(Press-News.org) DETROIT -- Early memory loss has been linked to wealth loss, but research has mostly focused on investments. Four years ago, clinical geropsychologist Peter Lichtenberg, Ph.D., wondered what clues might be found in an older person’s financial decisions to indicate their vulnerability to financial victimization. Lichtenberg is director of the Institute of Gerontology at Wayne State University and a national expert in the financial exploitation of older adults. The results of his curiosity have now been published as “The WALLET Study: Financial Decision Making and Key Financial Behaviors Associated with Excess Spending” in the May 2024 issue of Clinical Gerontologist.
To answer the vulnerability question, Lichtenberg devised the WALLET (Wealth Accumulations & Later-life Losses in Early cognitive Transitions) study. WALLET takes the unique approach of analyzing a year’s worth of participants’ checking account statements for signs of excess spending and other anomalies. Results from the study’s 150 participants offer important clues about the intersection of financial risk and early memory loss.
Participants ranged in age from 59 to 96, with about half having perceived or mild cognitive impairment. All were interviewed on health status and assessed for memory function, financial decision-making and financial literacy. Excess spending was determined by subtracting budgeted expenditures from income, with negative amounts receiving a percentage score.
Lichtenberg and his team hypothesized that three factors would be significantly associated with excess spending: early memory loss, as well as scores on two scales created by Lichtenberg, the Financial Decision Rating Scale and the Financial Vulnerability Index. Early memory loss was a predictor of excess spending. The association between early memory loss and excess spending was accounted for by scores on the Financial Decision Rating Scale and the Financial Vulnerability Index.
“Financial capacity is multidimensional,” Lichtenberg said. “The WALLET study demonstrates the important links between cognitive status, other financial abilities and excess spending.”
Lichtenberg is particularly pleased with the study’s successful use of financial data from actual bank statements. “Discussion of finances is often considered taboo,” he said. Yet, his team was able to sensitively acquire copies of participant bank statements – even during the isolating years of COVID-19.
“Establishing trust with each participant was paramount to reviewing this data,” he said. “Our results show the viability of this approach, however, and especially how financial decision-making and management can impact wealth loss.” Lichtenberg will present results of the WALLET study at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference in Philadelphia on July 31.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health P30 AG015281,
Michigan Center for Urban African American Aging Research; National Institutes of Health Michigan Alzheimer’s Center Core grant #P30AG072931 and the National Institutes of Health R21AG067405.
###
About Wayne State University
Wayne State University is one of the nation’s pre-eminent public research universities in an urban setting. Through its multidisciplinary approach to research and education, and its ongoing collaboration with government, industry and other institutions, the university seeks to enhance economic growth and improve the quality of life in the city of Detroit, state of Michigan and throughout the world. For more information about research at Wayne State University, visit research.wayne.edu.
Wayne State University’s research efforts are dedicated to a prosperity agenda that betters the lives of our students, supports our faculty in pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation further, and strengthens the bonds that interconnect Wayne State and our community. To learn more about Wayne State University’s prosperity agenda, visit president.wayne.edu/prosperity-agenda.
END
Bank statements reveal clues to excessive spending and cognitive decline
2024-06-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Even very small amounts of elements in follicular fluid may impact IVF success rates, according to new study from George Mason University researcher
2024-06-24
Though exposure to “trace” (an extremely small amount) elements has been shown to affect ovarian functions in experimental studies, there has been little research on the impact of trace levels of non-essential elements, such as lead (Pb) and mercury (Hg), on female reproduction. Studies have shown that high levels of these non-essential elements may lead to decreased female fertility and reduce the likelihood of getting pregnant. Taken together, this evidence raises concern about the potential negative impact of exposure ...
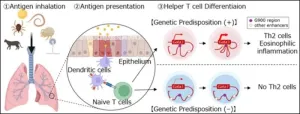
Study elucidates role of “G900” gene enhancers in asthma-associated inflammation
2024-06-24
Asthma patients experience respiratory distress due to allergens like house dust mites or pollen. However, the various triggers for asthma share a common pathway involving the release of proteins called type-2 cytokines by Type-2 helper T (Th2) cells and group-2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s). Both Th2 and ILC2 require high amounts of GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) for their maturation.
Specific gene sequences called enhancers are responsible for elevating the expression of GATA3 genes in humans. Studies have found that by controlling the production of GATA3, enhancers influence the development of Th2 and ILC2. The gene region G900, located close to ...
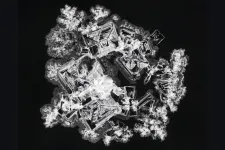
Secrets of drop stains unveiled: New FSU research decodes chemical composition from simple photos
2024-06-24
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Imagine zooming in on a dried drop of salt solution — each pattern a unique masterpiece, reminiscent of abstract art, yet no larger than the size of a penny.
New research by scientists in the Florida State University Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry uses the patterns formed by a dried salt solution to train a machine learning algorithm that can identify the chemical composition of different salts. The work will be published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“We are taking chemical fingerprints ...
New computational model of real neurons could lead to better AI
2024-06-24
Nearly all the neural networks that power modern artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT are based on a 1960s-era computational model of a living neuron. A new model developed at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Neuroscience (CCN) suggests that this decades-old approximation doesn’t capture all the computational abilities that real neurons possess and that this older model is potentially holding back AI development.
The new model developed at CCN posits that individual neurons exert more control over their surroundings than previously thought. The updated neuron model could ultimately lead to more powerful artificial neural ...
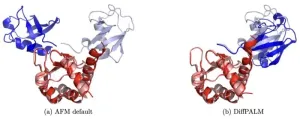
AI matches protein interaction partners
2024-06-24
Proteins are the building blocks of life, involved in virtually every biological process. Understanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for deciphering the complexities of cellular functions, and has significant implications for drug development and the treatment of diseases.
However, predicting which proteins bind together has been a challenging aspect of computational biology, primarily due to the vast diversity and complexity of protein structures. But a new study from the group of Anne-Florence Bitbol at EPFL might now change all that.
The team of scientists, ...
Navigating the labyrinth: How AI tackles complex data sampling
2024-06-24
The world of artificial intelligence (AI) has recently seen significant advancements in generative models, a type of machine-learning algorithms that “learn” patterns from set of data in order to generate new, similar sets of data. Generative models are often used for things like drawing images and natural language generation – a famous example are the models used to develop chatGPT.
Generative models have had remarkable success in various applications, from image and video generation to composing music and to language modeling. The problem ...
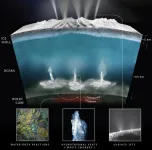
Hydrothermal vents on seafloors of ‘ocean worlds’ could support life, new study says
2024-06-24
We’ve all seen the surreal footage in nature documentaries showing hydrothermal vents on the frigid ocean floor—bellowing black plumes of super-hot water—and the life forms that cling to them. Now, a new study by UC Santa Cruz researchers suggests that lower-temperature vents, which are common across Earth's seafloor, may help to create life-supporting conditions on "ocean worlds" in our solar system.
Ocean worlds are planets and moons that have—or had in the past—a liquid ocean, often under an icy shell or within their rocky interior. In Earth's solar system, several of Jupiter's and Saturn's moons are ocean worlds, and ...
New USF study: Mindfulness and managing emotions lead to better sleep
2024-06-24
Media Contact:
John Dudley
(814) 490-3290 (cell)
jjdudley@usf.edu
TAMPA, Fla. (June 24, 2024) – Mindfulness – focusing on the present moment – can improve sleep, reduce stress and improve overall health. A new University of South Florida-led study helps explain why.
Researchers studied 144 nurses over two weeks to see how well they could stay focused on the present and how often they fixated on negative thoughts. The nurses completed surveys three times a day and reported their sleep quality the following morning.
The findings shed light on how mindfulness relates to emotion ...
JACC to serve cardiovascular community, shape future under new editor
2024-06-24
The first issue of JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology, under new Editor-in-Chief Harlan M. Krumholz, MD, SM, FACC, publishes today, ushering in a new era of one of the world’s leading scholarly journals.
“I envision JACC, with all its strengths, as a transformative platform for building community, elevating strong science, influencing clinical practice, supporting career development, and improving patient outcomes.” Krumholz said in his Editor’s Page. “JACC and its group of journals can play a pivotal role in serving our community and shaping the future.”
Under his editorship, JACC will be guided by ...
Revived technology used to count individual photons from distant galaxies
2024-06-24
Using an instrument on the 4.1-meter Southern Astrophysical Research Telescope, researchers obtained the first astronomical spectrum using skipper charge-coupled devices (CCDs).
The results were presented on June 16 at the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation meeting in Japan by Edgar Marrufo Villalpando, a physics PhD candidate at the University of Chicago and a Fermilab DOE Graduate Instrumentation Research Award Fellow.
“This is a major milestone for skipper-CCD technology,” said Alex Drlica-Wagner, a cosmologist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi ...