Clarifying the cellular mechanisms underlying periodontitis with an improved animal model
2024-05-21
(Press-News.org)
TMDU researchers have developed a technique that allows a detailed analysis of periodontitis development over time
Tokyo, Japan – Periodontal disease, represented by periodontitis, is the leading cause of tooth loss and affects close to one in five adults worldwide. In most cases, this condition occurs as a result of an inflammatory response to bacterial infection of the tissue around teeth. As the condition worsens, the gums begin to pull away, exposing teeth roots and bone. Notably, the incidence of periodontitis becomes more prevalent with age and with populations worldwide living longer, developing a solid understanding of its underlying causes and progression is important.
In a study recently published in Nature Communications on March 28, 2024, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) found a way to achieve this by improving upon a widely used animal model to study periodontitis.
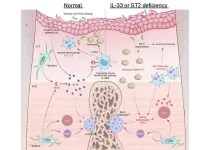
Studying periodontitis directly in humans is challenging. As a result, scientists often resort to animal models for preclinical research. For instance, the “mouse ligature-induced periodontitis model,” since its inception in 2012, has enabled researchers to study the cellular mechanisms underlying this condition. Simply put, with this model, periodontal disease is artificially induced by ligating silk threads onto the molars of mice models, which induces plaque accumulation. While convenient and effective, this model, however, fails to capture the complete picture of periodontitis. “Even though the periodontal tissue is composed of gingiva, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone, and cementum, analyses are usually performed exclusively on gingival samples due to technical and quantitative limitations,” remarks lead author Mr. Anhao Liu. “This sampling strategy limits the conclusions that may be drawn from these studies, so methods that allow for the simultaneous analysis of all tissue components are needed.”
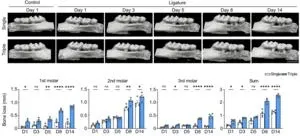
To address this limitation, the research team developed a modified ligature-induced periodontitis model. Instead of the classic single ligature, they used a triple ligature approach on the upper left molar of male mice. This strategy expanded the range of bone loss without causing severe bone destruction around the second molar, increasing the yield of the different types of periodontal tissue. “We isolated the three main tissue types and evaluated the RNA yield between the two models. The results showed that the triple-ligature model effectively increased the yield, achieving four times the yield of normal peri-root tissue and supporting the high-resolution analysis of different tissue types,” explains senior author Dr. Mikihito Hayashi.
After confirming the efficacy of their modified model, the researchers proceeded to investigate the effects of periodontitis on gene expression among the different tissue types over time, focusing on genes related to inflammation and osteoclast differentiation. One of their main findings was that the expression of the Il1rl1 gene was markedly higher in peri-root tissue five days after ligation. This gene encodes the protein ST2 in both receptor and decoy isoform, which binds to a cytokine called IL-33 that is involved in inflammatory and immunoregulation processes.
To gain further insights into the role of this gene, the team induced periodontitis in genetically modified mice that lacked the Il1rl1 or Il33 genes. These mice exhibited accelerated inflammatory bone destruction, highlighting the protective role of the IL-33/ST2 pathway. Further analysis of cells containing the ST2 protein in its receptor form, mST2, revealed that most of them were of macrophage lineage. “Macrophages are typically classified into two main types, pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory, based on their activation process. We found that mST2-expressing cells were unique in that they expressed some markers of both types of macrophages simultaneously,” comments senior author Dr. Takanori Iwata. “These cells were present in the peri-root tissue before inflammation was triggered, so we named them ‘periodontal tissue-resident macrophages.’”
Together, the findings of this study showcase the power of this modified animal model to study the full scope of periodontitis in greater detail, right down to the biomolecular level. “We suggest the possibility that a novel IL-33/ST2 molecular pathway regulating inflammation and bone destruction in periodontal disease, alongside specific macrophages in peri-root tissue, is deeply involved in periodontal disease. This will hopefully lead to the development of new treatment strategies and prevention methods,” concludes senior author Dr. Tomoki Nakashima.
We too hope that these and further efforts will help clarify the causes and progression of periodontitis, leading to a world with healthier teeth and gums.
###
The article, “The IL-33/ST2 axis is protective against acute inflammation during the course of
periodontitis,” was published in Nature Communications at DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46746-2
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-21
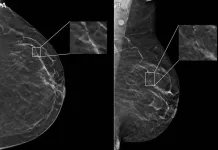
OAK BROOK, Ill. – In a study of nearly 5,000 screening mammograms interpreted by an FDA-approved AI algorithm, patient characteristics such as race and age influenced false positive results. The study’s results were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“AI has become a resource for radiologists to improve their efficiency and accuracy in reading screening mammograms while mitigating reader burnout,” said Derek L. Nguyen, M.D., assistant professor at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina. ...
2024-05-21
SAN ANTONIO — May 21, 2024 —As a leader in fuels and lubricants research, Southwest Research Institute is home to a world-class tribology laboratory and expert staff that are developing advanced techniques and technology to study wear, friction and lubrication. SwRI tribologists will share their expertise at the 2024 Society of Tribologists and Lubrication Engineers (STLE) Annual Meeting May 19-23 in Minneapolis.
The STLE Annual Meeting and Exhibition invites members of the lubricant industry ...
2024-05-21
Hope for a cure for visceral leishmaniasis, an often fatal infectious disease
A discovery by Simona Stäger’s team could help come up with a treatment to the most serious form of leishmaniasis.
Leishmaniasis is a tropical disease affecting a growing number of people worldwide. Each year, between 700,000 and 1 million new cases are reported. Caused by a protozoan parasite of the genus Leishmania, which is transmitted to humans by the simple bite of a sand fly, leishmaniasis comprises three clinical forms, of which the visceral ...
2024-05-21
Generative models like diffusion models are one of the most important recent developments in Machine Learning (ML), with models as Stable Diffusion and Dall.e revolutionizing the field of image generation. These models are able to produce high quality images based on some text description. “Our new model for programming quantum computers does the same but, instead of generating images, it generates quantum circuits based on the text description of the quantum operation to be performed”, explains Gorka Muñoz-Gil from the Department of Theoretical Physics of ...
2024-05-21
New MBARI research on a field of pockmarks—large, circular depressions on the seafloor—offshore of Central California has revealed that powerful sediment flows, not methane gas eruptions, maintain these prehistoric formations. A team of researchers from MBARI, the United States Geological Survey (USGS), and Stanford University published their findings today in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface. This work provides important information to guide decision-making about responsible use and management of the seafloor off California, including site assessments for the development of offshore wind farms.
The Sur Pockmark Field—an area about the size ...
2024-05-21
New York, NY [May 21, 2024]—Generative artificial intelligence (AI), such as GPT-4, can help predict whether an emergency room patient needs to be admitted to the hospital even with only minimal training on a limited number of records, according to investigators at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Details of the research were published in the May 21 online issue of the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association (JAMIA/DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocae103).
In the retrospective study, the researchers analyzed records from seven Mount Sinai Health System hospitals, using both structured data, such as vital signs, ...
2024-05-21
Highlights:
Periodontitis is linked to tooth loss and other health concerns.
Past studies suggest that green tea products can act against P. gingivalis, which causes periodontitis.
In a new study, researchers tested matcha extract, made from green tea, against the pathogen.
Lab studies suggest matcha inhibits the growth of the bacteria.
A clinical trial showed that matcha mouthwash inhibited P. gingivalis populations in saliva.
Washington, D.C.—Periodontitis is an inflammatory gum disease driven by bacterial infection and left untreated it can lead to complications including tooth loss. ...
2024-05-21
WARSAW, POLAND [May 21, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—a global nonprofit responsible for leading cancer treatment guidelines—is taking part in two events in Warsaw focused on advancing cancer care and highlighting the Poland-US bilateral achievements in health care from May 21-22, 2024. The meetings will be organized by Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, the Polish Oncological Society, and the Alliance for Innovation. ...
2024-05-21
LOS ANGELES — City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, has been awarded $5.4 million from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) to build and fund a stem cell research laboratory on its Duarte, California, campus that will further expand its scientific capabilities.
The mission of the unique Stem Cell-Based Disease Modeling Laboratory is two-fold. First, it will advance stem cell-based disease modeling to spur innovation in regenerative medicine. The laboratory leverages City of Hope’s infrastructure ...
2024-05-21
Thousands of top nutrition experts will gather next month for a dynamic program of research announcements, policy discussions and award lectures at NUTRITION 2024, the annual flagship meeting of the American Society for Nutrition. Reporters and bloggers are invited to apply for a complimentary press pass to attend the meeting in Chicago from June 29–July 2.
Explore the meeting schedule and register for a press pass to attend.
Hot topics to be explored at NUTRITION 2024 include:
Diet and cancer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Clarifying the cellular mechanisms underlying periodontitis with an improved animal model