(Press-News.org)
Losing a loved one to drug overdose has been a common experience for many Americans in recent years, crossing political and socioeconomic divides and boosting the perceived importance of the overdose crisis as a policy issue, according to a new survey led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
A nationally representative survey of more than 2,300 Americans, fielded in spring 2023, suggests that 32 percent of the U.S. adult population, or an estimated 82.7 million individuals, has lost someone they know to a fatal drug overdose. For nearly one-fifth of survey respondents—18.9 percent, representing an estimated 48.9 million adults—the person they knew who died of overdose was a family member or close friend.
The rates of reported loss due to overdose did not differ significantly by political party affiliation, but those who experienced overdose loss were more likely to view addiction as an extremely or very important policy issue.
The study will be published online May 31 in JAMA Health Forum.
“The drug overdose crisis is a national tragedy,” says Alene Kennedy-Hendricks, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Health Policy and Management at the Bloomberg School, who led the analysis. “Although large numbers of U.S. adults are bereaved due to overdose, they may not be as visible as other groups who have lost loved ones to less stigmatized health issues. Movements to build support for policy change to overcome the devastating toll of the overdose crisis should consider the role of this community.”
Over one million Americans have died from drug overdoses since the late 1990s, including more than 100,000 per year in the last few years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Last year, overdose deaths declined slightly for the first time in five years, decreasing three percent from 2022, according to preliminary data from the CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics. At about 108,000 estimated deaths, the CDC 2023 preliminary numbers remain near historic highs.
The overdose crisis has evolved over several phases, beginning with prescription opioids such as oxycodone playing a key role, followed by heroin and, more recently, powerful synthetic opioids like illicitly manufactured fentanyl and polysubstance use. Opioids can suppress breathing as a side effect, and the unpredictability of the illicit drug supply and the potency of fentanyl have dramatically increased the risk of overdose.
While the survey questions did not specifically identify opioids, the majority of overdose deaths over the last two decades have been opioid-related.
The overdose crisis has not only impacted its direct victims but also their relatives, friends, and acquaintances. Kennedy-Hendricks and her colleagues at the Bloomberg School’s Center for Mental Health and Addiction Policy set up the study to help illuminate this wider impact, which otherwise has been little studied.
The paper was co-written with colleagues from Boston University School of Public Health, the University of Minnesota, and the de Beaumont Foundation. The study’s senior author is Sandro Galea, MD, DrPH, MPH, dean of Boston University School of Public Health.
The survey is part of the CLIMB (COVID-19 and Life Stressors Impact on Mental Health and Well-being) study. Led by Catherine Ettman, PhD, an assistant professor in the Bloomberg School’s Department of Health Policy and Management, the CLIMB study has surveyed a nationally representative sample of adult Americans annually since 2020. For this overdose loss study, questions to participants from March 28 to April 17, 2023—CLIMB Wave 4—included “Do you personally know anyone who has died from a drug overdose?” A total of 2,326 participants responded to the question. Participants answering “yes” were then asked “Who do you know that has died from a drug overdose?”
Overdose losses were reported across all income groups. Forty percent of lower-income respondents (defined as annual household incomes less than $30,000) reported overdose loss. Over one-quarter—26 percent—of respondents in the $100,000 and higher annual household income category reported an overdose loss.
The rate of reported overdose loss was not significantly different across self-described Republicans, Democrats, and Independents, adding to the picture of a far-reaching phenomenon.
The data suggested a high level of endorsement across all groups—greater than 60 percent, even among those reporting no overdose loss—that addiction is an extremely or very important policy issue. Respondents who reported overdose loss had 37 percent greater odds of viewing addiction as a very or extremely important policy priority.
“This study contributes new evidence that the addiction crisis and the losses that come with it are common across Americans, but the burden is greater among those who are more economically precarious,” says Ettman. “Addressing addiction can be a unifying theme in increasingly divided times.”
The researchers plan to follow up with further studies in future CLIMB survey waves, looking at associations between overdose loss and other social variables such as trust in institutions.
“The Scale of Personal Loss Incurred by the Drug Overdose Crisis in the U.S.” was co-authored by Alene Kennedy-Hendricks, Catherine Ettman, Sarah Gollust, Sachini Bandara, Salma Abdalla, Brian Castrucci, and Sandro Galea.
CLIMB Study Wave 4 was funded by a grant from the de Beaumont Foundation.
# # #
END
About The Study: Higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 23% lower risk of all-cause mortality in this cohort study. This inverse association was partially explained by multiple cardiometabolic factors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Shafqat Ahmad, Ph.D., email shafqat.ahmad@medsci.uu.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14322)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Some 13% of older adults are diagnosed with traumatic brain injury (TBI), according to a study by UC San Francisco and the San Francisco VA Health Care System. These injuries are typically caused by falls from ground level.
Researchers followed about 9,200 Medicare enrollees, whose average age was 75 at the start of the study, and found that contrary to other studies of younger people, being female, white, healthier and wealthier was associated with higher risk of TBI.
The study publishes in JAMA Network Open on May 31, 2024.
The researchers, ...
A new study using stem cell-based models has shed new light on how the human embryo begins to develop, which could one day benefit the development of fertility treatment.
The study led by at the University of Exeter Living Systems Institute has revealed how early embryo cells decide between contributing to the foetus or to the supporting yolk sac.
Understanding this decision is important because the yolk sac is essential for later development in the womb. Producing the right number of yolk sac forming cells may be critical for infertility treatment using in vitro fertilised (IVF) embryos.
Only limited research ...
EMBARGOED by JAMA Network Open until 11 a.m., ET May 31, 2024
Contact: Maria Ober, mpober@bu.edu
BU Study Finds Policy Makers’ Use of In-Hospital Mortality as a Sepsis Quality Metric May Unfairly Penalize Safety-net Hospitals
(Boston)—Sepsis is a leading cause of death and disability and a key target of state and federal quality measures for hospitals. In-hospital mortality of patients with sepsis is frequently measured for benchmarking, both by researchers and policymakers. For example, in New York, sepsis regulations mandate reporting of risk-adjusted in-hospital mortality, and hospitals with lower or higher than expected in-hospital ...
Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital identified and assessed underlying mechanisms that may explain the Mediterranean diet’s 23 percent reduction in all-cause mortality risk for American women
The health benefits of the Mediterranean diet have been reported in multiple studies, but there is limited long-term data of its effects in U.S. women and little understanding about why the diet may reduce risk of death. In a new study that followed more than 25,000 initially healthy U.S. women for up ...
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research - If you dread public speaking you are not alone. It is a leading social phobia, one that can cause a state of anxiety that reduces otherwise articulate people to nervous incoherence.
A strong fear of public speaking is known as glossophobia. Academic studies estimate it affects 20 per cent of the population, but depending on the sample and methodology, the figure could be as high as 40 per cent.
As American writer and humourist Mark Twain said, ...
By Jovina Ang
SMU Office of Research – “Giving students immediate and frequent feedback makes online learning more effective,” Associate Professor Ouh Eng Lieh told the Office of Research.
However, based on how most online lessons are designed, questions could not be answered nor doubts clarified until students meet their instructor in the following face-to-face class.
The time delay of a few days to a few weeks can impede student learning as it might make it difficult for students to catch up and understand the subsequent topics in the course.
Learning also ...
Ishikawa, Japan -- Physical inactivity and sitting for prolonged hours are highly prevalent among office-based workers, known to be resulting in various health risks and economic constraints. However, to reduce sedentary time and increase physical activity, health promotion interventions alone are insufficient. The design of workplaces should also be considered to promote interactive behavior among workers.
Many models, such as the socio-ecological model, show how multiple factors interact to influence workers' active and sedentary behaviors. These models specifically magnify the impact of workplace environments in shaping these behaviors. Several studies ...
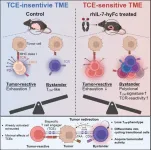
Professor Seung-Woo Lee and PhD candidate Kun-Joo Lee from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), in collaboration with NeoImmuneTech Director Donghoon Choi and Professors Dae Hee Kim and Sun Shim Choi from Kangwon National University, have revealed a groundbreaking method to significantly enhance the efficacy of bispecific antibody therapies in treating solid tumors. Their findings were published on May 13 in “Cell Reports Medicine”, an international journal of healthcare research.
Bispecific antibodies, which can simultaneously bind to two different ...
The fjords on Sweden’s west coast act as effective carbon traps regardless of whether the bottom water is oxygen-rich or not. This is the conclusion of a new study with researchers from the University of Gothenburg.
Large quantities of plant parts sink to the bottom of fjords on the Swedish west coast where they form sediment. This buries organic carbon, which would otherwise contribute to ocean acidification and the greenhouse effect. When the plant parts are exposed to oxygen and other substances, the organic carbon begins to decompose into inorganic carbon, which can be dissolved into carbonic acid in the water. Research ...