(Press-News.org) Endowed with the power of memory, certain alloys can magically return to their original shape when heated or deformed. However, the repeated back-and-forth between the original and new configuration may leave permanent imprints on the alloy’s microscopic features, which could then impact its ability to reversibly transform shape. Thus, unraveling the impact of the strain history on these alloys’ functionality is essential to improving predictive capabilities, but it has not received enough attention.
To fill this knowledge gap, the National Science Foundation has awarded a multiyear grant to Texas A&M University researchers Drs. Jean-Briac le Graverend, associate professor in the Department of Aerospace Engineering; Shuiwang Ji, professor in the Department of Computer Science & Engineering; and Daniel Bernard Hajovsky, associate professor in the Department of Educational Psychology. The investigators will also direct a portion of the NSF grant toward STEM outreach and education for neurodivergent middle and high schoolers.
“We are delighted to have received this grant, which not only lets us investigate important theoretical and scientific questions related to shape-memory alloys but also connect with kids in the community who may not have interacted with engineers or visited a lab,” said le Graverend. "We look forward to learning from them, too, since they might view engineering problems in untraditional ways.”
With critical applications spanning heart stents to airplane wing flaps, shape memory alloys have captured the imagination of researchers and engineers alike. The mechanism underlying shape memory is a phenomenon known as solid-state phase transformation. Simply put, this is when a material changes its internal structure from martensite to austenite, and vice versa, because of a change in temperature or stress.
Studies show that these martensite-austenite transformations are only sometimes perfectly reversible, especially if permanent deformations occur. Thus, the investigators will use a synergistic experimental and numerical approach combining sophisticated experiments, crystal-plasticity modeling, and a machine learning technique called graph neural network to understand and predict history effects in shape-memory alloys.
“Deformation history will make identical samples react differently to the thermo-mechanical loading applied,” said le Graverend. “Our research into improving predictions of history effects on solid-state transformation and shape-memory alloys, in particular, will directly affect cost savings and life-cycle management of any materials and structures depending on solid-state transformations.”
As part of the NSF grant, the team will also open the doors of the engineering departments to neurodivergent children, specifically those with learning disabilities. The team hopes to spark these students’ interest in cutting-edge engineering research.
“In 8th grade, 79% of the students with a learning disability are below basic in mathematics. One thing that tells us is that these children and adolescents are at higher risk for academic failure, school dropout and setbacks," said Hajovsky. "One of the goals is to help promote interest and skills in STEM fields by targeting this specific population, bringing them to campus, and working with them to familiarize themselves with STEM fields and bring new ways of thinking to the engineering fields.”
By Texas A&M Engineering
END
Do shape-memory alloys remember past strains in their life?
With an NSF grant, researchers will investigate the historical effects of shape memory alloys and divert a portion of the grant to STEM outreach.
2024-05-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
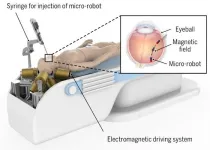
A novel electromagnetic driving system for 5-DOF manipulation in intraocular microsurgery
2024-05-31
The electromagnetic driving systems are proposed for the flexible 5-DOF magnetic manipulation of a micro-robot within the posterior eye, enabling precise targeted drug delivery. A research team has presented a novel electromagnetic driving system that consists of eight optimized electromagnets arranged in an optimal configuration and employs a control framework based on an active disturbance rejection controller (ADRC) and virtual boundary.
The team published their findings in Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Mar 23, 2024.
Intraocular microsurgery has witnessed a transition from the utilization of conventional handheld surgical tools to the adoption of robot-assisted surgery, owing ...
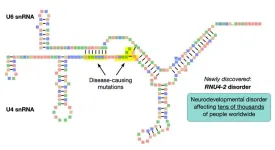
Researchers identify a genetic cause of intellectual disability affecting tens of thousands
2024-05-31
New York, NY [May 31, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and others have identified a neurodevelopmental disorder, caused by mutations in a single gene, that affects tens of thousands of people worldwide. The work, published in the May 31 online issue of Nature Medicine [DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03085-5], was done in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Bristol, UK; KU Leuven, Belgium; and the NIHR BioResource, currently based at the University of Cambridge, UK.
The findings will improve clinical diagnostic ...
EMBARGOED: Nearly one-third of US adults know someone who’s died of drug overdose
2024-05-31
Losing a loved one to drug overdose has been a common experience for many Americans in recent years, crossing political and socioeconomic divides and boosting the perceived importance of the overdose crisis as a policy issue, according to a new survey led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
A nationally representative survey of more than 2,300 Americans, fielded in spring 2023, suggests that 32 percent of the U.S. adult population, or an estimated 82.7 million individuals, has lost someone they know to a fatal drug overdose. ...
Mediterranean diet adherence and risk of all-cause mortality in women
2024-05-31
About The Study: Higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 23% lower risk of all-cause mortality in this cohort study. This inverse association was partially explained by multiple cardiometabolic factors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Shafqat Ahmad, Ph.D., email shafqat.ahmad@medsci.uu.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14322)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Traumatic brain injury strikes 1 in 8 older Americans
2024-05-31
Some 13% of older adults are diagnosed with traumatic brain injury (TBI), according to a study by UC San Francisco and the San Francisco VA Health Care System. These injuries are typically caused by falls from ground level.
Researchers followed about 9,200 Medicare enrollees, whose average age was 75 at the start of the study, and found that contrary to other studies of younger people, being female, white, healthier and wealthier was associated with higher risk of TBI.
The study publishes in JAMA Network Open on May 31, 2024.
The researchers, ...
Stem cells shed new light on how the human embryo forms
2024-05-31
A new study using stem cell-based models has shed new light on how the human embryo begins to develop, which could one day benefit the development of fertility treatment.
The study led by at the University of Exeter Living Systems Institute has revealed how early embryo cells decide between contributing to the foetus or to the supporting yolk sac.
Understanding this decision is important because the yolk sac is essential for later development in the womb. Producing the right number of yolk sac forming cells may be critical for infertility treatment using in vitro fertilised (IVF) embryos.
Only limited research ...
BU study finds policy makers’ use of in-hospital mortality as a sepsis quality metric may unfairly penalize safety-net hospitals
2024-05-31
EMBARGOED by JAMA Network Open until 11 a.m., ET May 31, 2024
Contact: Maria Ober, mpober@bu.edu
BU Study Finds Policy Makers’ Use of In-Hospital Mortality as a Sepsis Quality Metric May Unfairly Penalize Safety-net Hospitals
(Boston)—Sepsis is a leading cause of death and disability and a key target of state and federal quality measures for hospitals. In-hospital mortality of patients with sepsis is frequently measured for benchmarking, both by researchers and policymakers. For example, in New York, sepsis regulations mandate reporting of risk-adjusted in-hospital mortality, and hospitals with lower or higher than expected in-hospital ...
Mediterranean diet tied to one-fifth lower risk of death in women
2024-05-31
Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital identified and assessed underlying mechanisms that may explain the Mediterranean diet’s 23 percent reduction in all-cause mortality risk for American women
The health benefits of the Mediterranean diet have been reported in multiple studies, but there is limited long-term data of its effects in U.S. women and little understanding about why the diet may reduce risk of death. In a new study that followed more than 25,000 initially healthy U.S. women for up ...
Relieving a fear of public speaking
2024-05-31
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research - If you dread public speaking you are not alone. It is a leading social phobia, one that can cause a state of anxiety that reduces otherwise articulate people to nervous incoherence.
A strong fear of public speaking is known as glossophobia. Academic studies estimate it affects 20 per cent of the population, but depending on the sample and methodology, the figure could be as high as 40 per cent.
As American writer and humourist Mark Twain said, ...
Innovating learning with ChatGPT-based Prompt Tutor
2024-05-31
By Jovina Ang
SMU Office of Research – “Giving students immediate and frequent feedback makes online learning more effective,” Associate Professor Ouh Eng Lieh told the Office of Research.
However, based on how most online lessons are designed, questions could not be answered nor doubts clarified until students meet their instructor in the following face-to-face class.
The time delay of a few days to a few weeks can impede student learning as it might make it difficult for students to catch up and understand the subsequent topics in the course.
Learning also ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
[Press-News.org] Do shape-memory alloys remember past strains in their life?With an NSF grant, researchers will investigate the historical effects of shape memory alloys and divert a portion of the grant to STEM outreach.