(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this randomized clinical trial showed that a 15-day course of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in a population of patients with postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC) was generally safe but did not demonstrate a significant benefit for improving select PASC symptoms in a mostly vaccinated cohort with protracted symptom duration. Further studies are needed to determine the role of antivirals in the treatment of PASC.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding authors, email Linda N. Geng, M.D., Ph.D. (geng@stanford.edu) and Upinder Singh, M.D. (usingh@stanford.edu).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.2007)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being presented at the Demystifying Long COVID North American Conference 2024.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.2007?guestAccessKey=face4b31-1b6e-498a-a147-cf6a9dee6986&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=060724
END
Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and symptoms in adults with postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection
JAMA Internal Medicine
2024-06-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stanford Medicine trial:15-day Paxlovid regimen safe but adds no clear long-COVID benefit
2024-06-07
In a clinical trial conducted by Stanford Medicine investigators and their colleagues, a 15-day course of Paxlovid — an antiviral drug combination targeting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19 — proved safe as an extended-duration treatment but didn’t lessen select symptoms of the syndrome known as long COVID: the persistence, or reappearance, of COVID-related symptoms three months or more after an initial COVID-19 infection.
The findings are described in a paper to be published ...
Antioxidant gel preserves islet function after pancreas removal
2024-06-07
Northwestern University researchers have developed a new antioxidant biomaterial that someday could provide much-needed relief to people living with chronic pancreatitis.
The study will be published on June 7 in the journal Science Advances.
Before surgeons remove the pancreas from patients with severe, painful chronic pancreatitis, they first harvest insulin-producing tissue clusters, called islets, and transplant them into the vasculature of the liver. The goal of the transplant is to preserve a patient’s ability to control their own blood-glucose levels without insulin injections.
Unfortunately, the ...
Tiny new species of great ape lived in Germany 11 million years ago
2024-06-07
Ancient apes in Germany co-existed by partitioning resources in their environment, according to a study published June 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Madelaine Böhme of Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen, Germany and David R. Begun, of University of Toronto, Canada and colleagues.
The Hammerschmiede fossil site in Bavaria, Germany is best known for exceptional remains of the ancient great ape Danuvius dating to the late Miocene Epoch, 11.6 million years ago. Other experts contest the strength of the evidence to support whether Danuvius is a hominid or whether ...
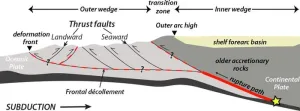
Cascadia Subduction Zone, one of Earth’s top hazards, comes into sharper focus
2024-06-07
Off the coasts of southern British Columbia, Washington, Oregon and northern California lies a 600 mile-long strip where the Pacific Ocean floor is slowly diving eastward under North America. This area, called the Cascadia Subduction Zone, hosts a megathrust fault, a place where tectonic plates move against each other in a highly dangerous way. The plates can periodically lock up and build stress over wide areas―eventually to be released when they finally lurch against each other. The result: the world’s greatest earthquakes, shaking both seabed and land, and generating tsunamis 100 feet high or more. Such a fault ...
Unlocking another piece of the Parkinson’s puzzle – scientists reveal workings of vital molecular switch
2024-06-07
Scientists at the University of Dundee have uncovered the inner relay of a molecular switch that protects the brain against the development of Parkinson’s disease.
The research provides new potential strategies to develop drugs that may benefit patients with Parkinson’s.
Parkinson’s is the fastest growing brain disorder in the world, however, there are currently no treatments that can slow or arrest the condition.
Previous research conducted at the University had found a gene called PINK1 is central to protecting brain cells against stress. In patients ...
A protein that enables smell—and stops cell death
2024-06-07
While smell plays a considerable role in the social interactions of humans—for instance, signaling fear or generating closeness—for ants, it is vitally important. Researchers from New York University and the University of Florida found that a key protein named Orco, essential for the function of olfactory cells, is also critical for the cells’ survival in ants.
Their study showed that mutating the orco gene in Harpegnathos saltator jumping ants dramatically decreased the number of olfactory neurons, suggesting that Orco is necessary for the development and life of these cells. The findings, published in Science Advances, offer insights into the cellular ...
New research finds lake under Mars ice cap unlikely
2024-06-07
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have provided a simple and comprehensive – if less dramatic – explanation for bright radar reflections initially interpreted as liquid water beneath the ice cap on Mars’ south pole.
Their simulations show that small variations in layers of water ice – too subtle for ground-penetrating radar instruments to resolve – can cause constructive interference between radar waves. Such interference can produce reflections whose intensity and variability match observations to date – not only in the area proposed to be liquid water, but across the so-called south ...
Study shows link between photo filter use and muscle dysmorphia among teens, young adults
2024-06-07
Toronto, ON, Canada - A new study conducted by researchers at the University of Toronto has unveiled a significant association between the use of photo filters on social media and increased symptoms of muscle dysmorphia among adolescents and young adults in Canada. This study, which analyzed data from 912 participants from the Canadian Study of Adolescent Health Behaviors, emphasizes the growing concern over the impact of digital image manipulation on body image and mental health.
The research reveals that the use of photo filters, commonly found on apps like Snapchat, Instagram, and TikTok, is linked to greater muscle dysmorphia symptomatology, a condition marked ...
Mushroom stump waste could be inexpensive, healthy chicken feed supplement
2024-06-07
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Feed costs for producing broiler chickens accounts for 60% to 70% of total production costs, and stump waste from the production of button mushrooms comprises nearly 30% of total mushroom weight. Marrying the two has the potential to reduce both cost and waste, especially in Pennsylvania, which is a national leader in the production of broiler chickens and button mushrooms.
To learn whether the two are compatible, a team of Penn State researchers conducted a new study to determine how supplementing the feed of broilers with mushroom stump waste affected the growth and health of the chickens.
In findings ...
Simply looking at the natural world in urban areas can reap benefits
2024-06-07
New eye-tracking research has shown that simply looking at natural elements during urban walks can offer significant mental health benefits.
The study, by Bangor University and Technion- Israel Institute of Technology, published in the scientific journal People and Nature, involved city-dwellers, and showed how paying visual attention to greenery, rather than human-made structures, can alleviate anxiety and enhance restorative feelings.
The 117 urban residents who took part in the study, were guided on a 45-minute urban walk, while wearing eye-tracking ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and symptoms in adults with postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infectionJAMA Internal Medicine