Efficient CO2 conversion to fuels and chemicals using ionic liquid electrolyte
Researchers discovered that combining ionic liquids electrolytes with metal hydroxides enables efficient electrochemical conversion of CO2 to hydrocarbons
2024-06-03
(Press-News.org)
Converting CO2 into fuel and chemicals using electricity, also known as electrochemical conversion of CO2, is a promising way to reduce emissions. This process allows us to use carbon captured from industries and the atmosphere and turn it into resources that we usually get from fossil fuels.
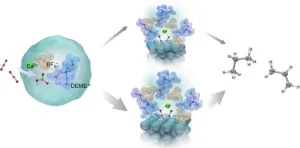
To advance ongoing research on efficient electrochemical conversion, scientists from Doshisha University have introduced a cost-effective method to produce valuable hydrocarbons from CO2. The study was made available online on 17 May 2024 and formally published in the journal Electrochimica Acta on 20 July 2024. The research team, led by Professor Takuya Goto and including Ms. Saya Nozaki from the Graduate School of Science and Engineering and Dr. Yuta Suzuki from the Harris Science Research Institute, produced ethylene and propane on a basic silver (Ag) electrode by utilizing an ionic liquid containing metal hydroxides as the electrolyte.
“Most studies on CO2 electrolysis with room-temperature liquid electrolyte have focused on the electrode's catalytic properties. In this groundbreaking study, we focused on the electrolyte and succeeded in producing valuable hydrocarbon gas even on a simple metal electrode,” says Prof. Goto.
Ionic liquids offer unique advantages for the electrochemical reduction of CO2. They operate over a wide range of voltages without decomposing, are non-flammable, and have high boiling points. This stability enables the electrolyte to withstand the high temperatures generated during exothermic CO2 reduction.
In their study, researchers investigated the electrochemical conversion of CO2 and water with N, N-diethyl-N-methyl-N-(2-methoxyethyl) ammonium tetrafluoroborate (DEME-BF4) as the electrolyte. The DEME-BF4 electrolyte provides optimal conditions for maximizing CO2 reduction. DEME+ ions enhance the solubility of CO2, allowing a greater number of CO2 molecules to participate in the reaction. Moreover, due to its hydrophilic nature, the hydrogen ions required for reducing CO2 to hydrocarbons can be easily supplied by mixing the electrolyte with water.
The researchers determined that the electrochemical conversion of CO2 to hydrocarbons could be increased with the addition of aqueous solutions containing metal hydroxides like calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and cesium hydroxide (CsOH) to the electrolyte. The hydroxides in the ionic liquid can react with CO2 to form bicarbonates (HCO3−) and carbonates (CO32−), further enhancing the availability of CO2 to participate in electrochemical reactions.
Under room temperature electrolysis (298 K or 25°C) in a CO2 atmosphere, the researchers successfully reduced CO2 to ethylene (C2H4), ethane (C2H6), propylene (C3H6), and propane (C3H8). They achieved the highest current efficiencies for each product using DEME-BF4 electrolyte mixed with water and containing Ca(OH)2, with efficiencies reaching up to 11.3% for propane and 6.49% for ethylene. This efficiency surpassed those obtained with other metal hydroxides by over 1000 times.
The reason for this high efficiency was explained using Raman spectroscopy and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. These analyses revealed that bicarbonate ions, formed when CO2 interacts with OH- ions in the electrolyte, interact with DEME+ and BF4- ions of the electrolyte to form a stable structure [DEME+-BF4−-HCO3−-Ca2+].
CO2 and HCO3- species then adsorb onto the electrode surface forming adsorbed species CO− ads. The adsorbed CO- ions then strongly interact with Ca2+ ions present in the electrolyte, forming two distinct intermediate structures: One structure A, consisting of a Ca2+ ion coordinated with two CO− ions adsorbed on three Ag atoms, and the other Structure B, where the Ca2+ ion is coordinated with two CO− ions adsorbed on two Ag atoms. This interaction with Ca2+ ions is crucial as it increases the stability of the adsorbed species, making the subsequent electrochemical reactions possible.
Among these structures, researchers suggest that structure B is more stable and is the preferred pathway for ethylene, while structure A leads to the production of propane. “We showed that tailoring the electrolyte can lead to molecular-level changes in the phase transformation of CO2 in bulk solution and at the electrode/ionic liquid electrolyte interface and proposed a process that enables the synthesis of unique hydrocarbons such as C3,” says Prof. Goto.
These findings shed light on the processes involved in the conversion of CO2 at the interface between ionic liquid-based electrolytes and metal electrodes, such as the role of calcium ions. Such insights can help in the development of electrolytes for the efficient production of useful hydrocarbons from CO2. “The physicochemical knowledge of this new route from CO2 decomposition to synthesizing useful hydrocarbons, as revealed in this study, will be instrumental in advancing CO2 utilization technology and contributing to academic progress in materials science.” concludes Prof. Goto.
About Professor Takuya Goto from Doshisha University, Japan
Takuya Goto is a Professor in the Faculty of Science and Engineering, Department of Environmental Systems Science. He specializes in research areas such as Energy/Earth resource engineering, energy science, and electrochemistry. Prof. Goto has published more than 94 papers in scientific journals, on topics that include molten salt electrolysis and the utilization of captured CO2. He received his Doctor of Energy Science degree from Kyoto University. For more information, visit his researcher profile at https://researchmap.jp/takuya_goto
Funding information
This research was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP22K14700 and the steel carbon neutrality research grant from The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan.
Media contact:
Organization for Research Initiatives & Development
Doshisha University
Kyotanabe, Kyoto 610-0394, JAPAN
E-mail:jt-ura@mail.doshisha.ac.jp
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-03
How can someone have alcohol intoxication without consuming alcohol? Auto-brewery syndrome, a rare condition in which gut fungi create alcohol through fermentation, is described in a case study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231319.
“Auto-brewery syndrome carries substantial social, legal, and medical consequences for patients and their loved ones,” writes Dr. Rahel Zewude, University of Toronto, with coauthors. “Our patient had several [emergency department] visits, was assessed by internists and psychiatrists, and was certified ...
2024-06-03
Implementing human papillomavirus (HPV)-based screening in British Columbia could eliminate cervical cancer in the province before 2040, according to a modelling study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231682.
More than 90% of cervical cancer cases worldwide are caused by 9 types of high-risk HPV. The World Health Organization and the Canadian Partnership Against Cancer (CPAC) have both set targets to eliminate cervical cancer by 2040, defined as an annual rate of less than 4 per 100 000 women.
The Pap test has been the primary screening ...
2024-06-03
Berlin, Germany: While influenza infection is a significant public health threat, causing serious illness in between three and five million people worldwide per year and leading to about up to 650,000 deaths, the effectiveness of influenza vaccines varies considerably between individuals depending on vaccine types and individual circumstances. A person’s ability to resist infection (host immunity) plays an important role in this. Now, researchers have developed a way of classifying host immunity in individuals, which may lead to the early identification of those who will not respond well to a regular vaccine schedule and therefore ...
2024-06-03
Berlin, Germany: Aneuploidy (the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes) in embryos is a major cause of impaired embryo development, leading to conditions such as Down syndrome, as well as to pregnancy loss. The transfer of such embryos in women undergoing IVF is therefore usually avoided because of unfavourable pregnancy outcomes. But mosaic embryos, comprising both genetically normal and abnormal cells, can result in perfectly normal babies. Now, researchers have been able to understand how these mosaic ...
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Metformin is safe to use during pregnancy to manage diabetes, with no long-term adverse effects on the children born and their mothers for at least 11 years after childbirth, according to research presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass. This is the first study to look at longer term effects of metformin use during pregnancy.
“Metformin has been extensively used for managing raised blood glucose values in pregnancy for many decades now. It is the only blood glucose-lowering oral medication approved ...
2024-06-02
BOSTON—GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1s) and SGLT-2 inhibitors lower the risk of major cardiovascular events like heart attacks and severe liver complications compared to other diabetes treatments, according to data being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Before this study, there was limited information about how these specific diabetes medications work in patients with both type 2 diabetes and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD),” said Alexander Kutz, M.D., M.P.H., M.Sc., a research fellow in the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, at Brigham ...
2024-06-02
Immunotherapy before surgery for patients with metastatic melanoma appears to be especially successful. Fifty-nine percent of patients responds so well to this therapy that adjuvant treatment is no longer needed, according to the results of the NADINA study that were published today.
The NADINA study, led by researchers from the Netherlands Cancer Institute, was named one of the eleven clinical studies with the biggest impact on health care in 2024 by Nature Medicine. The study now proves that this was not an empty claim, as shown by the results presented by medical oncologist and research leader Christian Blank today during ASCO 2024, the international congress ...
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Vitamin D tests certified by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Clinical Standardization Programs (CSP) are well calibrated overall, according to a new study presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass. However, the researchers found some inaccuracies among the assays studied.
The blood tests show an “appropriate” level of analytical accuracy, said the study’s lead researcher, Otoe Sugahara, manager of the CDC Vitamin D Standardization-Certification Program (VDSCP) in Atlanta, Ga.
Analytical accuracy is the test’s ability to correctly analyze vitamin D in this ...
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Among transgender and gender-diverse adults whose gender identity is nonbinary—not exclusively male or female—and who choose low-dose hormone treatment, most prefer to continue testosterone therapy at lower-than-recommended doses after at least six months of treatment, a new study finds. The study will be presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Current guidelines for initiation of testosterone for gender affirmation assume that transgender and gender-diverse, or trans, individuals desire both rapid and complete masculinization,” ...
2024-06-02
BOSTON—High insulin levels contribute to worse outcomes for Black women compared to white women who have an aggressive form of breast cancer called triple-negative breast cancer, according to a study presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for about 10-15% of all breast cancers. The term triple-negative breast cancer refers to the fact that the cancer cells do not have estrogen or progesterone receptors and do not make any or too much of the protein called HER2. The cells test ‘negative’ on all 3 tests. Triple-negative breast ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Efficient CO2 conversion to fuels and chemicals using ionic liquid electrolyte
Researchers discovered that combining ionic liquids electrolytes with metal hydroxides enables efficient electrochemical conversion of CO2 to hydrocarbons