(Press-News.org) Professor Dariusz Stramski of Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego has been selected by The Oceanography Society as the 2024 recipient of the Nils Gunnar Jerlov Medal in recognition of his significant and wide-ranging contributions to the field of optical oceanography.
With a distinguished career spanning over 40 years, Dr. Stramski has made profound impacts on the study of ocean optics. Born in Poland, Stramski received his M.S. with honors in oceanography (1978) and Ph.D. in Earth sciences (1985) from the University of Gdańsk. His research began with groundbreaking measurements of wave-induced underwater light fluctuations during his graduate studies, which laid the foundation for his lifelong dedication to understanding the complex interactions between light and seawater. His subsequent work has encompassed a diverse array of topics spanning radiative transfer in the ocean, the application of optical methods in oceanography, and the development of innovative optical technologies.
Dr. Stramski’s contributions in more than 100 peer-reviewed publications are vast and varied. He has explored the interactions of light with numerous marine particles, from viruses and colloids to phytoplankton, minerals, and bubbles. His meticulous experiments have measured both absorption and scattering properties across a broad spectral range, in addition to detailed characterizations of concentration, composition, and size distribution of suspended particulate matter. His theoretical work has pushed the boundaries of the field, employing novel reductionist concepts and approaches to advance inverse optical models and algorithms. These models support studies of the world’s oceans using satellite remote sensing and in situ optical observations. His contributions notably also encompass the development of innovative technologies to measure the particle size distribution of submicron particles as well as the spatial and temporal variability in underwater light fields, including low-light environments. Dr. Stramski’s multifaceted contributions continue to shape ocean optics research, benefiting both scientific understanding and practical applications.
Beyond his research, Dr. Stramski is celebrated as a distinguished collaborator, thorough editor, excellent educator, and influential mentor. He has led numerous research projects, participated in many oceanographic expeditions in various regions of the world’s ocean, and has been actively involved in teaching and various professional activities. He has served as an Associate Editor of the journal Limnology and Oceanography and a member of expert panels, working groups, and science teams, with notable contributions to IOCCG and NASA MODIS, VIIRS, and PACE missions. At Scripps Oceanography, where he has worked since 1997, he has taught and mentored students from diverse backgrounds, significantly impacting their academic and professional trajectories.
Dr. Stramski will be honored during the Ocean Optics XXVI Conference in Las Palmas, Gran Canaria, Spain from October 6-11, 2024. Learn more at oceanopticsconference.org.
ABOUT THE MEDAL
The Dr. Nils Gunnar Jerlov Medal is awarded biennially to an individual for advancing our knowledge of how light interacts with the ocean. Additionally, the Jerlov Medal also seeks to recognize individuals who have made significant contributions toward educating and mentoring students and early career ocean professionals or who have conducted significant interdisciplinary research in ocean science and/or collaborative work towards meaningful societal impact. Learn more at: tos.org/jerlov-medal
###
The Oceanography Society (TOS) was founded in 1988 to advance oceanographic research, technology, and education, and to disseminate knowledge of oceanography and its application through research and education. TOS promotes broad understanding of oceanography, facilitates consensus building across all the disciplines of the field, and informs the public about ocean research, innovative technology, and educational opportunities throughout the spectrum of oceanographic inquiry. TOS welcomes members from all nations. Learn more at tos.org
END
Dariusz Stramski selected as 2024 recipient of the Nils Gunnar Jerlov Medal
In recognition of his significant and wide-ranging contributions to the field of optical oceanography
2024-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI health coach lowers blood pressure and boosts engagement in patients with hypertension
2024-05-29
(Toronto, May 28, 2024) A new study in JMIR Cardio, published by JMIR Publications, shows that a fully digital, artificial intelligence (AI)–driven lifestyle coaching program can effectively reduce blood pressure (BP) in adults with hypertension. This AI-based program leverages data from wearable activity trackers and BP monitors as well as a mobile app questionnaire to tailor lifestyle guidance. The research team, led by Jared Leitner of the University of California, San Diego, used this innovative intervention to help manage ...
AI saving humans from the emotional toll of monitoring hate speech
2024-05-29
A team of researchers at the University of Waterloo have developed a new machine-learning method that detects hate speech on social media platforms with 88 per cent accuracy, saving employees from hundreds of hours of emotionally damaging work.
The method, dubbed the Multi-Modal Discussion Transformer (mDT), can understand the relationship between text and images as well as put comments in greater context, unlike previous hate speech detection methods. This is particularly helpful in reducing false positives, which are often ...
Chicken feathers to deliver chemotherapy drugs and repair enzymes
2024-05-29
A new method of drug delivery using proline, an amino acid found in chicken feathers and skin tissue, could be used to limit the side effects of chemotherapy and repair important enzymes, new research suggests.
Published in the journal Chem today, researchers have designed a cage (a box made of single molecules) from biologically compatible peptides, short amino acids that form the basis of proteins. These cages can house drugs of different sizes and transport them in the body with high levels of precision.
The negative ...
Bio-inspired cameras and AI help drivers detect pedestrians and obstacles faster
2024-05-29
It’s every driver’s nightmare: a pedestrian stepping out in front of the car seemingly out of nowhere, leaving only a fraction of a second to brake or steer the wheel and avoid the worst. Some cars now have camera systems that can alert the driver or activate emergency braking. But these systems are not yet fast or reliable enough, and they will need to improve dramatically if they are to be used in autonomous vehicles where there is no human behind the wheel.
Quicker detection using less computational ...
Graphene gets cleaned up
2024-05-29
Graphene has been called “the wonder material of the 21st century.” Since its discovery in 2004, the material—a single layer of carbon atoms—has been touted for its host of unique properties, which include ultra-high electrical conductivity and remarkable tensile strength. It has the potential to transform electronics, energy storage, sensors, biomedical devices, and more. But graphene has had a dirty little secret: it's dirty.
Now, engineers at Columbia University and colleagues at the University of Montreal and the National Institute of Standards and Technology are poised to clean things up with an oxygen-free chemical vapor ...
Study finds older adults hospitalized for heart failure had high risk of kidney complications
2024-05-29
In a study of Medicare beneficiaries, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital found that one year after hospitalization for heart failure, 6 percent of patients had progressed to dialysis.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Study led by Brigham researchers found that among older adults hospitalized for heart failure, nearly 3 in 4 were discharged with reduced kidney function.
Lower kidney function was associated with substantially higher risk of kidney complications and other adverse clinical outcomes among older adults, with more than 1 in 20 progressing to dialysis within one year after heart failure hospitalization.
These findings emphasize the need ...
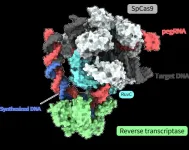
Editing without “cutting”: Molecular mechanisms of new gene-editing tool revealed
2024-05-29
Joint research led by Yutaro Shuto, Ryoya Nakagawa, and Osamu Nureki of the University of Tokyo determined the spatial structure of various processes of a novel gene-editing tool called “prime editor.” Functional analysis based on these structures also revealed how a “prime editor” could achieve reverse transcription, synthesizing DNA from RNA, without “cutting” both strands of the double helix. Clarifying these molecular mechanisms contributes greatly to designing gene-editing tools accurate enough for gene therapy treatments. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
The ...
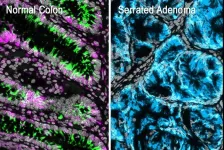
Identifying the initial steps in colorectal cancer formation
2024-05-29
Research led by Weill Cornell Medicine provides new evidence that most colorectal cancers begin with the loss of intestinal stem cells, even before cancer-causing genetic alterations appear. The results, published on May 29 in Developmental Cell, overturn the prevailing theory for colorectal tumor initiation and suggest new ways to diagnose the disease before it has a chance to become established.
“Colorectal cancer is very, very heterogeneous, which has made it difficult for many years to classify these tumors in order to inform therapy,” said senior author Dr. ...
hnRNPM, a guardian of the integrity of cellular protein production
2024-05-29
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have discovered that a protein called hnRNPM helps protect the integrity of the process cells use to make proteins. hnRNPM works by preventing the cell from making mistakes while it is putting together the different components leading to newly produced proteins. In cancer cells, loss of hnRNPM triggers an interferon immune response, suggesting that this protein may hold clinical promise. The findings appeared in Molecular Cell.
“Synthesizing a protein is like putting together the different parts of a machine. If during the assembly process parts that do not belong are incorporated ...
Children often exposed to problematic click bait during YouTube searches
2024-05-29
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – When a child peruses YouTube, the content recommended to them is not always age appropriate, a new study suggests.
Researchers mimicked search behaviors of children using popular search terms, such as memes, Minecraft and Fortnite, and captured video thumbnails recommended at the end of each video.
Among the 2,880 thumbnails analyzed, many contained problematic click bait, such as violence or frightening images, according to the Michigan Medicine led research in JAMA Network Open.
“Children spend a significant amount of time on free video sharing platforms that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
[Press-News.org] Dariusz Stramski selected as 2024 recipient of the Nils Gunnar Jerlov MedalIn recognition of his significant and wide-ranging contributions to the field of optical oceanography