(Press-News.org) European space mission Euclid has released early scientific papers based on observations made by the space telescope, along with five new astronomical images of the Universe, as the project sets about unravelling the secrets of the cosmos.
The new images are part of Euclid’s Early Release Observations (EROs) and accompany the mission’s first scientific data and 10 forthcoming science papers. Their publication comes less than a year after the space telescope’s launch and some six months after it returned its first full-colour images of the cosmos.
The scientific papers are based on observations and analysis of 17 targets and contain exciting scientific results including:
the discovery of free-floating new-born planets
newly identified extragalactic star clusters
new low-mass dwarf galaxies in a nearby cluster of galaxies
the discovery of very distant bright galaxies
The five new ERO images follow the release of an initial five images last November. The images obtained by Euclid are at least four times sharper than those that can be taken from ground-based telescopes. They cover large patches of sky at unrivalled depth, looking far into the distant Universe using both visible and infrared light.
The latest Euclid images include observations of:
Messier 78, a reflection nebula
Abell 2390 and Abell 2764, two giant clusters of galaxies
NGC 6744, a spiral galaxy very similar to the Milky Way
the Dorado Group, a loose agglomeration of galaxies
Speaking about the data release, Prof Peter Coles of Maynooth University’s Department of Theoretical Physics, the only Irish-based academic involved in the Euclid consortium, said: “Today's release of new data and technical papers from Euclid is exciting in itself but also marks the start, after months of painstaking calibration and testing of the instruments, of Euclid's main cosmological survey. We are on the threshold of a new era in cosmology.”
“Maynooth is the only University in Ireland to be involved in this mission and it is very exciting to be at the forefront of such an important scientific development.”
Launched from Cape Canaveral on July 1, 2023, Euclid’s mission is to map the distribution of distant galaxies across more than one-third of the sky to extract information about the constituents of the universe, and test whether current ideas about cosmic evolution are correct.
“Euclid is a unique, ground-breaking mission, and these are the first datasets to be made public – it’s an important milestone,” says Valeria Pettorino, ESA’s Euclid Project Scientist. “The images and associated science findings are impressively diverse in terms of the objects and distances observed. They include a variety of science applications, and yet represent a mere 24 hours of observations. They give just a hint of what Euclid can do. We are looking forward to six more years of data to come!”
The next thing to look forward to from Euclid is a taster for the main Euclid survey around March 2025. The first year of survey data (DR1) will be released in June 2026 while the full survey will be completed in 2031.
Prof Peter Coles is available to discuss Euclid and the recent data release.
END
Euclid space mission releases first scientific results and new images of the cosmos
The release marks the start of Euclid’s main survey, says physicist at Maynooth University, the only Irish university in the Euclid consortium. We are on the threshold of a new era in cosmology,” says MU’s Prof Peter Coles
2024-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sociodemographic heterogeneity in the associations of social isolation with mortality
2024-05-24
About The Study: Social isolation was associated with increased risks of all-cause, cardiovascular diseases, and malignant neoplasm mortality, with associations varying across populations. This study fills an important gap in research on social isolation, emphasizing its varied associations across demographic and socioeconomic groups.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Atsushi Nakagomi, M.D., Ph.D., email anakagomi0211@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.13132)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
COVID-19 admission rates and changes in care quality in us hospitals
2024-05-24
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, COVID-19 surges were associated with declines in hospital quality, highlighting the importance of identifying and implementing strategies to maintain care quality during periods of high hospital use.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Giacomo Meille, Ph.D., email giacomo.meille@ahrq.hhs.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.13127)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Preterm and early-term delivery after heat waves in 50 US metropolitan areas
2024-05-24
About The Study: Preterm and early-term birth rates increased after heat waves, particularly among socioeconomically disadvantaged subgroups in this cohort study. Extreme heat events have implications for perinatal health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lyndsey A. Darrow, Ph.D., email ldarrow@unr.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12055)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Research spotlight: Virtual scribes reduced physicians’ time spent on electronic health records
2024-05-24
Lisa Rotenstein, MD, of the Department of Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is the lead author of a new study published in JAMA Network Open, “Virtual Scribes and Physician Time Spent on Electronic Health Records.”
What question were you investigating?
We sought to understand the impact of virtual scribes (human scribes who are not physically present in the exam room with the physician and patient) on how physicians spend their time and which characteristics are associated with physicians responding best to scribes.
What methods or approach did you use?
We studied the experiences of 144 physicians across specialties treating patients ...
Duke-NUS researchers develop new light-controlled ‘off switch’ for brain cells
2024-05-24
Researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School have found that a new class of light-sensitive proteins are capable of turning off brain cells with light, offering scientists an unprecedentedly effective tool to investigate brain function. The study, recently published in Nature Communications, opens exciting new opportunities to apply optogenetics to investigate the brain activity underlying neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and depression.
Optogenetics is a technique where specific cells are bioengineered to include light-sensitive proteins that act as switches, allowing ...
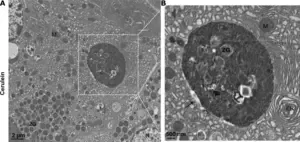
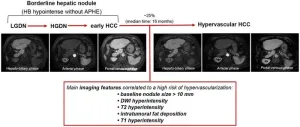
Liver lesions at risk of transformation into hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients
2024-05-24
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents a significant global health burden as one of the most common malignancies in individuals with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis. This malignancy evolves through a multistep process, beginning with dysplastic nodules (DNs) and early HCC, progressing to overt HCC. Recent advancements in liver imaging, particularly the use of hepatocyte-specific contrast agents, have enhanced the detection of these precursor lesions, known as borderline hepatic nodules. These nodules, especially those hypointense in the hepatobiliary phase (HBP) without arterial phase hyperenhancement (APHE), present ...
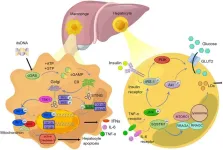
Update on the STING signaling pathway in developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
2024-05-24
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most prevalent chronic liver condition worldwide, affecting about 25% of the global population due to the increasing rates of obesity and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from simple hepatic steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Despite its prevalence, there are limited effective treatment options available. Inflammation driven by metabolic disturbances is a key factor in the development and progression of ...
Autonomous medical intervention extends ‘golden hour’ for traumatic injuries with emergency air transport
2024-05-24
For the first time, a closed loop, autonomous intervention nearly quadrupled the “golden hour” during which surgeons could save the life of a large animal with internal traumatic bleeding while in emergency ground and air transport.
This breakthrough in trauma care, announced today in Intensive Care Medicine Experimental by physician-scientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, has enormous potential for saving the lives of traumatically injured ...
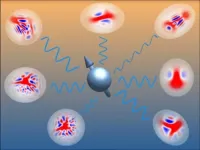
More than spins: Exploring uncharted territory in quantum devices
2024-05-24
Many of today’s quantum devices rely on collections of qubits, also called spins. These quantum bits have only two energy levels, the ‘0’ and the ‘1’. However, spins in real devices also interact with light and vibrations known as bosons, greatly complicating calculations. In a new publication in Physical Review Letters, researchers in Amsterdam demonstrate a way to describe spin-boson systems and use this to efficiently configure quantum devices in a desired state.
Quantum devices use the quirky behaviour of quantum ...
SG ramps up cancer fight with S$50 million in national grant funding for precision oncology
2024-05-24
Singapore, 24 May 2024 – Two multi-institution and multidisciplinary Singapore teams of clinician-scientists and researchers have been awarded grants of S$25 million each, by the Singapore Ministry of Health through the NMRC Office, MOH Holdings Pte Ltd, under the NMRC Open Fund-Large Collaborative Grant (OF-LCG) programme. The S$50 million support for cancer research establishes the SYMPHONY 2.0 and Colo-SCRIPT research programmes to drive precision oncology research in Singapore aimed at improving the understanding, diagnosis and treatment of lymphoma and colorectal cancer.
Led by the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
[Press-News.org] Euclid space mission releases first scientific results and new images of the cosmosThe release marks the start of Euclid’s main survey, says physicist at Maynooth University, the only Irish university in the Euclid consortium. We are on the threshold of a new era in cosmology,” says MU’s Prof Peter Coles