Study finds that older adults with sleep apnea have higher odds of hospitalization
New research underscores significance of treating sleep apnea to reduce health care utilization
2024-06-03
(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that sleep apnea is associated with increased odds of future utilization of health care services including hospitalization among older adults.
Results show that participants aged 50 years and older with sleep apnea had a 21% higher odds of reporting future use of any health service compared with those without sleep apnea. Specifically, individuals with sleep apnea had 21% higher odds of hospitalization after controlling for potential confounders including demographics, body mass index, health conditions, and depressive symptoms.
“Our research indicates that older adults who have sleep apnea are more likely to use health services in the future than those who don't have sleep apnea,” said lead author Christopher Kaufmann, who has a doctorate in public mental health and is an assistant professor in the department of health outcomes and biomedical informatics at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville. “The findings hold true even after taking into account other factors that may contribute to an increased risk of health service utilization.”
According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, nearly 30 million adults in the U.S. have obstructive sleep apnea, a chronic disease that involves the repeated collapse of the upper airway during sleep. Untreated, moderate to severe sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of medical problems such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, stroke, and Type 2 diabetes.
The researchers analyzed data from 20,115 participants in the 2016 and 2018 Health and Retirement Study, a nationally representative cohort of middle-aged and older adults in the U.S. Participants were surveyed about sleep disorders, including sleep apnea, in 2016 and their subsequent use of health services in 2018. Nearly 12% of participants reported being told by a doctor that they have sleep apnea.
Kaufmann emphasized the need for timely identification and management of sleep apnea in older adults to mitigate its downstream effects on health care utilization.
“Addressing sleep apnea can not only improve individual health outcomes but also alleviate the strain on health care resources, leading to more efficient and effective health care delivery,” said Kaufmann.
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging and the Sleep Research Society Foundation. The research abstract was published recently in an online supplement of the journal Sleep and will be presented Tuesday, June 4, during SLEEP 2024 in Houston. SLEEP is the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society.
###
Abstract Title: Association Between Sleep Apnea and Health Service Utilization: Results from the Health and Retirement Study
Abstract ID: 1083
Poster Presentation Date: Tuesday, June 4, from 11-11:45 a.m. CDT, Board 332
Presenter: Christopher Kaufmann, Ph.D.
About the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, LLC
The APSS is a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society. The APSS organizes the SLEEP annual meeting each June (sleepmeeting.org).
About the American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Established in 1975, the AASM advances sleep care and enhances sleep health to improve lives. The AASM has a combined membership of 12,000 accredited sleep centers and individuals, including physicians, scientists and other health care professionals who care for patients with sleep disorders. As the leader in the sleep field, the AASM sets standards and promotes excellence in sleep medicine health care, education and research (aasm.org).
About the Sleep Research Society
The SRS is a professional membership society that advances sleep and circadian science. The SRS provides forums for the exchange of information, establishes and maintains standards of reporting and classifies data in the field of sleep research, and collaborates with other organizations to foster scientific investigation on sleep and its disorders. The SRS also publishes the peer-reviewed, scientific journals Sleep and Sleep Advances (sleepresearchsociety.org).
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-03
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that most sleep tips shared on TikTok are supported by empirical evidence.
The research findings show that of 35 unique sleep tips shared in popular videos, there was empirical support for 29. Only six sleep tips were unsupported by scientific evidence.
“These results suggest that the sleep research and sleep medicine communities have done a good job of promoting appropriate tips for sleep hygiene,” said lead author Brian T. Gillis, who has studied sleep for eight years and is an assistant professor of marriage and family therapy in the College of Human Sciences ...
2024-06-03
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that low-dose acetylsalicylic acid, also known as aspirin, can reduce inflammatory responses to sleep restriction.
Results show that compared with placebo, preemptive administration of low-dose aspirin during sleep restriction reduced pro-inflammatory responses. Specifically, aspirin reduced interleukin-6 expression and COX-1/COX-2 double positive cells in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated monocytes, as well as C-reactive protein serum levels.
“The novelty of this study is that it investigated whether we can pharmacologically reduce the inflammatory consequences of sleep restriction,” ...
2024-06-03
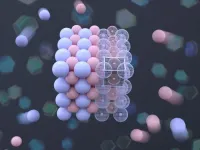
A team of New York University researchers has created a new way to visualize crystals by peering inside their structures, akin to having X-ray vision. Their new technique—which they aptly named “Crystal Clear”—combines the use of transparent particles and microscopes with lasers that allow scientists to see each unit that makes up the crystal and to create dynamic three-dimensional models.
“This is a powerful platform for studying crystals,” says Stefano Sacanna, professor of chemistry at NYU and the principal investigator for the study, published in the journal Nature ...
2024-06-03
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of scientists led by François Lapointe, a research associate at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, has combined paleoclimatic data from the last 2,000 years with powerful computer modeling and in-the-field research on lake sediments and tree rings to show that an understudied phenomenon, known as atmospheric blocking, has long influenced temperature swings in the Arctic. As temperatures warm due to climate change, atmospheric blocking will help drive ever-wilder weather events. The study focused ...
2024-06-03
Nextdoor is the world’s largest hyperlocal social media network, used by 13% of American adults. Yet little is known about the make-up of the actual neighborhoods—numbering approximately 220,000 across the United States—in which these accounts exist and what people in those communities talk about on the platform.
To address our limited understanding of this population, a team of New York University and University of Michigan researchers generated a demographic portrait of communities in which Nextdoor neighborhoods exist, the presence of public agencies in those communities, and what topics are most often discussed. Using U.S. Census data, other publicly available ...
2024-06-03
Permafrost soils store large quantities of organic carbon and are often portrayed as a critical tipping element in the Earth system, which, once global warming has reached a certain level, suddenly and globally collapses. Yet this image of a ticking timebomb, one that remains relatively quiet until, at a certain level of warming, it goes off, is a controversial one among the research community. Based on the scientific data currently available, the image is deceptive, as an international team led by the Alfred Wegener Institute has shown in a recently released study. According to their findings, there is no single ...
2024-06-03
San Antonio, Texas – June 3, 2024 – Recognizing an unusual prevalence of bloodstream infections (BSI) that threatened extremely ill patients receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation, or ECMO, Tampa General Hospital (TGH) infection preventionists started an intervention that eliminated these infections completely from their 18-bed Cardiothoracic Intensive Care Unit (CTICU).
At the APIC 2024 Annual Conference, presenters from the 1,000-bed, tertiary care, academic medical system reported on how they reduced bloodstream infections in ECMO patients from a rate of 36% in October 2021 to a rate of 0% in April 2022. This rate was sustained for seven ...
2024-06-03
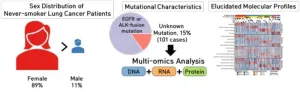
The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking. However, the incidence of lung cancer among never-smokers has been steadily increasing, especially among women. While approximately 80% of never-smoking lung cancer patients are prescribed targeted therapies that focus on mutations in proteins such as EGFR and ALK, the remaining patients often receive cytotoxic chemotherapy with high side effects and relatively low response rates, highlighting the urgent need for targeted therapies.
Dr. Lee Cheolju's ...
2024-06-03
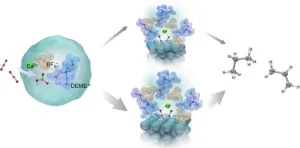
Converting CO2 into fuel and chemicals using electricity, also known as electrochemical conversion of CO2, is a promising way to reduce emissions. This process allows us to use carbon captured from industries and the atmosphere and turn it into resources that we usually get from fossil fuels.
To advance ongoing research on efficient electrochemical conversion, scientists from Doshisha University have introduced a cost-effective method to produce valuable hydrocarbons from CO2. The study was made available online on 17 May 2024 and formally published in the journal Electrochimica Acta on 20 July 2024. The research team, led by Professor Takuya Goto and including Ms. Saya Nozaki from ...
2024-06-03
How can someone have alcohol intoxication without consuming alcohol? Auto-brewery syndrome, a rare condition in which gut fungi create alcohol through fermentation, is described in a case study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231319.
“Auto-brewery syndrome carries substantial social, legal, and medical consequences for patients and their loved ones,” writes Dr. Rahel Zewude, University of Toronto, with coauthors. “Our patient had several [emergency department] visits, was assessed by internists and psychiatrists, and was certified ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study finds that older adults with sleep apnea have higher odds of hospitalization
New research underscores significance of treating sleep apnea to reduce health care utilization