(Press-News.org) As more and more people drive electric cars, congestion and queues can occur when many people need to charge at the same time. A new study from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden shows how AI-controlled charging stations, through smart algorithms, can offer electric vehicle users personalised prices, and thus minimise both price and waiting time for customers. But the researchers point to the importance of taking the ethical issues seriously, as there is a risk that the artificial intelligence exploits information from motorists.
Today's commercial charging infrastructure can be a jungle. The market is dynamic and complex with a variety of subscriptions and free competition between providers. At some fast charging stations, congestion and long queues may even occur. In a new study, researchers at Chalmers have created a mathematical model to investigate how fast charging stations controlled by artificial intelligence, AI, can help by offering electric car drivers personalised prices, which the drivers can choose to accept or refuse. The AI uses algorithms that can adjust prices based on individual factors, such as battery level and the car's geographic location.
“The electric car drivers can choose to share information with the charging station providers and receive a personal price proposal from a smart charging station. In our study, we could show how rational and self-serving drivers react by only accepting offers that are beneficial to themselves. This leads to both price and waiting times being minimized”, says Balázs Kulcsár, professor at the department of electrical engineering at Chalmers.
In the study, the drivers always had the option to refuse the personal price, and choose a conventional charging station with a fixed price instead. The personal prices received by the drivers could differ significantly from each other, but were almost always lower than the market prices. For the providers of charging stations, the iterative AI algorithm can find out which individual prices are accepted by the buyer, and under which conditions. However, during the course of the study, the researchers noted that on some occasions the algorithm raised the price significantly when the electric car's batteries were almost completely empty, and the driver consequently had no choice but to accept the offer.
“Smart charging stations can solve complex pricing in a competitive market, but our study shows that they need to be developed and introduced with privacy protection for consumers, well in line with responsible-ethical AI paradigms”, says Balázs Kulcsár.
More about the study
The researchers created a mathematical model of the interaction between profit-maximising fast charging stations and electric car users. The "charging stations" could offer public market prices or AI-driven profit-maximising personal prices, which the "electric car users" could then accept or reject based on their own conditions and needs. In most cases, the results were promising, as the AI-generated prices were lower than the market prices.
The research is presented in the paper: Personalized dynamic pricing policy for electric vehicles: Reinforcement learning approach published in the journal Transportation Research, Part C: Emerging Technologies
The researchers involved in the study are Balázs Kulcsár, Sangjun Bae and Sebastian Gros, and they are active at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden; Seyong Cyber University, China, and Norwegian University of Science and Technology.
The research has been financed by the Swedish Electromobility Center and partially by the EU project E-Laas.
For more information, please contact
Balázs Kulcsár, Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, Chalmers University of Technology, +46 31-772 17 85, kulcsar@chalmers.se
The contact person speaks English and is available for live and pre-recorded interviews. At Chalmers, we have podcast studios and broadcast filming equipment on site and would be able to assist a request for a television, radio or podcast interview.
END
AI-controlled stations can charge electric cars at a personal price
2024-05-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The world’s most powerful anti-fungal chemistries cause fungal pathogens to self-destruct
2024-05-31
Scientists have discovered that the most widely-used class of antifungals in the world cause pathogens to self-destruct. The University of Exeter-led research could help improve ways to protect food security and human lives.
Fungal diseases account for the loss of up to a quarter of the world’s crops. They also pose a risk to humans and can be fatal for those with weakened immune systems.
Our strongest "weapon" against fungal plant diseases are azole fungicides. These chemical products account for to a quarter of the world agricultural ...
Could the world famous Roman Baths help scientists counter the challenge of antibiotic resistance?
2024-05-31
The world-famous Roman Baths are home to a diverse range of microorganisms which could be critical in the global fight against antimicrobial resistance, a new study suggests.
The research, published in the journal The Microbe, is the first to provide a detailed examination of the bacterial and archaeal communities found within the waters of the popular tourist attraction in the city of Bath (UK).
Scientists collected samples of water, sediment and biofilm from locations within the Roman Baths complex including the King’s Spring (where the waters reach around 45°C) and the Great Bath, where the temperatures ...
Fast charging electric vehicles with stable high-energy density lithium-ion batteries
2024-05-31
A research team led by Dr. Choi Jeong Hee at the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) Battery Materials and Process Research Center, in cooperation with a Hanyang University team mentored by Professor Lee Jong-Won and a Kyunghee University team mentored by Professor Park Min-Sik, developed a core technology to ensure the charging/discharging stability and long-life of lithium-ion batteries under fast-charging conditions.
A crucial prerequisite for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is the enhancement of lithium-ion battery performance in terms of driving ...
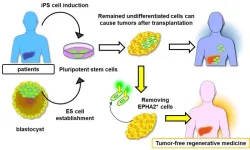
Tackling the hurdle of tumor formation in stem cell therapies
2024-05-31
Ikoma, Japan – Pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) are a type of stem cells capable of developing into various cell types. Over the past few decades, scientists have been working towards the development of therapies using PSCs. Thanks to their unique ability to self-renew and differentiate (mature) into virtually any given type of tissue, PSCs could be used to repair organs that have been irreversibly damaged by age, trauma, or disease.
However, despite extensive efforts, regenerative therapies involving PSCs still have many hurdles to overcome. One being the formation of tumors (via ...
A 20-year-old puzzle solved: KAIST research team reveals the 'three-dimensional vortex' of zero-dimensional ferroelectrics
2024-05-31
Materials that can maintain a magnetized state by themselves without an external magnetic field (i.e., permanent magnets) are called ferromagnets. Ferroelectrics can be thought of as the electric counterpart to ferromagnets, as they maintain a polarized state without an external electric field. It is well-known that ferromagnets lose their magnetic properties when reduced to nano sizes below a certain threshold. What happens when ferroelectrics are similarly made extremely small in all directions (i.e., into a zero-dimensional structure such as nanoparticles) has been a topic of controversy for a long time.
The research team led by Dr. Yongsoo ...
Children’s Hospital Los Angeles team finds new potential causes of rare and lethal bone cancer
2024-05-31
Little is known about the genetics and biology of chordoma, a rare and aggressive bone tumor. Chordomas occur in approximately one in a million people in the U.S. a year and only five percent of these are in children. These tumors can arise anywhere along the spine in adults. However, in children these tumors occur mostly at the base of the skull, making complete surgical removal challenging or impossible. Any tumor remnants are treated with high doses of radiation—which can cause significant damage to the developing brain.
A team of researchers led by Xiaowu Gai, PhD and Jaclyn Biegel, PhD, FACMG, at the Center for Personalized Medicine ...
One in four Thai concerned about colorectal cancer screening cost
2024-05-31
According to research led by Prof. Varut Lohsiriwat, Professor of Surgery, Division of General Surgery (Section of Colorectal Surgery) of Siriraj Hospital, at Mahidol University, CRC is the third most common cancer in Thailand, accounting for 11% of the cancer burden. It is the only malignancy with an increased incidence in both genders in the country.
By 2040, the burden of CRC is projected to increase to 3.2 million new cases and 1.6 million deaths per year representing a 66% and 71% rise in new cases and deaths respectively relative ...
Infants hear significantly more speech than music at home, UW study finds
2024-05-31
Speech and music are the dominant elements of an infant’s auditory environment. While past research has shown that speech plays a critical role in children’s language development, less is known about the music that infants hear.
A new University of Washington study, published May 21 in Developmental Science, is the first to compare the amount of music and speech that children hear in infancy. Results showed that infants hear more spoken language than music, with the gap widening as the babies get older.
“We wanted to get a snapshot of what’s happening in infants’ home environments,” said corresponding author ...
New coral disease forecasting system led by University of Hawai'i team
2024-05-31
Research led by the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) has led to a new tool for forecasting coral disease that could help conservationists step in at the right times with key interventions. Ecological forecasts are critical tools for conserving and managing marine ecosystems, but few forecasting systems can account for the wide range of ecological complexities in near-real-time.
Using ecological and marine environmental conditions, the Multi-Factor Coral Disease Risk product predicts the risk of two diseases across reefs in the central and western Pacific and along the east coast of Australia. An article ...
Tobacco funded research still appearing in top medical journals
2024-05-31
Tobacco-funded research is still appearing in highly-cited medical journals - despite attempts by some to cut ties altogether, finds an investigation by The Investigative Desk and The BMJ today.
Although the tobacco industry has a long history of subverting science, most leading medical journals don’t have policies which ban research wholly or partly funded by the industry.
And even when publishers, authors and universities are willing to restrict tobacco industry ties, they struggle ...