Teens with later sleep schedules are less active, eat more carbohydrates
Circadian rhythm misalignment is linked with sedentary behavior and higher carb consumption
2024-06-05
(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that circadian misalignment, which is highly prevalent in adolescents, is linked with carbohydrate consumption and sedentary behavior in teens.
Results show that a later sleep schedule was significantly associated with greater intake of carbohydrates, and this relationship was partially explained by irregular sleep timing. A later sleep schedule also was associated with greater sedentary behavior, even after adjusting for variables such as demographics, sleep disorders, and insufficient sleep.
“Delaying sleep schedules is normal during puberty and adolescence; however, some adolescents delay their sleep schedule to an extent that they become misaligned with the day-night cycle, their social schedules, and responsibilities,” said principal investigator Julio Fernandez-Mendoza, who is a professor and clinical psychologist at Penn State College of Medicine in Hershey, Pennsylvania. “Our data supports that this lack of alignment may be associated with inadequate diet and physical activity, further contributing to the obesity epidemic and poor cardiometabolic health.”
The study involved 377 adolescents from the Penn State Child Cohort who had a minimum of three nights of at-home actigraphy and one night of in-lab polysomnography. These tests helped calculate their sleep midpoint and sleep regularity. Physical activity was also measured by actigraphy, and carbohydrate intake was assessed using a survey.
According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, sleep is essential to health, and healthy sleep requires adequate duration, good quality, appropriate timing and regularity, and the absence of sleep disturbances or disorders. A delayed sleep schedule, characterized by sleep timing that is later than conventional or socially acceptable timing, is more common among adolescents and young adults.
Fernandez-Mendoza noted that proper circadian alignment is necessary for the health of adolescents.
“Circadian misalignment of the sleep-wake cycle, and its associated variability in sleep duration, should be an integral part of interventions targeting poor dietary choices and sedentarism in youth,” Fernandez-Mendoza said.
This study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The research abstract was published recently in an online supplement of the journal Sleep and will be presented Wednesday, June 5, during SLEEP 2024 in Houston. SLEEP is the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, a joint venture of the AASM and the Sleep Research Society.
###
Abstract Title: Association of Circadian Misalignment with Diet and Physical Activity in Adolescents
Abstract ID: 0165
Poster Presentation Date: Wednesday, June 5, from 10-10:45 a.m. CDT, Board 19
Presenter: Pura Ballester-Navarro, Ph.D. in Bioengineering
About the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, LLC
The APSS is a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society. The APSS organizes the SLEEP annual meeting each June (sleepmeeting.org).
About the American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Established in 1975, the AASM advances sleep care and enhances sleep health to improve lives. The AASM has a combined membership of 12,000 accredited sleep centers and individuals, including physicians, scientists and other health care professionals who care for patients with sleep disorders. As the leader in the sleep field, the AASM sets standards and promotes excellence in sleep medicine health care, education and research (aasm.org).
About the Sleep Research Society
The SRS is a professional membership society that advances sleep and circadian science. The SRS provides forums for the exchange of information, establishes and maintains standards of reporting and classifies data in the field of sleep research, and collaborates with other organizations to foster scientific investigation on sleep and its disorders. The SRS also publishes the peer-reviewed, scientific journals Sleep and Sleep Advances (sleepresearchsociety.org).
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-05
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that it is common for foster caregivers to give melatonin to their child, and these children who have taken melatonin have worse sleep and more daytime behavioral problems.
Results show that 48% of foster caregivers reported administering melatonin to their child. Children given melatonin had poorer overall sleep quality compared to children not given melatonin, yet even after adjustment for sleep quality and other potential confounders, melatonin use was associated with increased severity of daytime behavioral problems in foster ...
2024-06-05
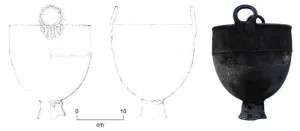
Bronze cauldrons were used by the inhabitants of the Mongolian steppe around 2,700 years ago to process animal blood and milk. This is shown by a protein analysis of archaeological finds from this period.
Scattered across the Eurasian steppe, archaeologists repeatedly come across metal cauldrons from the Bronze Age during excavations. However, it was previously unclear exactly what they were used for. Now, an international study led by researchers at the University of Basel and published in the journal Scientific Reports reveals their secret: Mongolian nomads collected blood ...
2024-06-05
Scientists have discovered genetic clues to the cause of restless leg syndrome, a condition common among older adults. The discovery could help identify those individuals at greatest risk of the condition and point to potential ways to treat it.
Restless leg syndrome can cause an unpleasant crawling sensation in the legs and an overwhelming urge to move them. Some people experience the symptoms only occasionally, while others get symptoms every day. Symptoms are usually worse in the evening or at night-time and can severely impair sleep.
Despite the condition ...
2024-06-05
Scientists have detected what they believe to be a neutron star spinning at an unprecedentedly slow rate —slower than any of the more than 3,000 radio emitting neutron stars measured to date.
Neutron stars - the ultra-dense remains of a dead star - typically rotate at mind-bendingly fast speeds, taking just seconds or even a fraction of a second to fully spin on their axis.
However, the neutron star, newly discovered by an international team of astronomers, defies this rule, emitting radio signals on a comparatively ...
2024-06-05
Even widespread species could be genomically vulnerable to the climate crisis, scientists warn. By studying the DNA of puddle frogs living in central African rainforests, the scientists found that areas of high environmental variation foster high genetic variation. If these varied habitats and the frogs that live there are lost, genetic variants that could have allowed the species to evolve to survive the climate crisis could be lost too. Meanwhile, populations with low genetic variation could become extinct quickly, unable to adapt.
“Generally, the more genomic variation within ...
2024-06-05
WASHINGTON, D.C. — June 5, 2024 — Concerns over the potential insolvency of Medicare among those under 65 have risen, with 73% now expressing worry that it won’t be available when they need it, up from 67% in 2022, according to the new West Health-Gallup 2024 Survey on Aging in America. Worry rose most amongst those aged 50 to 64, up 13 percentage points to 74%. Higher percentages of adult’s express concern about the future of Social Security, with 80% of people under 62 and 86% of people aged 40 to 49 fearing it will not be around once they are eligible.
According ...
2024-06-05
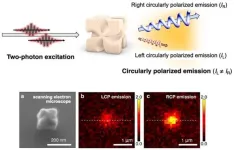
doi.org/10.1002/adom.202400699When chiral(1) gold nanoparticles(2) are irradiated with near-infrared(3) femtosecond pulses(4), visible emission of luminescence is observed. In this study, this luminescence was found to yield high selectivity for left- or right-handed circularly polarized(5) light, depending on the chirality of the nanoparticles, with a dissymmetry factor(6) of approximately 0.7. This finding suggests the potential to elevate various applications using circularly polarized light to practical levels.
Abstruct
The research group led by Project Assistant Professor Dr. Hyo-Yong AHN, ...
2024-06-05
More than 3.4 million people in the US and 65 million people worldwide have epilepsy, a neurological disorder that affects the nervous system and causes seizures. One in 26 people will develop epilepsy at some point in their lives, and 1 out of 1000 people with epilepsy die from unexpected deaths each year.
Like many conditions, epilepsy treatment starts with early detection. The World Health Organization estimates that 70% of people with epilepsy could live seizure-free if adequately diagnosed and treated.
Over the years, ...
2024-06-05
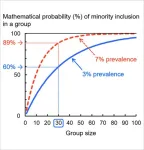
Niigata, Japan - Human society includes various minority groups. However, it is often difficult to know whether someone is a minority member simply by looking at the person, as minority traits may not be visually apparent (e.g., sexual orientation, color vision deficiency). In addition, minorities may hide their minority traits or identities. Consequently, we may have been unaware of the presence of minorities in daily life. Probabilistic thinking is critical in such uncertain situations. The people with whom we interact in our daily lives are typically a group of several dozen individuals (e.g., a school class). How do we judge the probability of including at least one minority ...
2024-06-05
DALLAS, June 4, 2024 — According to the American Heart Association, when someone suffers a cardiac arrest, immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is critical and can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. More than 350,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur in the United States each year. Of those, 90% will not survive, according to the Association, which is working to turn more bystanders into lifesavers who can use CPR in an emergency. The American Heart Association, celebrating one hundred years of lifesaving service as a global ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Teens with later sleep schedules are less active, eat more carbohydrates
Circadian rhythm misalignment is linked with sedentary behavior and higher carb consumption