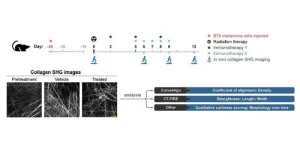
(Press-News.org) Collagen, a major component of the extracellular matrix, plays a crucial role in tumor development. During the development of tumors (“tumorigenesis”), collagen fibers become linearized and densely deposited, hindering immune cell infiltration and promoting tumor metastasis. However, quantifying these collagen changes during melanoma progression has been challenging.
In-vivo imaging of collagen
As reported in Biophotonics Discovery, researchers from the Morgridge Institute for Research and University of Wisconsin – Madison recently addressed this challenge by using quantitative imaging to visualize collagen in preclinical mouse melanoma models during immunotherapy. In their study, animals received a combination of curative radiation and immunotherapy; quantifying collagen morphology at both the image and single-fiber levels obtained insights into collagen remodeling over time.
Sensitive biomarkers: Single-fiber collagen features
In immunotherapy-treated mice, collagen fibers exhibited a healthier phenotype. These fibers were shorter, wider, and curlier, with modestly higher density.
The study found that single-fiber collagen features, calculated using CT-FIRE software, were more sensitive to treatment-induced changes than bulk collagen features. These single-fiber characteristics could serve as valuable biomarkers for assessing immunotherapy response.
Implications for cancer treatment
Understanding collagen dynamics during immunotherapy is crucial for improving treatment outcomes. The study’s findings highlight the potential of quantitative imaging to enhance immunotherapy response in melanoma and other cancers. By identifying new biomarkers associated with collagen changes, researchers aim to optimize therapeutic strategies and personalize cancer treatments.
This groundbreaking research opens doors to novel approaches in cancer therapy, emphasizing the importance of collagen as a dynamic player in the tumor microenvironment. As scientists continue to unravel the complexities of collagen’s role, patients may benefit from more effective and tailored treatments.
For details, see the Gold Open Access article by A. R. Heaton et al., “Quantifying in vivo collagen reorganization during immunotherapy in murine melanoma with second harmonic generation imaging,” Biophoton. Discovery 1(1), 015004 (2024) doi 10.1117/1.BIOS.1.1.015004.
END
New biomarkers of response in melanoma immunotherapy
Quantitative imaging reveals collagen changes in melanoma tumors during immunotherapy
2024-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI headphones let wearer listen to a single person in a crowd, by looking at them just once
2024-05-23
Noise-canceling headphones have gotten very good at creating an auditory blank slate. But allowing certain sounds from a wearer’s environment through the erasure still challenges researchers. The latest edition of Apple’s AirPods Pro, for instance, automatically adjusts sound levels for wearers — sensing when they’re in conversation, for instance — but the user has little control over whom to listen to or when this happens.
A University of Washington team has developed an artificial intelligence system that lets a ...
Electromechanical material doesn’t get ‘clamped’ down
2024-05-23
HOUSTON – (May 23, 2024) – Lighting a gas grill, getting an ultrasound, using an ultrasonic toothbrush ⎯ these actions involve the use of materials that can translate an electric voltage into a change in shape and vice versa.
Known as piezoelectricity, the ability to trade between mechanical stress and electric charge can be harnessed widely in capacitors, actuators, transducers and sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes for next-generation electronics. However, integrating these materials into miniaturized systems has been difficult ...
Most young women treated for breast cancer can have children, study shows
2024-05-23
In a study of nearly 200 young women who have survived breast cancer, most of those who tried to conceive were able to become pregnant and give birth
This study fills in major gaps from previous studies of fertility among breast cancer survivors
BOSTON – New research by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators has encouraging news for young women who have survived breast cancer and want to have children.
The study, which tracked nearly 200 young women treated for breast cancer, found that the majority of those who tried to conceive during a median of 11 years after treatment were able to become pregnant and give birth to a child.
The findings, ...
SWOG researchers will present key results at ASCO 2024
2024-05-23
Researchers from SWOG Cancer Research Network, a cancer clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), will share results of their work in 30 presentations at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, which takes place May 31 – June 4 in Chicago.
The clinical trials reported on in this work are led by SWOG and conducted by the NIH-funded NCI National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) and the NCI Community Oncology Research ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights: ASCO 2024 Special Edition
2024-05-23
ABSTRACTS: 2018, 2517, 3513, 5504, 6016, 7007, 9515, 12017, LBA8007, LBA9516
CHICAGO ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
This special edition features presentations by MD Anderson researchers at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting. In addition to the ...
Dae Hyun Kim, MD, ScD, receives 2024 Harvard Medical School Mentoring Award
2024-05-23
Dae Hyun Kim, MD, ScD is the recipient of a 2024 A. Clifford Barger Excellence in Mentoring Award at Harvard Medical School.
Kim is an associate scientist at the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife, an HMS Associate Professor of Medicine, a geriatrician at the Division of Gerontology in the Department of Medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and a Harvard School of Public Health Instructor in the Department of Epidemiology.
The Excellence in Mentoring Awards were established to recognize the value of quality mentoring ...
A new study reveals key role of plant-bacteria communication for the assembly of a healthy plant microbiome supporting sustainable plant nutrition
2024-05-23
The results in Nature Communications find that symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing bacteria can ensure dominance among soil microbes due to its signalling-based communication with the legume plant host. Researchers discovered that when legumes need nitrogen, they will send out from the roots and into the soil specific molecules that are in turn recognized by the symbiotic bacteria to produce another molecule, the Nod factor which is recognized back by the legume plant. When this mutual recognition was established, the plant will modify the panel of root secreted molecules and by this will affect which soil bacteria can grow in the vicinity ...
Colleen Ryan named Tufts University's Vice Provost for Faculty
2024-05-23
Colleen Ryan, associate vice provost in the Office of the Vice Provost for Faculty & Academic Affairs Indiana University Bloomington (IUB), has been named vice provost for faculty at Tufts University. She will start in the position on July 1.
Ryan currently holds the rank of professor of Italian in the Department of French and Italian at IUB, is an affiliate faculty member in the Department of Gender Studies, and was the director of undergraduate studies for Italian from 2015-2023. Her areas of expertise ...
Scientists map networks regulating gene function in the human brain
2024-05-23
A consortium of researchers has produced the largest and most advanced multidimensional maps of gene regulation networks in the brains of people with and without mental disorders. These maps detail the many regulatory elements that coordinate the brain’s biological pathways and cellular functions. The research, supported the National Institutes of Health (NIH), used postmortem brain tissue from over 2,500 donors to map gene regulation networks across different stages of brain development and multiple ...
Does it matter if your kids listen to you? When adolescents reject mom’s advice, it still helps them cope
2024-05-23
URBANA, Ill. – Parents are often eager to give their adolescent children advice about school problems, but they may find that youth are less than receptive to their words of wisdom. However, kids who don’t seem to listen to their parents may still benefit from their input, a new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign shows.
The researchers looked at conversations between fifth-grade students and their mothers about academic problems, identifying mom’s advice strategies and the youth’s response. Then they correlated these findings with how ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] New biomarkers of response in melanoma immunotherapyQuantitative imaging reveals collagen changes in melanoma tumors during immunotherapy