(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester have identified mechanisms in the brain’s hippocampal network that are rescued by ketones. These findings build on previous research showing that ketones can alleviate neurological and cognitive affects.
As we age our brain naturally becomes more insulin resistant. This creates a breakdown in communication between neurons, causing symptoms like changes in mood, cognitive decline, and eventually neurodegeneration. Nathan A. Smith, MS, PhD ('13), associate professor of Neuroscience, and fellow researchers studied the mechanisms in the brain that break down when insulin resistance is suddenly present, like in trauma, but before symptoms manifest into chronic conditions, like diabetes or Alzheimer’s.
"Once neuronal function is lost, there is no recovering the connection, so we need to identify when the function first becomes impaired," said Smith, the principal investigator of this research, published in the journal PNAS Nexus. "This study accomplishes that by bringing us closer to understanding how to rescue the function of impaired neurons and prevent or delay devastating diseases like Alzheimer's."”
Using mice as a model system, researchers focused on the hippocampus, a well understood region of the brain responsible for learning and memory. They found acute insulin resistance impairs several aspects of neuronal function, including synaptic activity, axonal conduction, network synchronization, synaptic plasticity, and action potential properties—the processes critical to support the communication flow in and out of neurons.
Researchers then administered D-βHb, a form of ketones, a byproduct released by the liver when the body burns fat instead of glucose for energy. They found that the synaptic activity that was previously impacted by acute insulin resistance was rescued, conduction in axons increased, neurons were resynchronized, and synaptic plasticity.
“This research has implications for developing ketone-based therapies targeting specific neuronal dysfunctions in conditions involving insulin resistance/hypoglycemia like diabetes or Alzheimer's disease,” Smith said. “We are now looking to understand the role that astrocytes and other glia cells play in acute insulin resistance.”
Additional authors include Bartosz Kula, PhD, of the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester, Botond Antal and Lilianne Mujica-Parodi, PhD, of Stony Brook University and Harvard Medical School, Corey Weistuch, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, Florian Gackiere, PhD, Alexander Barre, PhD, and Jeffrey Hubbard, PhD, of Neuroservices Alliance, and Maria Kukley, PhD, of Achucarro Basque Center for Neuroscience and Basque Foundation for Science. This research was supported by The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, and the Department of Defense.
END
Can ketones enhance cognitive function and protect brain networks?
2024-05-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AMS Science Preview: Sea-ice loss may accelerate; tornadoes and flying cars
2024-05-31
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form.
Below is a selection of articles published early online recently. Some articles are open-access; to view others, members of the media can contact kpflaumer@ametsoc.org for press login credentials.
JOURNAL ARTICLES
Large-Scale Climate Modes Drive Low-Frequency Regional Arctic Sea Ice Variability
Journal of Climate
Arctic sea ice loss may accelerate in the coming decade. This study examined the dominant natural climate ...
UT Arlington, Microsoft host AI “Prompt-a-Thon”
2024-05-31
Faculty, staff and researchers from higher education and K-12 schools throughout Texas gathered in Arlington for the state’s first “Prompt-a-Thon” hosted by Microsoft and UTA’s offices of Research and Innovation and Information Technology. Together, educators and researchers learned how to best use artificial intelligence (AI) tools to improve their work.
“This Prompt-a-Thon is a significant step toward promoting AI literacy across multiple universities and establishing UTA as a frontrunner for AI use in the state,” said Jeremy Forsberg, associate ...
Children’s visual experience may hold key to better computer vision training
2024-05-31
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A novel, human-inspired approach to training artificial intelligence (AI) systems to identify objects and navigate their surroundings could set the stage for the development of more advanced AI systems to explore extreme environments or distant worlds, according to research from an interdisciplinary team at Penn State.
In the first two years of life, children experience a somewhat narrow set of objects and faces, but with many different viewpoints and under varying lighting conditions. Inspired by this developmental insight, the researchers introduced a new machine learning approach that uses information about spatial position to train AI visual ...
2024 Mahoney Life Sciences Prize goes to food scientist Lynne McLandsborough
2024-05-31
University of Massachusetts Amherst food scientist Lynne McLandsborough has won the 2024 Mahoney Life Sciences Prize for her research that offers a solution to a sticky sanitation and food safety dilemma hounding the peanut butter and chocolate industries.
“I was really surprised and excited,” McLandsborough says of winning the prize. “I think our research is innovative and there’s a need in the industry. It was a fun project.”
She is already in talks with Mars, the world’s ...
Ancient medicine blends with modern-day research in new tissue regeneration method
2024-05-31
For centuries, civilizations have used naturally occurring, inorganic materials for their perceived healing properties. Egyptians thought green copper ore helped eye inflammation, the Chinese used cinnabar for heartburn, and Native Americans used clay to reduce soreness and inflammation.
Flash forward to today, and researchers at Texas A&M University are still discovering ways that inorganic materials can be used for healing.
In two recently published articles, Dr. Akhilesh Gaharwar, a Tim and Amy Leach Endowed Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, and Dr. Irtisha Singh, assistant professor in the Department of Cell Biology ...
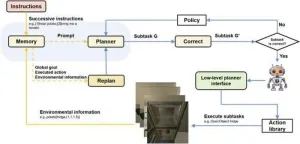
Navigating new horizons: Pioneering AI framework enhances robot efficiency and planning
2024-05-31
In a groundbreaking study published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, researchers from Shanghai University have unveiled a new artificial intelligence framework that revolutionizes the way robots interpret and execute tasks. The "Correction and Planning with Memory Integration" (CPMI) framework leverages large language models (LLMs) to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of robots performing complex, instruction-based tasks.
Traditionally, robots required explicit programming and extensive data to navigate ...
Tirzepatide for weight reduction in Chinese adults with obesity
2024-05-31
About The Study: In Chinese adults with obesity or overweight, once-weekly injection with tirzepatide 10 mg or 15 mg resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful weight reduction with an acceptable safety profile.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Xiaoying Li, M.D., email li.xiaoying@zshospital.sh.cn.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.9217)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
U of T researchers discover ‘trojan horse’ virus hiding in human parasite
2024-05-31
An international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has found a new RNA virus that they believe is hitching a ride with a common human parasite.
The virus, called Apocryptovirus odysseus, along with 18 others that are closely related to it, was discovered through a computational screen of human neuron data – an effort aimed at elucidating the connection between RNA viruses and neuroinflammatory disease. The virus is associated with severe inflammation in humans infected with the ...
Clues to mysterious disappearance of North America’s large mammals 50,000 years ago found within ancient bone collagen
2024-05-31
50,000 years ago, North America was ruled by megafauna. Lumbering mammoths roamed the tundra, while forests were home to towering mastodons, fierce saber-toothed tigers and enormous wolves. Bison and extraordinarily tall camels moved in herds across the continent, while giant beavers plied its lakes and ponds. Immense ground sloths weighing over 1,000 kg were found across many regions east of the Rocky Mountains.
And then, sometime at the end of the Last Ice Age, most of North America’s megafauna disappeared. How and why remains hotly contested. Some researchers believe the arrival of humans was pivotal. Maybe the animals were hunted and eaten, or maybe humans just altered ...
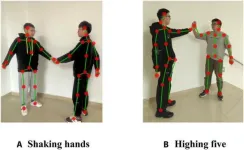
Revolutionizing interaction recognition: The power of merge-and-split graph convolutional networks
2024-05-31
In a significant advancement for robotics and artificial intelligence, researchers at Chongqing University of Technology, along with their international collaborators, have developed a cutting-edge method for enhancing interaction recognition. The study, published in Cyborg and Bionic Systems, introduces the Merge-and-Split Graph Convolutional Network (MS-GCN), a novel approach specifically designed to address the complexities of skeleton-based interaction recognition.
Human interaction recognition plays a crucial role in various applications, ranging from enhancing human-computer interfaces ...