidences are lacking.
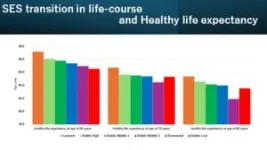
The new study, led by Osaka University researchers and published in JAMA Network Open, provides data-backed evidence that upward social mobility is associated with a lower dementia risk. Specifically, a downward SES transition was associated with the highest loss of healthy longevity from age 75 onward in their lifetime. Yet, an upward transition was linked with the longest period of healthy longevity. Interestingly, these result from upward are more favorable than those with stable high SES since childhood.
“Thanks to a large and robust dataset, our findings solidify the association between socioeconomic mobility and dementia risk,” the study’s lead author Ryoto Sakaniwa says. “Our finding that upward social mobility throughout a person’s life correlates with a prolonged period of dementia-free aging means that improving socioeconomic conditions could be a key to dementia prevention and healthier longevity.”
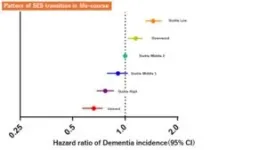
The researchers used data from the Japan Gerontological Evaluation Study, which followed 9,186 participants aged 65 and over from 2010 to 2016. The study employed unsupervised clustering analysis and data-driven classification to analyze changes in participants’ SES throughout their lives. The analysis identified six distinct SES transition patterns. The researchers used a national registry of long-term nursing care services to determine dementia incidence, which enabled a detailed examination of the relationship between these transitions and dementia risk.
The analysis found that upward SES transitions were associated with a notably lower risk of dementia incidence compared with stable SES patterns. Conversely, downward SES transitions had a significantly increased risk.
The study also explored the mediating effects of lifestyle behaviors, comorbidities, and social factors on the association of SES transitions and dementia risk. These factors were found to play significant roles in mediating that risk, particularly physical characteristics and lifestyle behaviors in upward transitions and social factors in downward transitions.
“Future research should delve deeper into the mechanisms by which SES influences cognitive health, including potential interventions for mitigating dementia risk,” senior author Hiroyasu Iso says.” Understanding the nuances of how SES and its transitions impact dementia is vital for developing targeted strategies addressing underlying socioeconomic factors throughout one’s life.
So, it seems that climbing the social ladder can indeed lead to healthier, dementia-free lives.
###
The article, “Socioeconomic status transition throughout the life course and the risk of dementia,” was published in JAMA Network Open at DOI: https://10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12303
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
Climbing the social ladder slows dementia, Japanese study reveals
Research from Osaka University uncovers that socioeconomic status transition considerably extends years lived without dementia, offering new insights into preventive strategies
2024-05-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover hidden step in dinosaur feather evolution
2024-05-21
Scientists discover ‘zoned development’ in dinosaur skin, with zones of reptile-style scales and zones of bird-like skin with feathers
New dinosaur skin fossil found to be composed of silica – the same as glass
Discovery sheds light on evolution from scales to feathers
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC) in Ireland have discovered that some feathered dinosaurs had scaly skin like reptiles today, thus shedding new light on the evolutionary transition from scales to feathers.
The researchers studied a new specimen of the feathered dinosaur Psittacosaurus from the early Cretaceous ...
Studies reveal cell-by-cell changes caused when pig hearts and kidneys are transplanted into humans
2024-05-21
Surgical teams at NYU Langone Health performed the world’s first genetically modified pig kidney transplants into a human body in September and November 2021, and then transplanted two pig hearts in the summer of 2022. These procedures were done in patients declared dead based on neurologic criteria (decedents) and maintained on ventilators with the consent of their families. Demonstrating the field’s progress, NYU Langone in April 2024 transplanted a pig kidney into a living patient.
Now two new analyses, one published online on May 17 in Nature Medicine and the other May ...
SRI earns FDA Orphan Drug Designation for pancreatic cancer
2024-05-21
SRI’s Targeted Antigen Loaded Liposomes (TALL) — a treatment that expands the benefits of immunotherapy such as check-point inhibitors — has been granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the U.S. Federal Drug Administration (FDA).
As a result, SRI’s future strategic partners can gain tax credits for qualified clinical trials and potentially receive market exclusivity for a period of seven years after the drug’s approval, among other benefits.
“FDA's orphan drug designation brings worthy attention to the demonstrated impact of SRI's TALL biotherapeutic for pancreatic cancer,” said Kathlynn Brown, ...
A new gene-editing system tackles complex diseases
2024-05-21
The human genome consists of around 3 billion base pairs and humans are all 99.6% identical in their genetic makeup. That small 0.4% accounts for any difference between one person and another. Specific combinations of mutations in those base pairs hold important clues about the causes of complex health issues, including heart disease and neurodegenerative diseases like schizophrenia.
Current methods to model or correct mutations in live cells are inefficient, especially when multiplexing — installing multiple point mutations simultaneously across the genome. Researchers from the University of California San Diego ...
Tracking down toxic metals from tobacco smoke
2024-05-21
Cigarette smoke has been studied for years, revealing a multitude of contaminants, including toxic metals. But exactly which of those metals can be traced to secondhand or thirdhand smoke? Solving this problem has been a challenge for the research community because many of the metals found in tobacco smoke could also come from industrial or naturally occurring pollutants contaminating indoor and outdoor air.
Now, a recent study by scientists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has identified 28 trace metals in tobacco smoke. The findings reported in the journal ...
Clarifying the cellular mechanisms underlying periodontitis with an improved animal model
2024-05-21
TMDU researchers have developed a technique that allows a detailed analysis of periodontitis development over time
Tokyo, Japan – Periodontal disease, represented by periodontitis, is the leading cause of tooth loss and affects close to one in five adults worldwide. In most cases, this condition occurs as a result of an inflammatory response to bacterial infection of the tissue around teeth. As the condition worsens, the gums begin to pull away, exposing teeth roots and bone. Notably, the incidence of periodontitis becomes more prevalent with age and with populations worldwide living ...
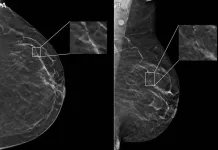
Age, race impact AI performance on digital mammograms
2024-05-21
OAK BROOK, Ill. – In a study of nearly 5,000 screening mammograms interpreted by an FDA-approved AI algorithm, patient characteristics such as race and age influenced false positive results. The study’s results were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“AI has become a resource for radiologists to improve their efficiency and accuracy in reading screening mammograms while mitigating reader burnout,” said Derek L. Nguyen, M.D., assistant professor at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina. ...
SwRI leads courses at 2024 Society of Tribologists & Lubrication Engineers Annual Meeting
2024-05-21
SAN ANTONIO — May 21, 2024 —As a leader in fuels and lubricants research, Southwest Research Institute is home to a world-class tribology laboratory and expert staff that are developing advanced techniques and technology to study wear, friction and lubrication. SwRI tribologists will share their expertise at the 2024 Society of Tribologists and Lubrication Engineers (STLE) Annual Meeting May 19-23 in Minneapolis.
The STLE Annual Meeting and Exhibition invites members of the lubricant industry ...
Hope for a cure for visceral leishmaniasis, an often fatal infectious disease
2024-05-21
Hope for a cure for visceral leishmaniasis, an often fatal infectious disease
A discovery by Simona Stäger’s team could help come up with a treatment to the most serious form of leishmaniasis.
Leishmaniasis is a tropical disease affecting a growing number of people worldwide. Each year, between 700,000 and 1 million new cases are reported. Caused by a protozoan parasite of the genus Leishmania, which is transmitted to humans by the simple bite of a sand fly, leishmaniasis comprises three clinical forms, of which the visceral ...
How AI helps programming a quantum computer
2024-05-21
Generative models like diffusion models are one of the most important recent developments in Machine Learning (ML), with models as Stable Diffusion and Dall.e revolutionizing the field of image generation. These models are able to produce high quality images based on some text description. “Our new model for programming quantum computers does the same but, instead of generating images, it generates quantum circuits based on the text description of the quantum operation to be performed”, explains Gorka Muñoz-Gil from the Department of Theoretical Physics of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Climbing the social ladder slows dementia, Japanese study revealsResearch from Osaka University uncovers that socioeconomic status transition considerably extends years lived without dementia, offering new insights into preventive strategies