Sweetpotato’s sweet revenge
Scientists identify key pathogen targets to tackle black rot
2024-06-12
(Press-News.org) Sweetpotato black rot is a devastating disease caused by the fungus Ceratocystis fimbriata. Since the late 1800s, black rot of sweetpotato has threatened to destroy as much as 30% of the sweetpotato crop in the United States. In 2015, all sweetpotato-producing states in the United States experienced one of the worst outbreaks recorded in history, with up to 60% losses reported. While fungicides can help manage the disease, they are not a sustainable solution, especially with volatile restrictions on fungicide residues among major export markets. An additional management strategy is effector-assisted breeding—a novel approach to developing disease-resistant crops.
Effectors are secreted proteins from pathogens that modulate their plant hosts at the molecular and cellular levels. Instead of traditional breeding methods, which can take many years and involve extensive trial and error, effector-assisted breeding uses specific effectors from the pathogen to quickly identify and select plants that have resistance to the disease. This will accelerate breeding programs, leading to the development of black rot–resistant sweetpotato varieties and the reduction of crop losses.
Until now, researchers had limited knowledge of C. fimbriata biology, thus creating a barrier in managing this disease. To address this, researcher Camilo Parada-Rojas from Lina Quesada-Ocampo’s lab at North Carolina State University and colleagues focused on identifying the effector proteins produced by C. fimbriata during infection. The study, published in Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions (MPMI), identified 31 C. fimbriata effector genes. By cataloging these effectors, researchers can better understand how the fungus infects sweetpotato and identify potential host targets for breeding resistant varieties. Additionally, the study suggests a biotrophic phase, in which the fungus lives off living sweetpotato storage roots before killing it, providing a new perspective on how the disease progresses.
This research provides pioneering knowledge on C. fimbriata’s biology and highlights potential targets for effector-assisted breeding. While the findings are promising, practical applications in disease control and plant breeding will require more time and research. Parada-Rojas states, “It's a long journey from basic research to real-world application, but the potential to make a significant impact on crop resilience and food security makes it incredibly rewarding.” In the meantime, the study's insights into pathogen evolution and stability can inform disease monitoring, helping to track and manage the spread of C. fimbriata more effectively—taking science one step closer to futureproofing sweetpotato.
For additional details, read “Effector Repertoire of the Sweetpotato Black Rot Fungal Pathogen Ceratocystis fimbriata” published in Volume 37, Number 3 of MPMI.
Follow the authors on X
Camilo Parada-Rojas: @cahuparo
Lina Quesada-Ocampo: @LinaQuesadaO
Quesada Lab: @QuesadaLabNCSU
About Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions (MPMI)
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions® (MPMI) is a gold open access journal that publishes fundamental and advanced applied research on the genetics, genomics, molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics of pathological, symbiotic, and associative interactions of microbes, insects, nematodes, or parasitic plants with plants.
Follow us on X @MPMIjournal and visit https://apsjournals.apsnet.org/journal/mpmi to learn more.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-12
Gray whales that spend their summers feeding in the shallow waters off the Pacific Northwest coast have undergone a significant decline in body length since around the year 2000, a new Oregon State University study found.
The smaller size could have major consequences for the health and reproductive success of the affected whales, and also raises alarm bells about the state of the food web in which they coexist, researchers say.
“This could be an early warning sign that the abundance of this population is starting to decline, or is not healthy,” said K.C. Bierlich, co-author on the study and an assistant professor at OSU’s ...
2024-06-12
Shelter dogs awaiting adoption fare better with a canine companion than when they’re housed alone, according to new research from Virginia Tech.
The study, led by Erica Feuerbacher, associate professor in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences’ School of Animal Sciences, revealed that companiable dogs housed together showed fewer signs of stress and were adopted more quickly than dogs that were housed by themselves.
Nearly 4 million dogs enter shelters every year, according to the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals. The study’s findings offer one possible solution for animal shelters ...
2024-06-12
Thousands of years ago, people in ancient Syria likely ate mostly grains, grapes, olives and a small amount of dairy and meat — similar to today’s “Mediterranean diet,” according to a study published June 12 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Benjamin T. Fuller from the University of Leuven, Belgium, Simone Riehl from the University of Tübingen, Germany, and colleagues.
Tell Tweini, an archeological site located near the Syrian coastal city of Jableh, contains relics dating ...
2024-06-12
The Greek island of Aegina was home to a Late Bronze Age purple dye workshop, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Lydia Berger of Paris Lodron University of Salzburg, Austria and colleagues.
Colored dyes were a significant commodity in the Mediterranean region during the Late Bronze Age, and understanding the production of these dyes is valuable for interpretations of culture and trade at the time. In this study, Berger and colleagues describe the site of a purple dye workshop from the 16th century BC located at Aegina Kolonna in the Saronic Gulf.
The presence of a dye workshop at this site is inferred from three main lines of ...
2024-06-12
Housing compatible shelter dogs together could reduce stress and might help them find homes sooner
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0301137
Article Title: Effects of single- or pair-housing on the welfare of shelter dogs: Behavioral and physiological indicators
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The current research was funded by a grant to ENF from the Waltham Foundation (grant number) www.waltham.com. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to ...
2024-06-12
When the TV show Neighbours ended, surveyed fans experienced strong grief, loss, and sometimes a lack of closure - implying that strong "parasocial" relationships link TV viewers and favorite shows
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302160
Article Title: When TV neighbours become good friends: Understanding Neighbours fans’ feelings of grief and loss at the end of the series
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: The author received no ...
2024-06-12
Some honeybees learn tasks better than others, and gene expression patterns in their brains may be associated with this difference in ability
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304563
Article Title: Behavioral and genetic correlates of heterogeneity in learning performance in individual honeybees, Apis mellifera
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
2024-06-12
Including “tactile emoticons” into social media communications can enhance communication, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Alkistis Saramandi and Yee Ki Au from University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues.
Digital communications rely exclusively on visual and auditory cues (text, emoticons, videos, and music) to convey tone and emotion. Currently lacking from these platforms is touch, which can convey feelings of love and support, impact emotions, and influence behaviors. Technology companies are developing devices to incorporate touch into digital interactions, such as interactive kiss ...
2024-06-12
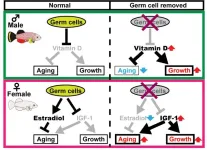
Osaka, Japan – Women live longer than men. This isn’t unique to humans, either; we see this trend in a wide range of other animals. Biologists have theorized that the discrepancy in life expectancy between sexes might be partly related to reproduction, but how?
In a study published in Science Advances, researchers from Osaka University have discovered for the first time that germ cells, the cells that develop into eggs in females and sperm in males, drive sex-dependent lifespan differences in vertebrate animals.
The researchers ...
2024-06-12
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed microscopic robots, known as microrobots, capable of swimming through the lungs to deliver cancer-fighting medication directly to metastatic tumors. This approach has shown promise in mice, where it inhibited the growth and spread of tumors that had metastasized to the lungs, thereby boosting survival rates compared to control treatments.
The findings are detailed in a paper published on June 12 in Science Advances.
The microrobots are an ingenious combination of biology ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Sweetpotato’s sweet revenge
Scientists identify key pathogen targets to tackle black rot