(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found a distinct relationship between sleep duration, social media usage, and brain activation across brain regions that are key for executive control and reward processing.
Results show a correlation between shorter sleep duration and greater social media usage in teens. The analysis points to involvement of areas within the frontolimbic brain regions, such as the inferior and middle frontal gyri, in these relationships. The inferior frontal gyrus, key in inhibitory control, may play a crucial role in how adolescents regulate their engagement with rewarding stimuli such as social media. The middle frontal gyrus, involved in executive functions and critical in assessing and responding to rewards, is essential in managing decisions related to the balancing of immediate rewards from social media with other priorities like sleep. These results suggest a nuanced interaction between specific brain regions during adolescence and their influence on behavior and sleep in the context of digital media usage.
“As these young brains undergo significant changes, our findings suggest that poor sleep and high social media engagement could potentially alter neural reward sensitivity,” said Orsolya Kiss, who has a doctorate in cognitive psychology and is a research scientist at SRI International in Menlo Park, California. “This intricate interplay shows that both digital engagement and sleep quality significantly influence brain activity, with clear implications for adolescent brain development.”
This study involved data from 6,516 adolescents, ages 10-14 years, from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study. Sleep duration was assessed from the Munich Chronotype questionnaire, and recreational social media use through the Youth Screen Time Survey. Brain activities were analyzed from functional MRI scans during the monetary incentive delay task, targeting regions associated with reward processing. The study used three different sets of models and switched predictors and outcomes each time. Results were adjusted for age, COVID-19 pandemic timing, and socio-demographic characteristics.
Kiss noted that these results provide new insights into how two significant aspects of modern adolescent life – social media usage and sleep duration – interact and impact brain development.
“Understanding the specific brain regions involved in these interactions helps us identify potential risks and benefits associated with digital engagement and sleep habits,” Kiss said. “This knowledge is especially important as it could guide the development of more precise, evidence-based interventions aimed at promoting healthier habits.”
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends that teenagers 13 to 18 years of age should sleep 8 to 10 hours on a regular basis. The AASM also encourages adolescents to disconnect from all electronic devices at least 30 minutes to an hour before bedtime.
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The research abstract was published recently in an online supplement of the journal Sleep and will be presented Sunday, June 2, and Wednesday, June 5, during SLEEP 2024 in Houston. SLEEP is the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society.
###
Abstract Title: Interconnected Dynamics of Sleep Duration, Social Media Engagement, and Neural Reward Responses in Adolescents
Abstract ID: 0148
Oral Presentation Date: Sunday, June 2, from 2:45-3 p.m. CDT, Room #340
Poster Presentation Date: Wednesday, June 5, from 11-11:45 a.m. CDT, Board 18
Presenter: Orsolya Kiss, Ph.D.
About the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, LLC
The APSS is a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society. The APSS organizes the SLEEP annual meeting each June (sleepmeeting.org).
About the American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Established in 1975, the AASM advances sleep care and enhances sleep health to improve lives. The AASM has a combined membership of 12,000 accredited sleep centers and individuals, including physicians, scientists and other health care professionals who care for patients with sleep disorders. As the leader in the sleep field, the AASM sets standards and promotes excellence in sleep medicine health care, education and research (aasm.org).
About the Sleep Research Society
The SRS is a professional membership society that advances sleep and circadian science. The SRS provides forums for the exchange of information, establishes and maintains standards of reporting and classifies data in the field of sleep research, and collaborates with other organizations to foster scientific investigation on sleep and its disorders. The SRS also publishes the peer-reviewed, scientific journals Sleep and Sleep Advances (sleepresearchsociety.org).
About SRI
SRI is an independent nonprofit research institute headquartered in Menlo Park, Calif., with a rich history of supporting government and industry. SRI creates and delivers world-changing solutions for a safer, healthier, and more sustainable future. For more than 75 years, SRI has collaborated across technical and scientific disciplines to discover and develop groundbreaking products and technologies and bring innovations and ideas to the marketplace. Learn more at www.sri.com.
END
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that better sleep health was associated with lower levels of loneliness, and this association was stronger among younger adults.
Results indicate that better sleep health was associated with significantly lower total loneliness, emotional loneliness and social loneliness. While better sleep health was associated with lower total and emotional loneliness across ages, this association was stronger for younger adults. However, age did not moderate the association ...
WHAT:
Using a combination of cutting-edge immunologic technologies, researchers have successfully stimulated animals’ immune systems to induce rare precursor B cells of a class of HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs). The findings, published today in Nature Immunology, are an encouraging, incremental step in developing a preventive HIV vaccine.
HIV is genetically diverse making the virus difficult to target with a vaccine, but bNAbs may overcome that hurdle because they bind to parts of the virus that remain constant even when it mutates. ...
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting demonstrates that when individuals with obstructive sleep apnea use their positive airway pressure machine more regularly, it benefits their relationship with their partner.
Results show that greater adherence to PAP therapy was associated with higher levels of relationship satisfaction and lower levels of relationship conflict. Higher sleep efficiency among patients also was associated with higher levels of relationship satisfaction as reported by both the patient and their partner.
“Recognizing that sleep ...
New research from the University of Lausanne reveals that both the excess and the deficiency of a single protein can lead to severe intellectual deficiencies. The discovery offers critical insights for early diagnosis of a rare developmental disorder.
A team of scientists led by Alexandre Reymond, an expert in human genetics at the Center for Integrative Genomics (CIG) and professor at the Faculty of Biology and Medicine (FBM) of the University of Lausanne (UNIL), presents a major step forward in the detection of a rare genetic disease. For ...
Boston – Four teams of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators have found that people experience discrimination and bias in different ways and in more realms of cancer care than previously understood. The findings, in different studies, suggest that oncology professionals and the systems they work in have more work to do to adapt to the realities of increasing diversity and inclusion, not only in the patient population but also in the oncology workforce. The research teams will present their findings at the 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) in Chicago. ASCO is the world’s largest clinical cancer ...
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Early detection improves treatment outcomes for endometrial and ovarian cancers, yet far too often women are diagnosed in advanced stages of these diseases. Unlike many other cancers, there are no standard screenings for early detection of endometrial and ovarian cancers. The incidence rate for endometrial cancer is expected to rise, driven by environmental factors, obesity and diabetes.
Marina Walther-Antonio, Ph.D., and colleagues at Mayo Clinic's Center for Individualized Medicine are on a mission to catch these cancers early.
Their research dives deep into the microbiome, a community of ...
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – RNA transcription is the genomic process in which a cell produces a duplicate of a gene’s DNA sequence.
In a study published in Nucleic Acids Research, University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Chemistry Professor Jun Zhang, Ph.D., and his team reveal how the protein SRSF1 possesses the novel function of binding and unfolding complex RNA Guanine-quadruplexes.
Present in both DNA and RNA sequences, a G-quadruplex (GQ) is a structure of four guanine bases attached in a planar array. ...
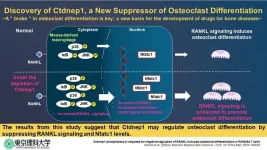
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by porous and fragile bones, poses a significant threat to skeletal health. As the very framework of the human body, bones provide crucial structural support. When bone mass diminishes, it not only compromises this support but also impairs overall function, leading to a diminished quality of life. With the aging population experiencing a surge in osteoporosis cases, the strain on healthcare resources for long-term care is evident. Hence, there is a need to understand the mechanisms that contribute to osteoporosis and develop effective targeted therapies ...
Transgender individuals often face unique challenges in aligning their physical bodies with their true gender identity. Among the various methods employed, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) stands as a vital means for transgender men to achieve physical changes in consonance with their gender identity. Navigating the complexities that come with gender transition, transgender individuals seek medical interventions to alleviate gender dysphoria and align their bodies with their gender identity.
For transgender men, testosterone therapy holds promise in inducing masculinizing effects such as increased muscle mass, cessation of ...
Recommendations designed to reframe the evaluation of in vitro diagnostic tests have been published today by the Royal Statistical Society in its Series A journal.
The report, which will be submitted to the UK Covid-19 Inquiry, is intended to help prevent future scenarios in which IVDs are marketed widely, but later attract serious concerns about the standards applied to their evaluation.
The research was prompted by concerns about the standards applied to the evaluation of diagnostic tests during the Covid-19 pandemic – particularly lateral flow tests – however the recommendations cover all new tests, especially those ...