(Press-News.org) By Jake Siegel
SEATTLE, WASH.—June 4, 2024—New research by scientists at the Allen Institute’s Brain and Consciousness group and Cedars-Sinai offers an unprecedented look at how neurons respond to ES. Far from being uniform, different types of neurons showed distinct patterns of ‘syncing up’ with electrical fields. These patterns varied depending on the rate at which the ES was delivered.
The findings, published today in Neuron, could help doctors fine tune where, when, and how to apply ES to the brain, said Soo Yeun Lee, Ph.D., the paper’s first author and a Senior Scientist at the Allen Institute.
“With this study, we now have a much better idea of what types of stimulation work for specific cell classes,” she said. “We can use that knowledge to develop more efficient ways of using electrical stimulation to treat disorders.”
Using tissue samples from mice and humans, the research team delivered oscillating waves of ES within tens of micrometers of individual neurons. This extraordinary precision enabled an unprecedented look at electrical stimulation’s impact at a single-cell level. They observed strong, cell-class-specific responses. Excitatory neurons synchronized firing with both slow and fast stimulation frequencies, while inhibitory neurons primarily responded to fast frequencies.
These class-specific responses are significant, Lee said, because they reveal that adjusting the stimulation frequency allows for the selective targeting of different neurons. That discovery could lead to more precise therapies to modulate neural activity.
For example, inhibitory neurons that express a protein called parvalbumin are implicated in epilepsy and in cognitive dysfunctions, she noted. This study shows that these cell classes are most responsive to certain frequencies. Future treatments could tailor ES to the most effective frequency, potentially improving outcomes and limiting side effects.
Beyond its clinical implications, the study also revealed a universal truth about how neurons function, Lee added. Regardless of cell class, cortical areas, or species, neurons exhibit a remarkable ability to synchronize with an external electric field.
This general property is superimposed on the brain’s dazzling cellular diversity, Lee said—and the newfound understanding of these underlying mechanisms could transform our approach to treating complex brain disorders.
Research described in this article was supported by award numbers R01NS120300 and R01NS130126 from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke of the National Institutes of Health. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of NIH and its subsidiary institutes.
About the Allen Institute
The Allen Institute is an independent, 501(c)(3) nonprofit research organization founded by philanthropist and visionary, the late Paul G. Allen. The Allen Institute is dedicated to answering some of the biggest questions in bioscience and accelerating research worldwide. The Institute is a recognized leader in large-scale research with a commitment to an open science model. Its research institutes and programs include the Allen Institute for Brain Science, launched in 2003; the Allen Institute for Cell Science, launched in 2014; the Allen Institute for Immunology, launched in 2018; and the Allen Institute for Neural Dynamics, launched in 2021. In 2016, the Allen Institute expanded its reach with the launch of The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group, which identifies pioneers with new ideas to expand the boundaries of knowledge and make the world better. For more information, visit alleninstitute.org.
# # #
Media Contact
Peter Kim, Sr. Manager, Communications and Media Relations
206-605-9884 | peter.kim@alleninstitute.org
END
Researchers from Indian Institute of Management Calcutta, University of Chicago, and Management Development Institute, Gurgaon published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines the unintended consequences of an Indian government healthcare policy.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Do No Harm? Unintended Consequences of Pharmaceutical Price Regulation in India” and is authored by Saravana Jaikumar, Pradeep K. Chintagunta, and Arvind Sahay.
In countries without universal health insurance or developed health care systems, governments try to make drugs affordable and accessible. For instance, ...
Maternal obesity impacts the eating behaviors of offspring via long-term overexpression of the microRNA miR-505-5p, according to a study publishing June 4th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Laura Dearden and Susan Ozanne from the MRC Metabolic Diseases Unit, Institute of Metabolic Science, University of Cambridge, UK, and colleagues.
Previous studies in both humans and animal models have shown that the offspring of obese mothers have a higher risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes. While this relationship is likely the result of a complex relationship between genetics and environment, emerging ...
Clinicians often default to treating mental health conditions with a variety of medication. This approach, however, largely ignores the role of environment, lifestyle, and social factors. Mental Health professionals must work toward a more holistic management picture, Sidarta Ribeiro, Ana Paula Pimentel, Paulo Amarante and colleagues at the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro and FIOCRUZ in Brazil argue in the new open-access journal PLOS Mental Health on June 4.
More people than ever are being diagnosed with mental health conditions—particularly children and young adults. The World Health Organization estimates that mental health ...
Max Chang and Irene Lee of University College London review neuroimaging studies of the effects of internet addiction on adolescent brains. Published June 4 in PLOS Mental Health, the study indicates that internet addiction is associated with disrupted signaling in the regions of the brain that are involved in multiple neural networks. These networks play an important role in controlling our attention, in association with intellectual ability, working memory, physical coordination, and emotional processing—all of which ...
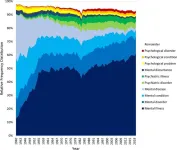
A new survey of nearly 340,000 texts spanning 79 years shows that generic terms in mental health have shifted away from words like “disease” and “disturbance” and toward “psychiatric” and “mental health,” with “mental illness” becoming the most-used term. Nick Haslam and Naomi Baes at the University of Melbourne in Australia present these findings in the new open-access journal PLOS Mental Health on June 4.
The authors state that while words such as “crazy” and “lunatic” ...
Sarah Jackson and colleagues from University College London and King’s College London branches of the SPECTRUM Consortium conducted a survey to study how mental health relates to methods people use to quit smoking, also known as smoking cessation aids. While the number of adults who smoke cigarettes has declined globally, people with mental health conditions are more likely to smoke and to do so more heavily. Because of these differences in tobacco use, the researchers theorized that the effectiveness of smoking cessation aids may be altered in individuals with a mental health condition. However, in their ...
Lived experience should be centered in future mental health research, say people with mental health conditions and their families and carers in nationwide Australian survey.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000010
Article Title: Experience is central and connections matter: A Leximancer analysis of the research priorities of people with lived experience of mental health issues in Australia
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: The ALIVE National Centre for Mental Health Research Translation is supported by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council (GNT2002047) ...
Adolescents with an internet addiction undergo changes in the brain that could lead to additional addictive behaviour and tendencies, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The findings, published in PLOS Mental Health, reviewed 12 articles involving 237 young people aged 10-19 with a formal diagnosis of internet addiction between 2013 and 2023.
Internet addiction has been defined as a person’s inability to resist the urge to use the internet, negatively impacting their psychological wellbeing, as well as their social, academic and professional lives.
The studies used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to inspect the functional connectivity (how regions of ...
Every spring when the sun rises in the Arctic after months of darkness, life returns. The polar bears pop up from their winter lairs, the arctic tern soar back from their long journey south and the musk oxen wade north.
But the animals are not the only life being reawakened by the spring sun. Algae lying dormant on the ice starts blooming in spring blackening large areas of the ice.
When the ice blackens it’s ability to reflect the sun diminishes and this accelerates the melting of the ice. Increased melting exacerbates global ...
WHAT: The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2024 Annual Meeting
The field of nuclear medicine is undergoing rapid and widespread growth—offering patients increasingly precise, tailored, painless diagnosis and treatment with minimal side effects and exceptional results.
This year’s program will focus on new radiopharmaceuticals, instrumentation, and techniques for managing a wide range of diseases, from cancer, brain, and heart disease to infection and inflammation.
The meeting will convene more than 6,500 attendees from around the globe. With more than 100 ...