(Press-News.org) An international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has found a new RNA virus that they believe is hitching a ride with a common human parasite.
The virus, called Apocryptovirus odysseus, along with 18 others that are closely related to it, was discovered through a computational screen of human neuron data – an effort aimed at elucidating the connection between RNA viruses and neuroinflammatory disease. The virus is associated with severe inflammation in humans infected with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii, leading the team to hypothesize that it exacerbates toxoplasmosis disease.
“We discovered A. odysseus in human neurons using the open-science Serratus platform to search through more than 150,000 RNA viruses” said Purav Gupta, first author on the study, recent high school graduate and current undergraduate student at U of T’s Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research. “Serratus identifies RNA viruses from public data by flagging an enzyme called RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which facilitates replication of viral RNA. This enzyme allows the virus to reproduce itself and for the infection to spread.”
The study was published recently in the journal Virus Evolution.
The parasite T. gondii is far-reaching, infecting an estimated one-third of the global population. It can live in any non-blood cell type, including neurons, forming cysts inside cells. The parasite is transmitted to nearby cells when the infected cell ruptures.
T. gondii infections often go unnoticed because they only lead to symptoms in rare cases. Regardless, toxoplasmosis merits investigation considering how widespread it is and the potential effects it may have on pregnant women and those who are immunocompromised, Gupta said.
“We believe the virus and parasite work hand-in-hand to cause disease in the human host, where the virus hides inside the parasite, like a soldier in a trojan horse, to gain entry to the human brain,” said Gupta. “Our research marks the first time that scientists have connected toxoplasmosis to a virus.”
The newly discovered A. odysseus is found in two hypervirulent strains of the T. gondii parasite, referred to as RUB and COUGAR.
RUB has been documented in French Guinea to cause severe fever and organ failure, while COUGAR has been shown in British Columbia to be connected to ocular toxoplasmosis – the leading cause of infectious blindness. Researchers found the strains in different geographical locations at different times, demonstrating their potentially wide-ranging impacts.
Symptoms of toxoplasmosis can be aggravated by a hyperactivated human immune response. The virus-carrying parasite triggers this type of response when the immune system senses the foreign RNA of the virus.
“The group of 19 RNA viruses we found are strong biomarkers for parasitic infection,” said Artem Babaian, principal investigator on the study and assistant professor of molecular genetics at the Donnelly Centre and the Temerty Faculty of Medicine. “It’s obvious now that the A. odysseus virus could be a valuable marker of disease-causing infections, like severe toxoplasmosis, in humans or other animals. The next step is to test if this raises the possibility that treating a parasite's viruses could be an effective means of treating symptoms that arise from parasitic infections.”
Zoonotic viruses that infect other living things in our environment in order to reach us are expected to cause the majority of emerging infectious diseases in humans, Babaian noted. “This study underscores the importance of looking beyond the viruses that infect humans directly into the extended virome,” he said.
This research was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
END
U of T researchers discover ‘trojan horse’ virus hiding in human parasite
2024-05-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clues to mysterious disappearance of North America’s large mammals 50,000 years ago found within ancient bone collagen
2024-05-31
50,000 years ago, North America was ruled by megafauna. Lumbering mammoths roamed the tundra, while forests were home to towering mastodons, fierce saber-toothed tigers and enormous wolves. Bison and extraordinarily tall camels moved in herds across the continent, while giant beavers plied its lakes and ponds. Immense ground sloths weighing over 1,000 kg were found across many regions east of the Rocky Mountains.
And then, sometime at the end of the Last Ice Age, most of North America’s megafauna disappeared. How and why remains hotly contested. Some researchers believe the arrival of humans was pivotal. Maybe the animals were hunted and eaten, or maybe humans just altered ...
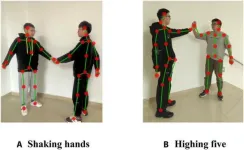
Revolutionizing interaction recognition: The power of merge-and-split graph convolutional networks
2024-05-31
In a significant advancement for robotics and artificial intelligence, researchers at Chongqing University of Technology, along with their international collaborators, have developed a cutting-edge method for enhancing interaction recognition. The study, published in Cyborg and Bionic Systems, introduces the Merge-and-Split Graph Convolutional Network (MS-GCN), a novel approach specifically designed to address the complexities of skeleton-based interaction recognition.
Human interaction recognition plays a crucial role in various applications, ranging from enhancing human-computer interfaces ...
Do shape-memory alloys remember past strains in their life?
2024-05-31
Endowed with the power of memory, certain alloys can magically return to their original shape when heated or deformed. However, the repeated back-and-forth between the original and new configuration may leave permanent imprints on the alloy’s microscopic features, which could then impact its ability to reversibly transform shape. Thus, unraveling the impact of the strain history on these alloys’ functionality is essential to improving predictive capabilities, but it has not received enough attention.
To fill this knowledge gap, the National Science Foundation ...
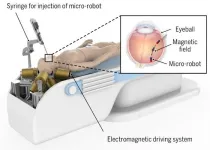
A novel electromagnetic driving system for 5-DOF manipulation in intraocular microsurgery
2024-05-31
The electromagnetic driving systems are proposed for the flexible 5-DOF magnetic manipulation of a micro-robot within the posterior eye, enabling precise targeted drug delivery. A research team has presented a novel electromagnetic driving system that consists of eight optimized electromagnets arranged in an optimal configuration and employs a control framework based on an active disturbance rejection controller (ADRC) and virtual boundary.
The team published their findings in Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Mar 23, 2024.
Intraocular microsurgery has witnessed a transition from the utilization of conventional handheld surgical tools to the adoption of robot-assisted surgery, owing ...
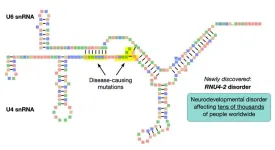
Researchers identify a genetic cause of intellectual disability affecting tens of thousands
2024-05-31
New York, NY [May 31, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and others have identified a neurodevelopmental disorder, caused by mutations in a single gene, that affects tens of thousands of people worldwide. The work, published in the May 31 online issue of Nature Medicine [DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03085-5], was done in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Bristol, UK; KU Leuven, Belgium; and the NIHR BioResource, currently based at the University of Cambridge, UK.
The findings will improve clinical diagnostic ...
EMBARGOED: Nearly one-third of US adults know someone who’s died of drug overdose
2024-05-31
Losing a loved one to drug overdose has been a common experience for many Americans in recent years, crossing political and socioeconomic divides and boosting the perceived importance of the overdose crisis as a policy issue, according to a new survey led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
A nationally representative survey of more than 2,300 Americans, fielded in spring 2023, suggests that 32 percent of the U.S. adult population, or an estimated 82.7 million individuals, has lost someone they know to a fatal drug overdose. ...
Mediterranean diet adherence and risk of all-cause mortality in women
2024-05-31
About The Study: Higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 23% lower risk of all-cause mortality in this cohort study. This inverse association was partially explained by multiple cardiometabolic factors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Shafqat Ahmad, Ph.D., email shafqat.ahmad@medsci.uu.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14322)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Traumatic brain injury strikes 1 in 8 older Americans
2024-05-31
Some 13% of older adults are diagnosed with traumatic brain injury (TBI), according to a study by UC San Francisco and the San Francisco VA Health Care System. These injuries are typically caused by falls from ground level.
Researchers followed about 9,200 Medicare enrollees, whose average age was 75 at the start of the study, and found that contrary to other studies of younger people, being female, white, healthier and wealthier was associated with higher risk of TBI.
The study publishes in JAMA Network Open on May 31, 2024.
The researchers, ...
Stem cells shed new light on how the human embryo forms
2024-05-31
A new study using stem cell-based models has shed new light on how the human embryo begins to develop, which could one day benefit the development of fertility treatment.
The study led by at the University of Exeter Living Systems Institute has revealed how early embryo cells decide between contributing to the foetus or to the supporting yolk sac.
Understanding this decision is important because the yolk sac is essential for later development in the womb. Producing the right number of yolk sac forming cells may be critical for infertility treatment using in vitro fertilised (IVF) embryos.
Only limited research ...
BU study finds policy makers’ use of in-hospital mortality as a sepsis quality metric may unfairly penalize safety-net hospitals
2024-05-31
EMBARGOED by JAMA Network Open until 11 a.m., ET May 31, 2024
Contact: Maria Ober, mpober@bu.edu
BU Study Finds Policy Makers’ Use of In-Hospital Mortality as a Sepsis Quality Metric May Unfairly Penalize Safety-net Hospitals
(Boston)—Sepsis is a leading cause of death and disability and a key target of state and federal quality measures for hospitals. In-hospital mortality of patients with sepsis is frequently measured for benchmarking, both by researchers and policymakers. For example, in New York, sepsis regulations mandate reporting of risk-adjusted in-hospital mortality, and hospitals with lower or higher than expected in-hospital ...