(Press-News.org) About The Study: Preterm and early-term birth rates increased after heat waves, particularly among socioeconomically disadvantaged subgroups in this cohort study. Extreme heat events have implications for perinatal health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lyndsey A. Darrow, Ph.D., email ldarrow@unr.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12055)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.12055?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=052424
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Preterm and early-term delivery after heat waves in 50 US metropolitan areas
JAMA Network Open
2024-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research spotlight: Virtual scribes reduced physicians’ time spent on electronic health records
2024-05-24
Lisa Rotenstein, MD, of the Department of Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is the lead author of a new study published in JAMA Network Open, “Virtual Scribes and Physician Time Spent on Electronic Health Records.”
What question were you investigating?
We sought to understand the impact of virtual scribes (human scribes who are not physically present in the exam room with the physician and patient) on how physicians spend their time and which characteristics are associated with physicians responding best to scribes.
What methods or approach did you use?
We studied the experiences of 144 physicians across specialties treating patients ...
Duke-NUS researchers develop new light-controlled ‘off switch’ for brain cells
2024-05-24
Researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School have found that a new class of light-sensitive proteins are capable of turning off brain cells with light, offering scientists an unprecedentedly effective tool to investigate brain function. The study, recently published in Nature Communications, opens exciting new opportunities to apply optogenetics to investigate the brain activity underlying neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and depression.
Optogenetics is a technique where specific cells are bioengineered to include light-sensitive proteins that act as switches, allowing ...
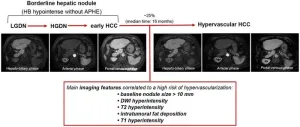
Liver lesions at risk of transformation into hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients
2024-05-24
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents a significant global health burden as one of the most common malignancies in individuals with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis. This malignancy evolves through a multistep process, beginning with dysplastic nodules (DNs) and early HCC, progressing to overt HCC. Recent advancements in liver imaging, particularly the use of hepatocyte-specific contrast agents, have enhanced the detection of these precursor lesions, known as borderline hepatic nodules. These nodules, especially those hypointense in the hepatobiliary phase (HBP) without arterial phase hyperenhancement (APHE), present ...
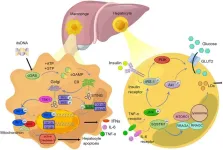
Update on the STING signaling pathway in developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
2024-05-24
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most prevalent chronic liver condition worldwide, affecting about 25% of the global population due to the increasing rates of obesity and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from simple hepatic steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Despite its prevalence, there are limited effective treatment options available. Inflammation driven by metabolic disturbances is a key factor in the development and progression of ...
Autonomous medical intervention extends ‘golden hour’ for traumatic injuries with emergency air transport
2024-05-24
For the first time, a closed loop, autonomous intervention nearly quadrupled the “golden hour” during which surgeons could save the life of a large animal with internal traumatic bleeding while in emergency ground and air transport.
This breakthrough in trauma care, announced today in Intensive Care Medicine Experimental by physician-scientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, has enormous potential for saving the lives of traumatically injured ...
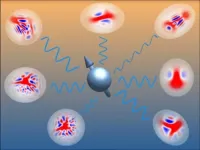
More than spins: Exploring uncharted territory in quantum devices
2024-05-24
Many of today’s quantum devices rely on collections of qubits, also called spins. These quantum bits have only two energy levels, the ‘0’ and the ‘1’. However, spins in real devices also interact with light and vibrations known as bosons, greatly complicating calculations. In a new publication in Physical Review Letters, researchers in Amsterdam demonstrate a way to describe spin-boson systems and use this to efficiently configure quantum devices in a desired state.
Quantum devices use the quirky behaviour of quantum ...
SG ramps up cancer fight with S$50 million in national grant funding for precision oncology
2024-05-24
Singapore, 24 May 2024 – Two multi-institution and multidisciplinary Singapore teams of clinician-scientists and researchers have been awarded grants of S$25 million each, by the Singapore Ministry of Health through the NMRC Office, MOH Holdings Pte Ltd, under the NMRC Open Fund-Large Collaborative Grant (OF-LCG) programme. The S$50 million support for cancer research establishes the SYMPHONY 2.0 and Colo-SCRIPT research programmes to drive precision oncology research in Singapore aimed at improving the understanding, diagnosis and treatment of lymphoma and colorectal cancer.
Led by the ...
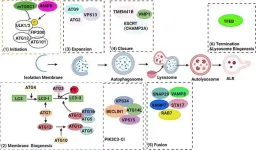
Autophagy in pancreatitis
2024-05-24
Researchers are exploring a new potential avenue for pancreatitis treatment: autophagy, a cellular recycling process. Autophagy helps maintain healthy pancreatic acinar cells by removing damaged organelles like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
A new review published in eGastroenterology highlights the link between defective autophagy and pancreatitis. Impaired autophagy contributes to pancreatitis by allowing damaged organelles to accumulate within acinar cells. This accumulation disrupts cellular function and can ultimately lead to cell death.
"Autophagy plays a vital role in keeping pancreatic acinar cells healthy," ...
To 6G and beyond: Penn engineers unlock the next generation of wireless communications
2024-05-24
In the early 2010s, LightSquared, a multibillion-dollar startup promising to revolutionize cellular communications, declared bankruptcy. The company couldn’t figure out how to prevent its signals from interfering with those of GPS systems.
Now, Penn Engineers have developed a new tool that could prevent such problems from ever happening again: an adjustable filter that can successfully prevent interference, even in higher-frequency bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
“I ...
USF researcher using VR to map the brain, understand and treat disorders such as autism
2024-05-24
TAMPA, Fla. (May 24, 2024) – Through high-tech imaging and virtual reality, a University of South Florida medical engineering professor is creating a detailed map of the brain that can be used to better understand developmental disorders, such as autism, and provide earlier, more effective treatments for brain injuries and diseases.
Funded by a $3.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, George Spirou is expanding on his four decades of brain research to focus on the part of the brain that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Preterm and early-term delivery after heat waves in 50 US metropolitan areasJAMA Network Open