(Press-News.org) BOSTON—Among transgender and gender-diverse adults whose gender identity is nonbinary—not exclusively male or female—and who choose low-dose hormone treatment, most prefer to continue testosterone therapy at lower-than-recommended doses after at least six months of treatment, a new study finds. The study will be presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Current guidelines for initiation of testosterone for gender affirmation assume that transgender and gender-diverse, or trans, individuals desire both rapid and complete masculinization,” said lead researcher Brendan Nolan, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of the University of Melbourne in Melbourne, Australia. “However, we have noted that an increasing number of trans individuals, particularly those with a nonbinary gender identity, desire lower testosterone doses than recommended in existing guidelines.”
Research evaluating low-dose hormone therapy for trans people is limited, Nolan said. He and his colleagues therefore studied the duration of low-dose testosterone treatment among 46 young adults assigned female at birth and who identified as nonbinary. The patients applied 1% testosterone gel to their skin beginning with a median (midpoint) dose of 25 milligrams per day (mg/day). By their last follow-up visit, the patients were treated with median dose of 37.5 mg/day, with a range from 25 to 50 mg/day, less than the recommended full dose of 50 mg/day.
The researchers found that after the first six months of hormone therapy, 87% of the study patients (40 of 46) continued testosterone doses lower than those recommended in current guidelines. Only six patients chose to change their treatment regimen to full-dose testosterone. When the investigators narrowed their analysis to the 30 patients who received at least one year of testosterone therapy, 87% remained on a low dose at their last follow-up, Nolan reported.
Guidelines from the Endocrine Society for testosterone treatment of trans adults wanting masculinizing characteristics recommend 50 to 100 mg/day of testosterone for a 1.6% gel formulation. No standardized guidelines exist for persons desiring low-dose hormone treatment.
Although the investigators did not study the patients’ physical changes with testosterone therapy, Nolan said, “Theoretically, low doses could lead to slower or a lower degree of physical changes.”
Final blood tests showed that patients had a median total testosterone level within the low-normal range for cisgender men, he noted.
Nolan speculated that their findings suggest current guidelines for hormone treatment of trans adults may not apply to the needs of all nonbinary persons, but he said more research is needed.
“Future research should evaluate the influence of low-dose testosterone on clinical outcomes in trans including nonbinary people,” Nolan said.
Nolan receives funding from a Royal Australasian College of Physicians-Endocrine Society of Australia Research Establishment Fellowship.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
Persons of nonbinary gender may desire lower-dose testosterone treatment than guidelines recommend
2024-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High insulin levels contribute to worse outcomes for Black women with aggressive form of breast cancer
2024-06-02
BOSTON—High insulin levels contribute to worse outcomes for Black women compared to white women who have an aggressive form of breast cancer called triple-negative breast cancer, according to a study presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for about 10-15% of all breast cancers. The term triple-negative breast cancer refers to the fact that the cancer cells do not have estrogen or progesterone receptors and do not make any or too much of the protein called HER2. The cells test ‘negative’ on all 3 tests. Triple-negative breast ...
Stress from living in violent neighborhoods tied to aggressive lung cancer in Black men
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Exposure to increased neighborhood violence has the power to change the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) for the stress hormone, cortisol, which may influence the aggressiveness of lung cancer, according to data presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“This research uncovers a previously unknown link between exposure to neighborhood violence, GR and lung tumor aggressiveness that can help us understand and fix the lung cancer health disparity seen in Black men” said Hannah Heath, B.S., a graduate research assistant ...
Thyroid eye disease patients report maintained improvement 2 years after teprotumumab infusions
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Most patients with thyroid eye disease treated with teprotumumab didn’t require additional treatments nearly 2 years later, according to industry-supported research being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass., and published in the journal Thyroid.
“Thyroid eye disease is a lifelong autoimmune disease that can worsen or flare, regardless of how it has been treated. This is the case for many autoimmune diseases,” said George Kahaly, M.D., Ph.D., professor of medicine and endocrinology at Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center in Mainz, Germany. “Given the enduring nature ...
More women report hip fractures earlier in life
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Older women with low bone density are more likely to experience their first hip fracture in their 60s compared to older ages, according to research being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Older women experience an increased risk of fragility hip fractures. These are hip fractures with minimal trauma or due to a fall from a standing height, and they are often deadly and disabling,” said Avica Atri, M.D., an Internal Medicine resident physician at Jefferson Einstein Hospital in Philadelphia, Pa. “As the population over 60 swells in the United States, a large proportion of women will be ...
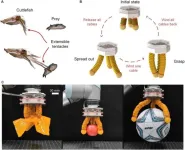
Cutting-edge robotics: Introducing the hybrid-driven origami gripper
2024-06-02
In an impressive leap forward for robotics technology, researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University have unveiled a novel hybrid-driven origami gripper, designed to tackle the challenge of grasping and manipulating objects with unprecedented versatility and precision. This innovative device, highlighted in a recent study published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, promises to reshape the capabilities of robotic systems in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare.
The newly developed gripper utilizes a combination of pneumatic and cable-driven mechanisms to control an origami-inspired structure, allowing for adjustable finger stiffness and variable finger lengths. This sophisticated ...
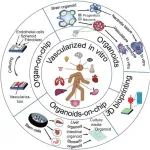
The future of drug testing: Vascularized organ-on-a-chip technologies
2024-06-02
In an era marked by rapid technological advancement in biomedical engineering, a groundbreaking development is set to revolutionize our approach to drug testing and disease modeling. Researchers from Shanghai University and the University of California Los Angeles have made significant strides in the field of in vitro vascularized organ-on-a-chip systems, offering a promising alternative to traditional methods that rely heavily on animal testing and simplistic two-dimensional cell cultures.
The organ-on-a-chip technology mimics human organs on a microscale by cultivating cells in a controlled microenvironment that simulates the 3D structure and physiological ...
New male birth control gel takes effect sooner than similar contraceptive methods
2024-06-02
BOSTON—A novel male contraceptive gel combining two hormones, segesterone acetate (named Nestorone) and testosterone, suppresses sperm production faster than similar experimental hormone-based methods for male birth control, according to a new study.
Results from an ongoing multicenter phase 2b clinical trial will be presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston.
“The development of a safe, highly effective and reliably reversible contraceptive method for ...
Study finds potentially treatable factors to improve symptoms in men stopping illicit steroids
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Men who illicitly used steroids to boost muscle size and physical performance and have stopped in the past year have impaired sexual function compared with men currently using steroids, according to a study being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Having a psychiatric diagnosis and stopping steroids was associated with greater impairment in sexual function, the researchers found.
“It is important to recognize the symptoms that men experience within the first year of stopping ...
Hot flashes in menopausal women may signal increased risk for heart and metabolic issues
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Women experiencing moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms face a three times greater risk for metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) compared to those with mild symptom severity, according to research being presented Monday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Vasomotor symptoms include hot flashes or night sweats—symptoms that have become synonymous with menopause.
“This research is significant as it contributes ...
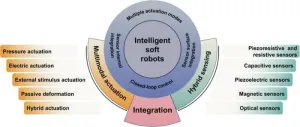
Revolutionizing robotics: Integrating actuation and sensing for smarter soft robots
2024-06-02
The world of robotics is witnessing a transformative shift with the rise of soft robotics, which offers unparalleled flexibility and adaptability in various applications, from medical interventions to intricate rescue operations. A groundbreaking review article by Zhou et al. published in Cyborg Bionic Systems in 2024, sheds light on this evolution, highlighting the crucial integration of actuation and sensing technologies that pave the way for truly intelligent soft robots.
Soft robots, unlike their rigid counterparts, are made from materials that mimic the mechanical properties of living tissues, allowing them to move and adapt with a life-like grace. This capability makes ...