(Press-News.org) Background: A long-term relationship between a patient and their doctor, known as continuity of care, has seen a decline in recent decades in both the UK and the U.S. This decline has negatively impacted patient and physician health outcomes and well-being.
Editorial Stance: Building on Terrence McDonald and colleagues' research, which distinguishes between the continuity contributions of a practice and an individual clinician, increased physician continuity has been linked to reduced emergency department usage for all patients and lower hospitalization for those with higher patient complexity. Notably, patients consistently seeing their regular family physician or a partner at the same practice had the best health outcomes. The author notes that this evidence is crucial and points to practical solutions that increase physician awareness of continuity's benefits and underscore the relationship between continuity and key health outcomes.
Why It Matters: Gradual benefits of improved continuity suggest that solutions don't have to be all-or-nothing but can come from various strategies that together enhance overall care. Possible improvements include 'buddy' systems among doctors, the use of e-health options, and focused training for family physician trainees on delivering continuity of care. These methods represent stepwise changes that can collectively improve continuity of care.
The Wall of Evidence for Continuity of Care: How Many More Bricks Do We Need?
Otto R. Maarsingh, MD, PhD
Department of General Practice, Amsterdam UMC, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam Public Health, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
PRE-EMBARGO LINK (Link expires at 5 p.m. EDT May 28th, 2024)
PERMANENT LINK
END
The wall of evidence for continuity of care
2024-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Parents of children with serious illness from Somali, Hmong, and Latin American communities desire better communication and support in pediatric health care
2024-05-28
Background and Goal: Nearly 500,000 children in the U.S. live with serious or life-threatening illnesses. Family caregivers, especially parents, face the challenges of managing complex medical needs, navigating the health system, and advocating for their children. This often leads to psychological distress, depression, and anxiety for caregivers. Understanding the experiences of parents of children with serious illnesses, especially those who are racially and ethnically diverse, remains limited. This study examined the experiences of Somali, Hmong, and Latin American parents in pediatric serious illness care, aiming to identify improvements and reduce disparities in pediatric ...
Primary care can improve hygienic practices while reducing waste
2024-05-28
Background & Goal: Exam table paper is perceived as necessary for hygienic care; however, there is limited evidence for its efficacy. It may not stop disease transmission, and it may create a false sense of cleanliness. The Ontario Guidelines for Prevention & Control of Infection in Healthcare Settings do not endorse exam table paper, but rather recommend cleaning with specific low-level disinfectants (for example, 0.5% accelerated hydrogen peroxide). Additionally, there are negative economic and climate change impacts of using exam table paper. The average clinic seeing ...
HKUST researchers enhance performance of eco-friendly cooling applications by developing sustainable strategy to manipulate interfacial heat transfer
2024-05-28
Researchers at the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have developed a sustainable and controllable strategy to manipulate interfacial heat transfer, paving the way for improving the performance of eco-friendly cooling in various applications such as electronics, buildings and solar panels.
As demand for effective cooling solutions continues to grow due to the rising global temperature, scientists worldwide have been actively exploring energy-saving cooling technologies that are more effective. Compared to active cooling, which entirely depends on energy consumption ...
Variations in medical assistant to primary care clinician staffing ratios may reflect differences in practice ownership and organizational culture
2024-05-28
Background and goal: Medical assistants (MAs) are among the fastest growing occupations within the U.S. primary care workforce, and many practices have expanded the roles and caregiving responsibilities of primary care MAs. However, little is known about organizational factors associated with MA support levels for primary care clinicians (PCCs).
Study Approach: This study analyzed the current ratio of medical assistants (MAs) to primary care clinicians based on responses to the second National Survey of Healthcare Organizations and Systems (NSHOS II), a 52-question survey ...
Better disciplinary structures in schools can help reduce hate speech directed against Asian American students
2024-05-28
Asian Americans have been the targets of hate speech for generations, particularly during the COVID pandemic. But new research by the University of California, Davis, suggests that Asian American adolescents experience fewer incidents of hate speech in schools with stronger disciplinary structures and adult support.
A new study looks at hate speech experiences even before COVID, during the period between 2015 and 2019. The article, “Hate Speech Against Asian American Youth: Pre-Pandemic Trends and The Role of School Factors,” was published May 4 in the Journal of Youth and Adolescents.
“Although hate against Asian American and Pacific Islander communities ...
Bringing back an ancient bird
2024-05-28
Using ancient DNA extracted from the toe bone of a museum specimen, Harvard biologists have sequenced the genome of an extinct, flightless bird called the little bush moa, shedding light into an unknown corner of avian genetic history.
Published in Science Advances, the work is the first complete genetic map of the turkey-sized bird whose distant living cousins include the ostrich, emu, and kiwi. It is one of nine known species of moa, all extinct for the last 700 years, that inhabited New Zealand before the late 1200s and the arrival of Polynesian human settlers.
“We’re pulling ...
Wistar research identifies mechanisms for selective multiple sclerosis treatment strategy
2024-05-28
PHILADELPHIA — (May 28, 2024) — The Wistar Institute’s Paul M. Lieberman, Ph.D., and lab team led by senior staff scientist and first author, Samantha Soldan, Ph.D., have demonstrated how B cells infected with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) can contribute to a pathogenic, inflammatory phenotype that contributes to multiple sclerosis (MS); the group has also shown how these problematic B cells can be selectively targeted in a way that reduces the damaging autoimmune response of multiple sclerosis. The lab’s findings were published in Nature Microbiology in the paper, “Multiple sclerosis patient derived spontaneous B cells have distinct EBV and ...
Fatherhood’s hidden heart health toll
2024-05-28
Among fathers, heart health was worse for men who became fathers under the age 25
First U.S. multiethnic longitudinal study to analyze cardiovascular health outcomes of fathers
Results differed by race and ethnicity subgroups
Age-adjusted rate of death for Black fathers was lower than for nonfathers
‘Fatherhood may be protective for Black men’
CHICAGO --- Heart disease is the leading cause of death among men, and being a father may put men at an even greater risk of poor heart health later in life, reports a new study from scientists at Northwestern University and Ann & ...
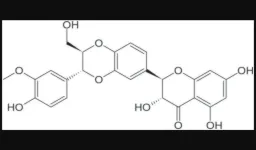
The importance of integrated therapies on cancer: Silibinin, an old and new molecule
2024-05-28
“This consideration could be the starting point to study whether Silibinin could contrast tumor progression, aging and inflammaging through molecular and cellular mechanisms [...].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 28, 2024 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on May 23, 2024, entitled, “The importance of integrated therapies on cancer: Silibinin, an old and new molecule.”
In this new review, researchers Elisa Roca, Giuseppe Colloca, Fiorella Lombardo, Andrea Bellieni, Alessandra Cucinella, Giorgio Madonia, Licia Martinelli, Maria Elisa Damiani, Ilaria Zampieri, and ...
Texas A&M-led team creates first global map of seafloor biodiversity activity
2024-05-28
A pioneering study has used extensive global datasets and machine learning to map the activities of seafloor invertebrate animals, including worms, clams and shrimps, across the entire ocean, revealing for the first time critical factors that support and maintain the health of marine ecosystems.
The international team, led by Texas A&M University and including investigators from Yale University and the University of Southampton, specifically focused on the unsung yet vital role burrowing animals play as "ecosystem engineers" in shaping nutrient ...