(Press-News.org) In a study of nearly 200 young women who have survived breast cancer, most of those who tried to conceive were able to become pregnant and give birth
This study fills in major gaps from previous studies of fertility among breast cancer survivors
BOSTON – New research by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators has encouraging news for young women who have survived breast cancer and want to have children.
The study, which tracked nearly 200 young women treated for breast cancer, found that the majority of those who tried to conceive during a median of 11 years after treatment were able to become pregnant and give birth to a child.
The findings, to be presented at the 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), are particularly noteworthy because they answer several questions left open by previous studies of pregnancy and live-birth rates among breast cancer survivors, the study authors say.
"Earlier studies were limited because they included select subgroups of patients, followed patients for a relatively short period of time, and didn't ask participants, during the study period, if they had attempted pregnancy," says the study's senior author, Ann Partridge, MD, MPH, the founder and director of the Program for Young Adults with Breast Cancer at Dana-Farber. "This study was designed to address those gaps by tracking pregnancy and live birth rates among a group of breast cancer survivors and patients who indicated they'd attempted to conceive following their cancer diagnosis."
The patients in the study were participants in the Young Women's Breast Cancer Study, which is tracking the health of a group of women diagnosed with breast cancer at or under age 40. Of 1,213 eligible participants, 197 reported an attempt of pregnancy over a median follow-up period of 11 years. Within this latter group, the median age at the time of diagnosis was 32 years, and most were diagnosed with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Participants were periodically surveyed about whether they had tried to become pregnant and whether they had conceived and given birth.
Over the course of the study, 73% of women attempting to conceive achieved a pregnancy and 65% had a live birth, researchers found. Those who opted for fertility preservation by egg/embryo freezing before cancer treatment tended to have a higher live birth rate, while older participants tended to have lower pregnancy and live birth rates.
Participants in the study had breast cancers ranging from stage 0, which are non-invasive and confined to the inside of the milk duct, to stage III, in which the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. Researchers found that the stage of the disease at diagnosis wasn't statistically associated with achieving a pregnancy or live birth.
"For many young women with breast cancer, the ability to have children following treatment is a major concern," says the study's first author, Kimia Sorouri, MD, MPH, of Dana-Farber. "The findings of our study can be helpful when counseling patients about fertility issues. The finding that egg/embryo freezing before treatment was associated with a higher live birth rate underscores the need for accessibility to fertility preservation services for this population."
This study was funded by Susan G. Komen and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation.
About Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute is one of the world’s leading centers of cancer research and treatment. Dana-Farber’s mission is to reduce the burden of cancer through scientific inquiry, clinical care, education, community engagement, and advocacy. We provide the latest treatments in cancer for adults through Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center and for children through Dana-Farber/Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center. Dana-Farber is the only hospital nationwide with a top 10 U.S. News & World Report Best Cancer Hospital ranking in both adult and pediatric care.
As a global leader in oncology, Dana-Farber is dedicated to a unique and equal balance between cancer research and care, translating the results of discovery into new treatments for patients locally and around the world, offering more than 1,100 clinical trials.
###
END
Most young women treated for breast cancer can have children, study shows
2024-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SWOG researchers will present key results at ASCO 2024
2024-05-23
Researchers from SWOG Cancer Research Network, a cancer clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), will share results of their work in 30 presentations at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, which takes place May 31 – June 4 in Chicago.
The clinical trials reported on in this work are led by SWOG and conducted by the NIH-funded NCI National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) and the NCI Community Oncology Research ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights: ASCO 2024 Special Edition
2024-05-23
ABSTRACTS: 2018, 2517, 3513, 5504, 6016, 7007, 9515, 12017, LBA8007, LBA9516
CHICAGO ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
This special edition features presentations by MD Anderson researchers at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting. In addition to the ...
Dae Hyun Kim, MD, ScD, receives 2024 Harvard Medical School Mentoring Award
2024-05-23
Dae Hyun Kim, MD, ScD is the recipient of a 2024 A. Clifford Barger Excellence in Mentoring Award at Harvard Medical School.
Kim is an associate scientist at the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife, an HMS Associate Professor of Medicine, a geriatrician at the Division of Gerontology in the Department of Medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and a Harvard School of Public Health Instructor in the Department of Epidemiology.
The Excellence in Mentoring Awards were established to recognize the value of quality mentoring ...
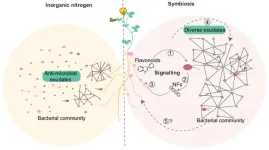
A new study reveals key role of plant-bacteria communication for the assembly of a healthy plant microbiome supporting sustainable plant nutrition
2024-05-23
The results in Nature Communications find that symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing bacteria can ensure dominance among soil microbes due to its signalling-based communication with the legume plant host. Researchers discovered that when legumes need nitrogen, they will send out from the roots and into the soil specific molecules that are in turn recognized by the symbiotic bacteria to produce another molecule, the Nod factor which is recognized back by the legume plant. When this mutual recognition was established, the plant will modify the panel of root secreted molecules and by this will affect which soil bacteria can grow in the vicinity ...
Colleen Ryan named Tufts University's Vice Provost for Faculty
2024-05-23
Colleen Ryan, associate vice provost in the Office of the Vice Provost for Faculty & Academic Affairs Indiana University Bloomington (IUB), has been named vice provost for faculty at Tufts University. She will start in the position on July 1.
Ryan currently holds the rank of professor of Italian in the Department of French and Italian at IUB, is an affiliate faculty member in the Department of Gender Studies, and was the director of undergraduate studies for Italian from 2015-2023. Her areas of expertise ...
Scientists map networks regulating gene function in the human brain
2024-05-23
A consortium of researchers has produced the largest and most advanced multidimensional maps of gene regulation networks in the brains of people with and without mental disorders. These maps detail the many regulatory elements that coordinate the brain’s biological pathways and cellular functions. The research, supported the National Institutes of Health (NIH), used postmortem brain tissue from over 2,500 donors to map gene regulation networks across different stages of brain development and multiple ...
Does it matter if your kids listen to you? When adolescents reject mom’s advice, it still helps them cope
2024-05-23
URBANA, Ill. – Parents are often eager to give their adolescent children advice about school problems, but they may find that youth are less than receptive to their words of wisdom. However, kids who don’t seem to listen to their parents may still benefit from their input, a new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign shows.
The researchers looked at conversations between fifth-grade students and their mothers about academic problems, identifying mom’s advice strategies and the youth’s response. Then they correlated these findings with how ...
Parents of the year: Scavenging raptors lead a collaborative home
2024-05-23
News Release
Journal of Raptor Research
For immediate release
Contact: [Zoey T. Greenberg]
science.writer@raptorresearchfoundation.com
360.739.7170
Parents of the Year: Scavenging Raptors Lead a Collaborative Home Life
Let’s face it, scavengers have a bad reputation. However, according to a new paper published in the Journal of Raptor Research, pairs of scavenging falcons called Chimango Caracaras (Milvago chimango) demonstrate an endearing level of collaboration while raising their chicks. In their paper, “Biparental Care in a Generalist Raptor, the Chimango Caracara in Central Argentina” Diego Gallego-García from ...
Latest from PsychENCODE: A cell-by-cell look at neuropsychiatric diseases
2024-05-23
Deciphering the genetic causes of common neurodevelopmental conditions like autism and common mental illnesses like bipolar disorder has been challenging – not least because of the size and complexity of the human brain – but a new package of research from a global group makes notable progress. Across Science, Science Translational Medicine, and Science Advances, more than a dozen reports from the PsychENCODE Consortium – established in 2015, and dedicated to illuminating the molecular ...
Researchers unveil shared and unique brain molecular dysregulations in PTSD and depression
2024-05-23
Study combines analyses of multiple genomic platforms over multiple brain regions to probe biological processes and underlying mechanisms of stress-related disorders
Results lay groundwork for future diagnostics and targeted treatments
BELMONT, Mass. (May 23, 2024) A comprehensive approach that examines the intersection of multiple biological processes is necessary to elucidate the development of stress-related disorders. In a new study, investigators from McLean Hospital, a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, ...