Treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma using immunotherapy: present and future
2024-05-22
(Press-News.org)
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a prevalent form of cancer, profoundly influences the progression and prognosis of the disease through immune response mechanisms. The tumor microenvironment plays a pivotal role in fostering immune suppression and maintaining self-tolerance, which are crucial in developing and refining immunotherapy approaches.
In our comprehensive review, we initially delve into the characteristics of the tumor microenvironment in HCC, elucidating the predominant immunosuppressive mechanisms at play and the biomarkers pivotal for tracking the disease progression and therapeutic response. Key biomarkers such as α-fetoprotein (AFP), used for diagnosis and monitoring, and emerging molecular markers are extensively discussed.
Central to our discussion is the transformative role of antibody-based therapies, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). These therapies, which include monoclonal antibodies targeting programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), have revolutionized the approach to HCC treatment. We delve into the specifics of how these therapies reinvigorate the immune system's ability to recognize and attack tumor cells, discussing their application both as monotherapies and in combination with other targeted therapies. This segment underscores the significance of ICIs in managing advanced HCC, providing new avenues for first-line and subsequent treatments.
Additionally, the review explores various cellular immunotherapies such as T cell receptor (TCR) T cell therapy and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy. The adaptability of these therapies to individual patient profiles illustrates the shift towards personalized medicine in oncology, aiming to optimize treatment efficacy based on unique tumor characteristics and patient immune profiles.
The potential of HCC vaccines, adjuvant immunotherapy, and oncolytic virotherapy is also thoroughly reviewed. Each of these therapeutic strategies exemplifies cutting-edge advances aiming to prime the immune system more effectively against HCC. We discuss the development stages of various vaccine types, their mechanisms of action, and the potential they hold in preventing recurrence and prolonging patient survival.
In conclusion, our detailed review highlights the dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape of HCC treatment. It reflects on the significant strides made in harnessing the immune system against HCC through innovative immunotherapies and sets the stage for future research that could unlock even more effective treatment modalities. The continuous refinement of immunotherapeutic approaches promises to enhance outcomes for patients with HCC, transforming the prognosis of this challenging cancer.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2023-00462
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
The Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (JCTH) is owned by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and published by XIA & HE Publishing Inc. JCTH publishes high quality, peer reviewed studies in the translational and clinical human health sciences of liver diseases. JCTH has established high standards for publication of original research, which are characterized by a study’s novelty, quality, and ethical conduct in the scientific process as well as in the communication of the research findings. Each issue includes articles by leading authorities on topics in hepatology that are germane to the most current challenges in the field. Special features include reports on the latest advances in drug development and technology that are relevant to liver diseases. Regular features of JCTH also include editorials, correspondences and invited commentaries on rapidly progressing areas in hepatology. All articles published by JCTH, both solicited and unsolicited, must pass our rigorous peer review process.
Follow us on X: @xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: Xia & He Publishing Inc.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-22
Boulder, Colo., USA: Chevron, a leading energy corporation committed to supporting educational initiatives in the geosciences, has announced a partnership with the Geological Society of America (GSA) to provide field trip grants, beginning with the organization’s annual meeting, GSA Connects 2024. This year’s meeting will take place in Anaheim, California, USA, 22–25 September.
The GSA/Chevron Field Trip Grant aims to support students or early career professionals in attending field trips during GSA Connects. GSA’s field trips provide valuable hands-on learning experiences, networking opportunities, ...
2024-05-22
Since cannabidiol (CBD), the non-intoxicating component of cannabis, was legalized in the United States by the 2018 Farm Bill, products containing the compound have flooded the consumer health sector. While there is a single FDA-approved medication containing CBD which can be used to treat rare forms of epilepsy, evidence for the efficacy of commercial CBD products, which generally contain low doses of CBD, is limited. However, this has not stopped their widespread and growing use.
Now, a new study published in Cannabis ...
2024-05-22
No parent wants to risk their child having a serious infection, least of all while still in the womb, but did you know that the immune response to a viral infection during pregnancy could also affect the development of the unborn offspring? Scientists from Harvard University in Cambridge, USA, have shown that immune reactions in pregnant mice are detected by a specific type of brain cell in the developing embryo and alter how genes are regulated in the brain – a change that persists in juvenile mice. Published today in the journal Development, this study provides ...
2024-05-22
Many countries around the world are considering revising cannabis policies. A new study by a researcher at Carnegie Mellon University assessed cannabis use in the United States between 1979 and 2022, finding that a growing share of cannabis consumers report daily or near-daily use and that their numbers now exceed those of daily and near-daily alcohol drinkers. The study concludes that long-term trends in cannabis use parallel corresponding changes in policy over the same period. The study appears in Addiction.
“The data come from survey self-reports, but the enormous changes in ...
2024-05-22
New York, NY – The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR), a national non-profit organization whose mission is to support and advance healthy aging through biomedical research, is pleased to recognize the exemplary contributions of Bérénice Benayoun, PhD, to the field of aging research through the 2024 Vincent Cristofalo Rising Star Award in Aging Research.
This award is named in honor of the late Dr. Cristofalo, who dedicated his career to aging research and encouraged young scientists to investigate important issues in the biology of aging. Established in 2008, the award ...
2024-05-22
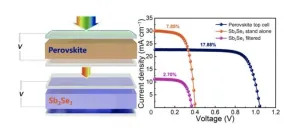
A research team has demonstrated for the first time a proof-of-concept tandem solar cell using antimony selenide as the bottom cell material and a wide-bandgap organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite material as the top cell material. The device achieved a power conversion efficiency of over 20 percent. This study shows that antimony selenide has great potential for bottom cell applications.
The research is published in the journal Energy Materials and Devices on March 4, 2024.
Photovoltaic technology, that harnesses sunlight and converts it into electricity, is popular because it provides a clean, renewable energy source. Scientists ...
2024-05-22
This study is led by Professor Yan Wang (School of Pharmacy, Second Military Medical University (Naval Medical University), Shanghai, China). Her team found that the lack of MIR1 gene, which encodes mitochondrial phosphate carrier, can lead to severe virulence defects in Candida albicans.
In the Caenorhabditis elegans candidiasis model, the survival rate of the wild-type strain infected group dropped to about 20% at 120 h, while the survival rate of the mir1Δ/Δ-infected group remained about 90% at 120 h. Similar results were obtained in the murine model. None of the mice infected with mir1Δ/Δ mutant died during 21 days of ...
2024-05-22
Spontaneous coagulation casting (SCC), a new type of colloidal forming process, has garnered significant attention since 2011 due to various advantages of a high bulk density and non-toxicity, as well as the ability to achieve dispersion and coagulation with very low additions (< 1 wt%) of copolymers of isobutylene and maleic anhydride (PIBM). Further research has revealed that the green bodies formed by this method are brittle, and the smaller the powder particle size used the more brittle the green bodies are. This paper reports ...
2024-05-22
Background and Aims
Olaparib is a selective poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor. However, its clinical application is hindered by low solubility and undesired pharmacokinetic profiles (e.g., relatively short circulation). Therefore, the present study aims to exploit polymeric micelles as a safe solubilizer and nanocarrier of olaparib, in order to improve its solubility and pharmacokinetics.
Methods
Poly (ε-caprolactone)-co-poly (benzyl 5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylate), i.e., benzyl-functionalized trimethylene carbonate)-b-poly (ethylene glycol) (P(CL-co-TMC-Bz)-PEG), was synthesized by ring-opening polymerization, ...
2024-05-22
Background and Aims
Clinical unmet need in managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a common liver disorder affecting 25–30% of American adults is to develop noninvasive and robust biomarkers.
Methods
We re-measured liver AC by placing a region of interest (ROI, 3 cm tall and 3 cm wide) at 4.5 cm, 6 cm, and 7.5 cm from the skin and a large ROI (6.0 cm tall and 7.3 cm wide) on pre-recorded ATI images from 117 participants screened for NAFLD. The difference in AC value at variable ROI depths was tested using one-way ANOVA (analysis of variance). Diagnostic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma using immunotherapy: present and future