(Press-News.org) HOUSTON – (May 31, 2024) – For his “exceptional contributions to the field of dynamics,” Pol Spanos, the Lewis B. Ryon Professor of Mechanical and Civil Engineering at Rice University, has been awarded the 2024 Blaise Pascal Medal in Engineering by the European Academy of Sciences.
Spanos, who joined the Rice faculty in 1984, was recognized for his “theoretical insights, ranging from equivalent linearization to statistical quadratization, which have significantly advanced our understanding of structural behavior. These insights have not only led to more accurate predictions but have also empowered engineers to make better-informed decisions.”
The medal is named for Blaise Pascal (1623-62), the French mathematician, physicist, inventor and philosopher who developed an early version of a mechanical calculator. Spanos will formally receive the medal at the 2024 Symposium and Ceremony of the European Academy of Sciences to be held Oct. 29-30 in Lisbon, Portugal.
Along with the European Academy of Sciences, Spanos is a member of the National Academy of Engineering, the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the Academy of Europe, the European Academy of Sciences and Arts, the National Academy of Greece, the Russian Academy of Engineering, the Indian National Academy of Engineering, the Canadian Academy of Engineering and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He is a fellow of both the American Academy of Mechanics and the Engineering Mechanics Institute of the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE).
He has advised more than 55 doctorate and 75 master’s students and has a joint appointment in materials science and nanoengineering. He has published more than 400 technical papers and authored or edited more than 20 books and conference volumes. For more than three decades he has served as editor-in-chief for the International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics and Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics.
Spanos is a recent president of the Engineering Mechanics Institute and a recent chair of the executive board of the International Association for Structural Safety and Reliability. He has been elected an honorary member of the American Society of Mechanical Engineering (ASME) and the ASCE, the highest honor given by each organization; he is also an ASME Gold Medalist, its most prestigious medal.
⎯ by Patrick Kurp, science writer for the George R. Brown School of Engineering
-30-
This news release can be found online at news.rice.edu.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Image downloads:
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2024/05/Spanos-BART-1.jpg
CAPTION: Pol Spanos is the Lewis B. Ryon Professor of Mechanical and Civil Engineering at Rice University.
END
European Academy of Sciences honors Rice’s Pol Spanos with prestigious award
Rice engineer recognized for ‘exceptional contributions to the field of dynamics’
2024-05-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rice’s Jamie Padgett wins Charles Martin Duke Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Award
2024-05-31
HOUSTON – (May 31, 2024) – Jamie Padgett, the Stanley C. Moore Professor in Engineering and chair of civil and environmental engineering at Rice University, has received the 2024 Charles Martin Duke Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Award from the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE).
Padgett was recognized for her “contributions to fragility, risk and resilience modeling of multimodal transportation systems and their infrastructure components when subjected to earthquakes and other hazards.”
Her ...
Sleep moderates the link between bullying and suicide in teens
2024-05-31
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that sleep duration significantly moderates the association between bullying and suicide attempts among adolescents in the U.S.
The study revealed that 15% of adolescents reported they were bullied at school, and 16% were bullied electronically; 10.2% reported they had attempted suicide during the past year; and 77.3% did not adhere to sleep duration recommendations. Adolescents who reported 4 hours of sleep or less per night were two times as likely to attempt suicide, and sleep duration significantly moderated the association between bullying ...
AI-controlled stations can charge electric cars at a personal price
2024-05-31
As more and more people drive electric cars, congestion and queues can occur when many people need to charge at the same time. A new study from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden shows how AI-controlled charging stations, through smart algorithms, can offer electric vehicle users personalised prices, and thus minimise both price and waiting time for customers. But the researchers point to the importance of taking the ethical issues seriously, as there is a risk that the artificial intelligence exploits information from motorists.
Today's commercial ...
The world’s most powerful anti-fungal chemistries cause fungal pathogens to self-destruct
2024-05-31
Scientists have discovered that the most widely-used class of antifungals in the world cause pathogens to self-destruct. The University of Exeter-led research could help improve ways to protect food security and human lives.
Fungal diseases account for the loss of up to a quarter of the world’s crops. They also pose a risk to humans and can be fatal for those with weakened immune systems.
Our strongest "weapon" against fungal plant diseases are azole fungicides. These chemical products account for to a quarter of the world agricultural ...
Could the world famous Roman Baths help scientists counter the challenge of antibiotic resistance?
2024-05-31
The world-famous Roman Baths are home to a diverse range of microorganisms which could be critical in the global fight against antimicrobial resistance, a new study suggests.
The research, published in the journal The Microbe, is the first to provide a detailed examination of the bacterial and archaeal communities found within the waters of the popular tourist attraction in the city of Bath (UK).
Scientists collected samples of water, sediment and biofilm from locations within the Roman Baths complex including the King’s Spring (where the waters reach around 45°C) and the Great Bath, where the temperatures ...
Fast charging electric vehicles with stable high-energy density lithium-ion batteries
2024-05-31
A research team led by Dr. Choi Jeong Hee at the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) Battery Materials and Process Research Center, in cooperation with a Hanyang University team mentored by Professor Lee Jong-Won and a Kyunghee University team mentored by Professor Park Min-Sik, developed a core technology to ensure the charging/discharging stability and long-life of lithium-ion batteries under fast-charging conditions.
A crucial prerequisite for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is the enhancement of lithium-ion battery performance in terms of driving ...
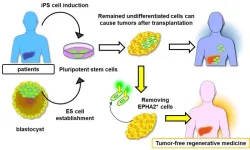
Tackling the hurdle of tumor formation in stem cell therapies
2024-05-31
Ikoma, Japan – Pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) are a type of stem cells capable of developing into various cell types. Over the past few decades, scientists have been working towards the development of therapies using PSCs. Thanks to their unique ability to self-renew and differentiate (mature) into virtually any given type of tissue, PSCs could be used to repair organs that have been irreversibly damaged by age, trauma, or disease.
However, despite extensive efforts, regenerative therapies involving PSCs still have many hurdles to overcome. One being the formation of tumors (via ...
A 20-year-old puzzle solved: KAIST research team reveals the 'three-dimensional vortex' of zero-dimensional ferroelectrics
2024-05-31
Materials that can maintain a magnetized state by themselves without an external magnetic field (i.e., permanent magnets) are called ferromagnets. Ferroelectrics can be thought of as the electric counterpart to ferromagnets, as they maintain a polarized state without an external electric field. It is well-known that ferromagnets lose their magnetic properties when reduced to nano sizes below a certain threshold. What happens when ferroelectrics are similarly made extremely small in all directions (i.e., into a zero-dimensional structure such as nanoparticles) has been a topic of controversy for a long time.
The research team led by Dr. Yongsoo ...
Children’s Hospital Los Angeles team finds new potential causes of rare and lethal bone cancer
2024-05-31
Little is known about the genetics and biology of chordoma, a rare and aggressive bone tumor. Chordomas occur in approximately one in a million people in the U.S. a year and only five percent of these are in children. These tumors can arise anywhere along the spine in adults. However, in children these tumors occur mostly at the base of the skull, making complete surgical removal challenging or impossible. Any tumor remnants are treated with high doses of radiation—which can cause significant damage to the developing brain.
A team of researchers led by Xiaowu Gai, PhD and Jaclyn Biegel, PhD, FACMG, at the Center for Personalized Medicine ...
One in four Thai concerned about colorectal cancer screening cost
2024-05-31
According to research led by Prof. Varut Lohsiriwat, Professor of Surgery, Division of General Surgery (Section of Colorectal Surgery) of Siriraj Hospital, at Mahidol University, CRC is the third most common cancer in Thailand, accounting for 11% of the cancer burden. It is the only malignancy with an increased incidence in both genders in the country.
By 2040, the burden of CRC is projected to increase to 3.2 million new cases and 1.6 million deaths per year representing a 66% and 71% rise in new cases and deaths respectively relative ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] European Academy of Sciences honors Rice’s Pol Spanos with prestigious awardRice engineer recognized for ‘exceptional contributions to the field of dynamics’