(Press-News.org) Scientists from the University of Copenhagen have made significant strides in understanding ancient ocean anoxia, with potential insights for today's marine environments.
500 million years ago the so-called Cambrian ‘SPICE’ event made oxygen levels in the oceans drop dramatically.
Now, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have investigated how large-scale ocean anoxia, or oxygen-depleted conditions, developed during the event, and its potential consequences today.
In the study, titled "Cascading oxygen loss shorewards in the oceans – insights from the Cambrian SPICE event" published in OneEarth researchers found that a chain reaction involving phosphorus recycling from ocean sediments played a key role in this decline of the oxygen levels in the oceans.
“Under anoxic conditions, phosphorus is released more efficiently from sediments, which further depleted oxygen levels and expanded anoxia at the global scale,” says Associate Professor Tais W. Dahl at the Globe Institute, senior author of the study. He adds:
“This self-amplifying loop led to a rapid and prolonged marine anoxia. The study warns that the feedback loop is still looming in today's oceans, where human activities might influence nutrient dynamics in ways that increase the risk setting off cascading anoxic conditions. Coastal zones, in particular, could be susceptible to anoxia that might propagate on a larger scale.”.
While global-scale anoxia is not an immediate threat today due to limited phosphorus resources and high atmospheric oxygen levels, the study highlights the importance of understanding nutrient dynamics and sedimentation processes, particularly in coastal zones. These insights are crucial for managing the health of marine ecosystems and their resident animal species.
By comparing ancient and modern marine systems, this study provides valuable insights into the potential evolution of ocean chemistry today. Emphasizing the importance of historical context, the research aims to improve predictive models and guide policy decisions to safeguard marine ecosystems and ensure their resilience in the face of ongoing environmental changes.
For more information, contact:
University of Copenhagen
Tais W. Dahl
Tais.dahl@sund.ku.dk
+45 3532 2356
About the University of Copenhagen:
The University of Copenhagen is a leading research and education institution, committed to advancing knowledge through high-quality research and innovative teaching. The university fosters an environment where academic excellence can thrive, contributing significantly to society through impactful research findings.
About the Globe Institute:
The Globe Institute is part of the Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen. The Institute’s main purpose is to address basic scientific questions through interdisciplinary approaches. The institute operates at the intersection of natural and medical sciences and the humanities.
END
Scientists document self-propelling oxygen decline in the oceans
2024-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Activating molecular target reverses multiple hallmarks of aging
2024-06-21
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have demonstrated that therapeutically restoring ‘youthful’ levels of a specific subunit of the telomerase enzyme can significantly reduce the signs and symptoms of aging in preclinical models. If these findings are confirmed in clinical studies, there may be therapeutic implications for age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, heart disease and cancer.
The study, published today in Cell, identified a small molecule compound ...
Cannabis use tied to increased risk of severe COVID-19
2024-06-21
As the deadly disease that came to be known as COVID-19 started spreading in late 2019, scientists rushed to answer a critical question: Who is most at risk?
They quickly recognized that a handful of characteristics — including age, smoking history, high body mass index (BMI) and the presence of other diseases such as diabetes — made people infected with the virus much more likely to become seriously ill and even die. But one suggested risk factor remains unconfirmed more than four years later: cannabis use. Evidence has emerged over time indicating both ...
How to make ageing a ‘fairer game’ for all wormkind
2024-06-21
Why do some people live for longer than others? The genes in our DNA sequence are important, helping avoid disease or maintain general health, but differences in our genome sequence alone explain less than 30% of the natural variance of human life expectancy.
Exploring how ageing is influenced at the molecular level could shed light on lifespan variation, but generating data at the speed, scale and quality necessary to study this in humans is unfeasible. Instead, researchers turn to worms (Caenorhabditis elegans). Humans share a lot of biology with these small creatures, who also have a large, natural variation in lifespan.
Researchers ...
Supporting the right small changes can have big impacts
2024-06-21
Small changes in our everyday actions can trigger significant, rapid societal shifts especially when it comes to climate action. A new IIASA-led study highlights the importance of analyzing these dynamics with a comprehensive framework to harness their full potential for reducing carbon emissions.
Making small changes in how we live day-to-day can quickly create significant changes in society, especially in ways that benefit the environment. This idea is captured in the term social tipping points.
According to the authors of a new paper just published in the journal One Earth, social tipping points are crucial for speeding up efforts to reduce carbon emissions. These points occur when ...
Grafted cucumbers get a boost: pumpkin's secret to withstanding salinity
2024-06-21
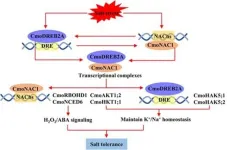
A pivotal study has discovered a genetic synergy between pumpkin and cucumber that fortifies the latter's resilience against salinity. The research illuminates the role of the CmoDREB2A transcription factor from pumpkin, which, when interacted with cucumber's CmoNAC1, forms a regulatory loop that enhances salt tolerance. This breakthrough could be key to developing crops that thrive in saline soils, safeguarding agricultural productivity.
Soil salinity, a silent blight on global agriculture, affects an estimated 10% of the world's arable land, leading to significant crop ...
Unlocking broccoli's genome: key to enhanced health benefits
2024-06-21
A detailed genomic study of broccoli has revealed the genetic foundations for the production of glucosinolates (GSLs), compounds celebrated for their health benefits, including anti-carcinogenic properties. By assembling a high-quality chromosome-level genome, researchers identified key genes involved in GSL biosynthesis. These findings offer critical insights for future genetic studies and the development of Brassica crops with enhanced nutritional value, paving the way for improved health benefits from these widely consumed vegetables.
Broccoli is renowned for its health benefits, primarily due to its rich glucosinolate (GSL) content, which has anti-carcinogenic ...
New insights into methyl jasmonate-induced saponin biosynthesis in balloon flower
2024-06-21
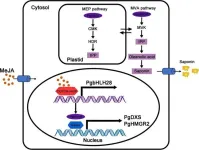
A cutting-edge study has pinpointed the PgbHLH28 gene as a crucial catalyst in the methyl jasmonate-induced (MeJA-induced) saponin biosynthesis in Platycodon grandiflorus. This genetic insight could significantly bolster the production of saponins, which are beneficial in combating cerebrovascular diseases and COVID-19, offering a novel therapeutic avenue in medicinal plant cultivation.
Platycodon grandiflorus, commonly known as balloon flower, is renowned for its medicinal properties, primarily due to its rich saponin content. Saponins are known for ...
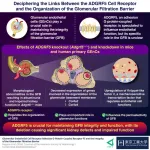
Unraveling the role of ADGRF5: Insights into kidney health and function
2024-06-21
Glomerulus, the fundamental filtering unit of the kidney, is an intricate network of capillaries — small blood vessels that regulate the movement of ions, water, and metabolites while maintaining impermeability to essential macromolecules such as proteins. The selectively permeable capillary wall, known as the glomerular filtration barrier (GFB), consists of three main components: glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs), the glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes. GEnCs line the inner surface of the capillary wall and are covered by a thin layer of glycoproteins and other carbohydrate-based moieties.
Adhesion G-protein-coupled ...
JMIR Dermatology accepted for MEDLINE indexing
2024-06-21
(Toronto, June 21, 2024) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce that JMIR Dermatology (JMIR Derm) has been accepted for inclusion in MEDLINE, which is the U.S. National Library of Medicine's premier bibliographic database.
JMIR Dermatology was previously already indexed in PubMed, but MEDLINE is a more selective subset of PubMed, consisting of the top 5200 biomedical journals, and indexing in MEDLINE also means that articles are now also indexed with NLM Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) and other metadata.
Selection for MEDLINE is a result of a thorough review of the ...
Reduced infections seen in CLL and NHL patients undergoing immunoglobulin testing and replacement therapy
2024-06-21
(WASHINGTON, June 21, 2024) – Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) who received frequent tests for immunoglobulin G (IgG) were less likely to experience severe infections compared with those who didn’t, according to a study published in Blood Advances. Moreover, only half of patients undergo such testing.
Patients with blood cancers such as CLL and NHL are at elevated risk for potentially life-threatening infections due to low blood levels of immunoglobulins — proteins ...