(Press-News.org) BOSTON--In new research, investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) show that the 100-year-old Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, originally developed to prevent tuberculosis, protects individuals with type 1 diabetes from severe COVID-19 disease and other infectious diseases.
Two back-to-back randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trials found that the BCG vaccine provided continuous protection for nearly the entire COVID-19 pandemic in the US, regardless of the viral variant.
“Individuals with type 1 diabetes are highly susceptible to infectious diseases and had worse outcomes when they were infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” said senior author Denise Faustman, MD, PhD, director of the Immunobiology Laboratory at MGH and an Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. “Published data from other investigators show mRNA COVID-19 vaccines are not very effective in this group of vulnerable patients. But we’ve shown that BCG can protect type 1 diabetics from COVID-19 and other infectious diseases.”
The 18-month Phase III trial, published in iScience, was conducted late in the US pandemic when the highly transmissible Omicron variant was circulating. A 15-month Phase II trial was conducted early in the pandemic; results of that trial were published in Cell Reports Medicine.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, several international trials tested if BCG as a single shot, or booster, given to previously BCG-vaccinated adults protected them from infection and COVID-19. This research expanded the large global clinical trial database showing that BCG administered to newborns works as a platform for all infectious disease, maybe for decades. But results from these COVID-19 booster trials in people previously vaccinated with BCG were mixed, with five randomized trials showing efficacy and seven trials showing no benefit.
The MGH Phase II and Phase III clinical trials testing BCG differed from other BCG trials in important ways. Instead of receiving one dose of BCG, participants received five or six doses of a particularly potent strain of BCG vaccine. The US participants were followed for a total of 36 months instead of weeks or months. “We know that in people who are naïve to BCG vaccine, the off-target effects can take at least two years to achieve full protection,” said Faustman. “Giving multiple doses of the vaccine may speed up that process.”
And importantly, the US population had never received BCG vaccines, so these clinical trials were not booster trials. “The Phase II and Phase III trials conducted at MGH were unique in that they were the only COVID trials in the world in which the study population had never received a BCG vaccine and was never exposed to TB,” said Faustman. “Trials conducted in countries where participants had previously received BCG vaccine as newborns or who had previous exposure to tuberculosis may have obscured any benefit from a BCG booster.”
The MGH trials enrolled 141 participants with type 1 diabetes; 93 people in the treatment group received five or six doses of BCG vaccine and the 48 individuals in the placebo group received sham vaccine and were followed for 36 months to capture diverse COVID-19 genetic variants and many infectious disease exposures.
During the earlier Phase II trial (January 2020 to April 2021) when the virus was more lethal but less transmissible, the BCG vaccine’s efficacy was 92%, comparable to the efficacy of the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines in healthy adults.
Over the full 34 months of the US COVID-19 pandemic, the BCG vaccine had a significant efficacy of 54.3%. The investigators also found that the BCG-treated participants had lower rates of viral, bacterial, and fungal infections as well as COVID-19 disease itself.
The BCG vaccine confers an immunity that likely lasts decades, a clear advantage to the COVID-19 vaccine and vaccines against other infectious diseases, such as influenza, where the duration of effectiveness is only two or three months. “The BCG vaccine offers the prospect of near-lifelong protection against every variant of COVID-19, the flu, respiratory syncytial virus, and other infectious diseases,” said Faustman.
Some of the BCG-treated participants also received the commercially available COVID-19 vaccines during the Phase III trial. The investigators observed that the Pfizer, Moderna, and Johnson & Johnson vaccines did not protect people with type 1 diabetes against COVID-19. “Our study showed that the BCG vaccine neither increased the efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccine, nor was it harmful to those who received the COVID-19 vaccine,” said Faustman. “As the pandemic continues to evolve it will interesting to see if we can work with the FDA to allow access to BCG vaccine for type 1 diabetics, who appear to be particularly at risk for all infectious diseases.”
This research was supported by The Iacocca Foundation, Boston, MA.
Other contributing authors include Willem M. Kühtreiber, Emma R. Hostetter, Grace E. Wolfe, Maya S. Vayshnaw, Rachel Goldstein, Emily R. Bulczynski, Neeshi S. Hullavarad, Joan E. Braley, and Hui Zheng.
About Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The Mass General Research Institute conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the nation, with annual research operations of more than $1 billion and comprises more than 9,500 researchers working across more than 30 institutes, centers and departments. MGH is a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
[AS1]Not available yet.
END
Century-old vaccine protects type 1 diabetics from infectious diseases
2024-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How and why different cell division strategies evolve
2024-05-22
Cell division is fundamental to life, enabling growth, reproduction, and survival across all organisms, from single-celled bacteria to complex multicellular animals. While animals and fungi share a common eukaryotic ancestry, their mechanisms of cell division, particularly mitosis, have diverged significantly, raising intriguing evolutionary questions.
Animals typically undergo open mitosis, where the nuclear envelope disassembles during cell division, while fungi exhibit closed mitosis, maintaining an intact nuclear envelope. The evolutionary reasons behind these divergent strategies ...
IPK research team uncovers mechanism for spikelet development in barley
2024-05-22
The inflorescence architecture of crop plants like barley is predominantly regulated by meristem activity and fate, which play a critical role in determining the number of floral structures for grain production. Spikelets are the basic reproductive unit of grass inflorescences. The identity and determinacy of many grass meristems are partially determined by a group of genes expressed specifically at organ boundaries, which can form local signalling centres that regulate adjacent meristem fate and activity.
These genes are critical for establishing and ...
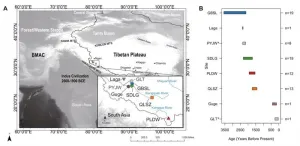
Ancient DNA study reveals population history of Western Tibetan Plateau
2024-05-22
According to a study published in Current Biology on May 22, the genetic components of the ancient populations in the western Tibetan Plateau are closest to ancient populations in the southern Tibetan Plateau, and their major genetic components have been maintained over the past 3,500 years. In addition, these ancient populations in the western Tibetan Plateau had complex and frequent interactions with ancient populations inside and outside the plateau.
The study was conducted by Prof. FU Qiaomei's team from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology ...
Exploring diversity in cell division
2024-05-22
Cell division is one of the most fundamental processes of life. From bacteria to blue whales, every living being on Earth relies on cell division for growth, reproduction, and species survival. Yet, there is remarkable diversity in the way different organisms carry out this universal process. A new study from EMBL Heidelberg’s Dey group and their collaborators, recently published in Nature, explores how different modes of cell division evolved in close relatives of fungi and animals, demonstrating, for the first time, the link between an organism’s ...
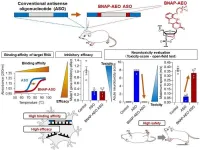
Sweet move: a modified sugar enhances antisense oligonucleotide safety and efficacy
2024-05-22
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and Osaka University find that a newly developed modified sugar increases the efficacy and safety of antisense oligonucleotides designed to treat central nervous system disease
Tokyo, Japan – Diseases that affect the brain and spinal cord can be particularly devastating, and finding new and more effective ways to treat these conditions is an important goal for researchers and clinicians alike. Now, a research group from Japan reports that slightly modifying an existing treatment for central nervous system (CNS) disease dramatically increases its ...
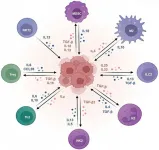
Treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma using immunotherapy: present and future
2024-05-22
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a prevalent form of cancer, profoundly influences the progression and prognosis of the disease through immune response mechanisms. The tumor microenvironment plays a pivotal role in fostering immune suppression and maintaining self-tolerance, which are crucial in developing and refining immunotherapy approaches.
In our comprehensive review, we initially delve into the characteristics of the tumor microenvironment in HCC, elucidating the predominant immunosuppressive mechanisms at play and the biomarkers pivotal for tracking the disease progression and therapeutic ...
Chevron partners with the Geological Society of America to offer geology field trip grants to students and early career professionals
2024-05-22
Boulder, Colo., USA: Chevron, a leading energy corporation committed to supporting educational initiatives in the geosciences, has announced a partnership with the Geological Society of America (GSA) to provide field trip grants, beginning with the organization’s annual meeting, GSA Connects 2024. This year’s meeting will take place in Anaheim, California, USA, 22–25 September.
The GSA/Chevron Field Trip Grant aims to support students or early career professionals in attending field trips during GSA Connects. GSA’s field trips provide valuable hands-on learning experiences, networking opportunities, ...
Nearly 3% of healthy adolescents use commercial CBD products, study finds
2024-05-22
Since cannabidiol (CBD), the non-intoxicating component of cannabis, was legalized in the United States by the 2018 Farm Bill, products containing the compound have flooded the consumer health sector. While there is a single FDA-approved medication containing CBD which can be used to treat rare forms of epilepsy, evidence for the efficacy of commercial CBD products, which generally contain low doses of CBD, is limited. However, this has not stopped their widespread and growing use.
Now, a new study published in Cannabis ...
Mimicking infection in pregnant mice provokes persistent changes in juvenile brains
2024-05-22
No parent wants to risk their child having a serious infection, least of all while still in the womb, but did you know that the immune response to a viral infection during pregnancy could also affect the development of the unborn offspring? Scientists from Harvard University in Cambridge, USA, have shown that immune reactions in pregnant mice are detected by a specific type of brain cell in the developing embryo and alter how genes are regulated in the brain – a change that persists in juvenile mice. Published today in the journal Development, this study provides ...
New study highlights significant increases in cannabis use in United States
2024-05-22
Many countries around the world are considering revising cannabis policies. A new study by a researcher at Carnegie Mellon University assessed cannabis use in the United States between 1979 and 2022, finding that a growing share of cannabis consumers report daily or near-daily use and that their numbers now exceed those of daily and near-daily alcohol drinkers. The study concludes that long-term trends in cannabis use parallel corresponding changes in policy over the same period. The study appears in Addiction.
“The data come from survey self-reports, but the enormous changes in ...