(Press-News.org) BOSTON—Vitamin D tests certified by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Clinical Standardization Programs (CSP) are well calibrated overall, according to a new study presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass. However, the researchers found some inaccuracies among the assays studied.
The blood tests show an “appropriate” level of analytical accuracy, said the study’s lead researcher, Otoe Sugahara, manager of the CDC Vitamin D Standardization-Certification Program (VDSCP) in Atlanta, Ga.
Analytical accuracy is the test’s ability to correctly analyze vitamin D in this case. The laboratory medicine community decides which level of analytical accuracy is appropriate, Sugahara said.
She said, “Some inaccuracies appear to be caused by a lack of analytical specificity and other factors. These inaccuracies may result in incorrect classification of patients’ vitamin D status.” Analytical specificity is the assay's ability to just measure vitamin D.
Vitamin D is important for bone health, and vitamin D tests are among the most requested laboratory tests in the U.S., Sugahara noted.
“Vitamin D tests help healthcare providers make a correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment decisions for patients,” she said. “However, many clinical organizations and experts have expressed concern about the accuracy and reliability of vitamin D assays.”
The VDSCP began in 2013 to help assess and improve the accuracy and reliability of vitamin D tests, according to the CDC. For vitamin D assays enrolled in the voluntary program, the VDSCP collects and annually reviews their performance data.
“Since 2013, the assays enrolled in the program have generally improved and become better calibrated,” Sugahara said.
The average calibration bias was less than 1% for all assays in the VDSCP in 2022, she reported. Bias is the deviation of the test result from the true value, which is determined with the CDC’s reference method for vitamin D.
U.S. scientists use two main types of technologies to measure vitamin D in the blood, Sugahara said. One is mass spectrometry, which separately measures 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 and D3 and sums the values. The other type, immunoassay, measures both compounds at the same time and reports one result for total 25-hydroxyvitamin D.
In 2022, the average calibration bias of VDSCP participants for immunoassays was 0.86% and for assays using mass spectrometry was 0.55%, Sugahara reported.
However, she added that with improved calibration, sample-specific inaccurate results became more apparent.
For example, some assays measure other compounds besides 25-hydroxyvitamin D, which Sugahara’s research found can falsely elevate results of some blood samples. Thus, for a sample with a reference value indicating vitamin D deficiency, which typically requires vitamin D supplementation, some tests misclassified the result as sufficient.
“Though most vitamin D tests in our program have improved, there still remain some sample-specific inaccuracies. The CDC is working with program participants to address these situations,” Sugahara said.
The VDSCP supports more than 35 assays, laboratories and researchers from approximately 15 countries annually, said co-investigator Hubert Vesper, Ph.D., director of the CDC Clinical Standardization Programs (CSP).
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
CDC reports its decade-long efforts in standardizing vitamin D tests
2024-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Persons of nonbinary gender may desire lower-dose testosterone treatment than guidelines recommend
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Among transgender and gender-diverse adults whose gender identity is nonbinary—not exclusively male or female—and who choose low-dose hormone treatment, most prefer to continue testosterone therapy at lower-than-recommended doses after at least six months of treatment, a new study finds. The study will be presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Current guidelines for initiation of testosterone for gender affirmation assume that transgender and gender-diverse, or trans, individuals desire both rapid and complete masculinization,” ...
High insulin levels contribute to worse outcomes for Black women with aggressive form of breast cancer
2024-06-02
BOSTON—High insulin levels contribute to worse outcomes for Black women compared to white women who have an aggressive form of breast cancer called triple-negative breast cancer, according to a study presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for about 10-15% of all breast cancers. The term triple-negative breast cancer refers to the fact that the cancer cells do not have estrogen or progesterone receptors and do not make any or too much of the protein called HER2. The cells test ‘negative’ on all 3 tests. Triple-negative breast ...
Stress from living in violent neighborhoods tied to aggressive lung cancer in Black men
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Exposure to increased neighborhood violence has the power to change the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) for the stress hormone, cortisol, which may influence the aggressiveness of lung cancer, according to data presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“This research uncovers a previously unknown link between exposure to neighborhood violence, GR and lung tumor aggressiveness that can help us understand and fix the lung cancer health disparity seen in Black men” said Hannah Heath, B.S., a graduate research assistant ...
Thyroid eye disease patients report maintained improvement 2 years after teprotumumab infusions
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Most patients with thyroid eye disease treated with teprotumumab didn’t require additional treatments nearly 2 years later, according to industry-supported research being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass., and published in the journal Thyroid.
“Thyroid eye disease is a lifelong autoimmune disease that can worsen or flare, regardless of how it has been treated. This is the case for many autoimmune diseases,” said George Kahaly, M.D., Ph.D., professor of medicine and endocrinology at Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center in Mainz, Germany. “Given the enduring nature ...
More women report hip fractures earlier in life
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Older women with low bone density are more likely to experience their first hip fracture in their 60s compared to older ages, according to research being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Older women experience an increased risk of fragility hip fractures. These are hip fractures with minimal trauma or due to a fall from a standing height, and they are often deadly and disabling,” said Avica Atri, M.D., an Internal Medicine resident physician at Jefferson Einstein Hospital in Philadelphia, Pa. “As the population over 60 swells in the United States, a large proportion of women will be ...
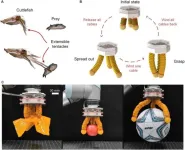
Cutting-edge robotics: Introducing the hybrid-driven origami gripper
2024-06-02
In an impressive leap forward for robotics technology, researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University have unveiled a novel hybrid-driven origami gripper, designed to tackle the challenge of grasping and manipulating objects with unprecedented versatility and precision. This innovative device, highlighted in a recent study published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, promises to reshape the capabilities of robotic systems in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare.
The newly developed gripper utilizes a combination of pneumatic and cable-driven mechanisms to control an origami-inspired structure, allowing for adjustable finger stiffness and variable finger lengths. This sophisticated ...
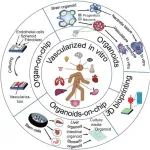
The future of drug testing: Vascularized organ-on-a-chip technologies
2024-06-02
In an era marked by rapid technological advancement in biomedical engineering, a groundbreaking development is set to revolutionize our approach to drug testing and disease modeling. Researchers from Shanghai University and the University of California Los Angeles have made significant strides in the field of in vitro vascularized organ-on-a-chip systems, offering a promising alternative to traditional methods that rely heavily on animal testing and simplistic two-dimensional cell cultures.
The organ-on-a-chip technology mimics human organs on a microscale by cultivating cells in a controlled microenvironment that simulates the 3D structure and physiological ...
New male birth control gel takes effect sooner than similar contraceptive methods
2024-06-02
BOSTON—A novel male contraceptive gel combining two hormones, segesterone acetate (named Nestorone) and testosterone, suppresses sperm production faster than similar experimental hormone-based methods for male birth control, according to a new study.
Results from an ongoing multicenter phase 2b clinical trial will be presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston.
“The development of a safe, highly effective and reliably reversible contraceptive method for ...
Study finds potentially treatable factors to improve symptoms in men stopping illicit steroids
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Men who illicitly used steroids to boost muscle size and physical performance and have stopped in the past year have impaired sexual function compared with men currently using steroids, according to a study being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Having a psychiatric diagnosis and stopping steroids was associated with greater impairment in sexual function, the researchers found.
“It is important to recognize the symptoms that men experience within the first year of stopping ...
Hot flashes in menopausal women may signal increased risk for heart and metabolic issues
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Women experiencing moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms face a three times greater risk for metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) compared to those with mild symptom severity, according to research being presented Monday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Vasomotor symptoms include hot flashes or night sweats—symptoms that have become synonymous with menopause.
“This research is significant as it contributes ...