(Press-News.org) Today, DRI, one of our nation’s leading applied environmental research institutes, together with its Foundation, announced a new global initiative with the first in a series of summits. The event will be held at Encore Las Vegas from August 21-23, 2024.
The AWE+ initiative will promote an Adaptable World Environment of strong, resilient communities in a climate shifting world. AWE+ 2024 - Wildfire Recovery and Resilience: Working Across Silos to Drive Solutions - is a global call-to-action for communities to implement measures that support resilience and human adaptability to devastating wildfire events.
“For more than six decades, DRI has tackled global climate challenges. But fortifying communities against future environmental devastation requires more than science — it demands the diversity of thought and collective resolve of leaders and subject matter experts across the full spectrum of public and private sectors,” said DRI President Kumud Acharya.
As the intensity of wildfire events continues to escalate, the summit will bring together a cross-section of industry, government, and non-government leaders to grapple with difficult questions, share ideas, and form collaborative relationships that enable them to identify and address areas of need in their communities.
“Participants will come away with actionable strategies for cultivating measures of resilience in their communities – not only to address the sheer destruction of wildfire and its lasting effects on devastated communities but also the societal costs that are felt over a wide spectrum from the human toll in lives to firefighter safety to financial impacts and disruptions in livelihoods to air pollution exposure.” said DRI Vice President for Research Vic Etyemezian.
“AWE+ 2024 transcends the traditional conference structure by unleashing the collective energy of participants who are serious about confronting the tough issues that are necessary to drive change in policies, practices, technologies, and behaviors,” said DRI Foundation Chair Kristin McMillan Porter.
Details
Dates: August 21-23, 2024
Location: Encore Las Vegas — 3121 S Las Vegas Blvd, Las Vegas, NV 89109
Program: Agenda details
END
DRI to host AWE+ wildfire summit
Inaugural global initiative to address wildfires
2024-05-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson Research Highlights for May 21, 2024
2024-05-21
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson offer insights into biomarkers that predict immunotherapy responses, a possible treatment strategy for patients with LKB1-deficient cancers, therapeutic targets to prevent acute myeloid leukemia (AML) progression ...
Polymer research aims to expand possibilities in sensor technology
2024-05-21
Sensors enable us to monitor changes in systems of all kinds.
The materials at the heart of those sensors, of course, ultimately determine their end-use application. Devices made of silicon, for example, enable ultrafast processing in computers and phones, but they aren’t pliable enough for use in physiological monitoring.
They also require a lot of energy to produce.
Lehigh University professor Elsa Reichmanis, Carl Robert Anderson Chair in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, recently received a grant from the National ...
New therapeutic avenues in bone repair
2024-05-21
Birmingham researchers have shown PEPITEM, a naturally occurring peptide (small protein) holds promise as a new therapeutic for osteoporosis and other disorders that feature bone loss, with distinct advantages over existing drugs.
PEPITEM (Peptide Inhibitor of Trans-Endothelial Migration) was first identified in 2015 by University of Birmingham researchers.
The latest research, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, show for the first time that PEPITEM could be used as a novel and early clinical intervention to reverse the impact of age-related musculoskeletal diseases, with ...
Socioeconomic status transition throughout life and risk of dementia
2024-05-21
About The Study: This cohort study of Japanese older adults identified that upward and downward socioeconomic status transitions were associated with risk of dementia and the length of dementia-free periods over the lifespan. The results may be useful to understand the association between social mobility and healthy longevity.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hiroyasu Iso, Ph.D., email iso@pbhel.med.osaka-u.ac.jp.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12303)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Climbing the social ladder slows dementia, Japanese study reveals
2024-05-21
Osaka, Japan – Upward social mobility may ward off dementia, according to a new study. Dementia, a collective term for conditions marked by memory loss and diminished cognitive functioning, strains healthcare systems and devastates quality of life for patients and their families. Research thus far has found correlations between socioeconomic status (SES) – Parent’s asset, education level, income, and work status – and susceptibility to dementia, and SES changes throughout a person’s life, known as social mobility, seem to influence this risk; however, scientific ...
Researchers discover hidden step in dinosaur feather evolution
2024-05-21
Scientists discover ‘zoned development’ in dinosaur skin, with zones of reptile-style scales and zones of bird-like skin with feathers
New dinosaur skin fossil found to be composed of silica – the same as glass
Discovery sheds light on evolution from scales to feathers
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC) in Ireland have discovered that some feathered dinosaurs had scaly skin like reptiles today, thus shedding new light on the evolutionary transition from scales to feathers.
The researchers studied a new specimen of the feathered dinosaur Psittacosaurus from the early Cretaceous ...
Studies reveal cell-by-cell changes caused when pig hearts and kidneys are transplanted into humans
2024-05-21
Surgical teams at NYU Langone Health performed the world’s first genetically modified pig kidney transplants into a human body in September and November 2021, and then transplanted two pig hearts in the summer of 2022. These procedures were done in patients declared dead based on neurologic criteria (decedents) and maintained on ventilators with the consent of their families. Demonstrating the field’s progress, NYU Langone in April 2024 transplanted a pig kidney into a living patient.
Now two new analyses, one published online on May 17 in Nature Medicine and the other May ...
SRI earns FDA Orphan Drug Designation for pancreatic cancer
2024-05-21
SRI’s Targeted Antigen Loaded Liposomes (TALL) — a treatment that expands the benefits of immunotherapy such as check-point inhibitors — has been granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the U.S. Federal Drug Administration (FDA).
As a result, SRI’s future strategic partners can gain tax credits for qualified clinical trials and potentially receive market exclusivity for a period of seven years after the drug’s approval, among other benefits.
“FDA's orphan drug designation brings worthy attention to the demonstrated impact of SRI's TALL biotherapeutic for pancreatic cancer,” said Kathlynn Brown, ...
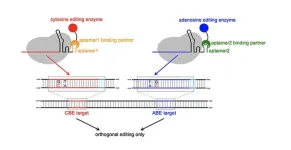
A new gene-editing system tackles complex diseases
2024-05-21
The human genome consists of around 3 billion base pairs and humans are all 99.6% identical in their genetic makeup. That small 0.4% accounts for any difference between one person and another. Specific combinations of mutations in those base pairs hold important clues about the causes of complex health issues, including heart disease and neurodegenerative diseases like schizophrenia.
Current methods to model or correct mutations in live cells are inefficient, especially when multiplexing — installing multiple point mutations simultaneously across the genome. Researchers from the University of California San Diego ...
Tracking down toxic metals from tobacco smoke
2024-05-21
Cigarette smoke has been studied for years, revealing a multitude of contaminants, including toxic metals. But exactly which of those metals can be traced to secondhand or thirdhand smoke? Solving this problem has been a challenge for the research community because many of the metals found in tobacco smoke could also come from industrial or naturally occurring pollutants contaminating indoor and outdoor air.
Now, a recent study by scientists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has identified 28 trace metals in tobacco smoke. The findings reported in the journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Highly stable self-rectifying memristor arrays: Enabling reliable neuromorphic computing via multi-state regulation
Composite superionic electrolytes for pressure-less solid-state batteries achieved by continuously perpendicularly aligned 2D pathways
Exploring why some people may prefer alcohol over other rewards
How expectations about artificial sweeteners may affect their taste
Ultrasound AI receives FDA De Novo clearance for delivery date AI technology
Amino acid residue-driven nanoparticle targeting of protein cavities beyond size complementarity
New AI algorithm enables scientific monitoring of "blue tears"
Insufficient sleep among US adolescents across behavioral risk groups
Long COVID and recovery among US adults
Trends in poverty and birth outcomes in the US
Heterogeneity of treatment effects of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss in adults
Within-person association between daily screen use and sleep in youth
Low-dose lithium for mild cognitive impairment
Catheter ablation and oral anticoagulation for secondary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
A new theory of brain development
Pilot clinical trial suggests low dose lithium may slow verbal memory decline
Bioprinting muscle that knows how to align its cells just as in the human body
A hair-thin fiber can read the chemistry of a single drop of body fluid
SwRI develops magnetostrictive probe for safer, more cost-effective storage tank inspections
National report supports measurement innovation to aid commercial fusion energy and enable new plasma technologies
Mount Sinai, Uniformed Services University join forces to predict and prevent diseases before they start
Science of fitting in: Do best friends or popular peers shape teen behavior?
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
[Press-News.org] DRI to host AWE+ wildfire summitInaugural global initiative to address wildfires