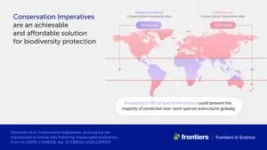
(Press-News.org) In a groundbreaking new article, a coalition of conservationists and researchers have shown how we can protect Earth’s remaining biodiversity by conserving just a tiny percentage of the planet’s surface. This affordable, achievable plan would make it possible for us to preserve the most threatened species from extinction, safeguarding Earth’s wildlife for the future.
“Most species on Earth are rare, meaning that species either have very narrow ranges or they occur at very low densities or both,” said Dr Eric Dinerstein of the NGO Resolve, lead author of the article in Frontiers in Science. “And rarity is very concentrated. In our study, zooming in on this rarity, we found that we need only about 1.2% of the Earth’s surface to head off the sixth great extinction of life on Earth.”
Prioritizing the planet
To meet ambitious conservation goals, an additional 1.2 million square kilometers of land were protected between 2018 and 2023. But do these new conservation areas effectively protect critical biodiversity? Dinerstein and his colleagues estimated that the 2018-2023 expansion only covered 0.11 million square kilometers with range-limited and threatened species. Planning protected areas is crucial, ensuring that we target our efforts and resources as effectively as possible.
The scientists started by mapping the entire world, using six layers of global biodiversity data. By combining these layers of data with maps of existing protected areas and a fractional land cover analysis, using satellite images to identify the remaining habitat available to rare and threatened species, the scientists were able to identify the most critical, currently unprotected areas of biodiversity. They called these Conservation Imperatives: a global blueprint to help countries and regions plan conservation at a more local level.
These 16,825 sites, covering approximately 164 Mha, could prevent all predicted extinctions if they were adequately protected. Just protecting the sites found in the tropics could stave off most predicted extinctions. 38% of Conservation Imperatives are also very close to already-protected areas, which could make it easier to absorb them into protected areas or to find other ways of conserving them.
“These sites are home to over 4,700 threatened species in some of the world's most biodiverse yet threatened ecosystems,” said Andy Lee of Resolve, a coauthor. “These include not only mammals and birds that rely on large intact habitats, like the tamaraw in the Philippines and the Celebes crested macaque in Sulawesi Indonesia, but also range-restricted amphibians and rare plant species.”
The cost of conservation
To calculate the price of this protection, the scientists modeled a cost estimate using data from hundreds of land protection projects over 14 years, and accounting for the type and amount of land acquired as well as country-specific economic factors. These numbers are approximate because a variety of land purchase or long-term lease options, each with different costs, might work well for protecting Conservation Imperatives. Stakeholders worldwide, including indigenous peoples, communities with jurisdiction over Conservation Imperative sites, and other members of civil society, will need to decide which options work best for them.
“Our analysis estimated that protecting the Conservation Imperatives in the tropics would cost approximately $34 billion per year over the next five years,” said Lee. “This represents less than 0.2% of the United States' GDP, less than 9% of the annual subsidies benefiting the global fossil fuel industry, and a fraction of the revenue generated from the mining and agroforestry industries each year.”
Preserving wildlife is also key to halting and reversing the climate crisis. Preserving biodiversity means protecting the Earth’s forest cover, which acts as a carbon sink: by conserving carbon-rich, wildlife-rich forested regions, we protect both threatened species and humans. While securing Conservation Imperatives is only part of the work — for example, just purchasing land won’t prevent poaching — it’s the first critical step we need to take.
“What will we bequeath to future generations? A healthy, vibrant Earth is critical for us to pass on,” said Dinerstein. “So we’ve got to get going. We’ve got to head off the extinction crisis. Conservation Imperatives drive us to do that.”
END
Scientists identify safe havens we must preserve to prevent ‘the sixth great extinction of life on Earth’
Conserving biodiversity hotspots which cover just 1.22% of the Earth’s terrestrial surface could stop extinctions in their tracks and protect the planet for future generations
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
FRONTIERS opens new call for science journalism in residency program
2024-06-25
Today, the FRONTIERS Science Journalism Initiative opens the second call for applications for its science journalism in residency programme. The application period will remain open until the 25th of September 2024, at 17:00 CEST.
Funded by the European Research Council (ERC), this initiative offers science journalists the opportunity to develop independent journalism while spending three to five months in a host research institution, located in an EU Member State or a country associated with the EU’s Horizon Europe Programme. The residency ...
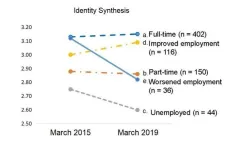
Beyond work: Employment affects identity in late 20-somethings
2024-06-25
Osaka, Japan — For people in their late 20s, “Your job doesn’t define you” is likely an unconvincing cliché.
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have unveiled critical insights into the intricate relationships between employment status, identity development and life satisfaction among Japanese individuals in late emerging adulthood, or their late 20s, highlighting the importance of stable employment during this pivotal life stage.
Their findings were published in the Journal of Youth and Adolescence on May 15.
Identity reflects a sense of self and is closely ...
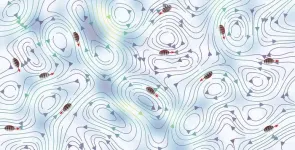
Model shows how plankton survive in a turbulent world
2024-06-25
How do particles move in turbulent fluids? The answer to this question can be found in a new model presented in a thesis from the University of Gothenburg. The model could help speed up the development of new drugs.
When you stir a glass of water, it is easy to think that any particles in the water will end up in chaos and move completely randomly. But this is not always the case. For example, the so-called active micro-swimmers can move through flow on their own. Navid Mousavi, a PhD student at the University of Gothenburg, has created a model including various hydrodynamic factors to study how these particles handle and even ...
Study: Teacher perceptions of chronically absent young students may add to the challenges of missing school
2024-06-25
Washington, June 25, 2024—A new study finds that early elementary school teachers report feeling less close to chronically absent students and view them less positively, even when those students do not cause trouble in the classroom. This “cooling down” in the relationship between teachers and their chronically absent students may exacerbate the academic challenges these children face.
The study—by Michael A. Gottfried and Phil H. Kim at the University of Pennsylvania, and Tina Fletcher at the ...
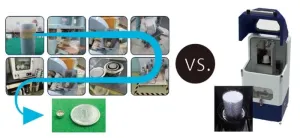
All-in-one method measures CO2 in concrete
2024-06-25
A new device can measure carbon dioxide captured in concrete more simply and in a third of the time of current methods. Researchers at the University of Tokyo worked with engineers in industry to create the boxlike device called the concrete thermal gravimetry and gas analyzer. The device heats concrete samples to almost 1,000 degrees Celsius, causing the CO2 within to be released so it can be measured. Compared to the current technique, which involves a time-consuming and complicated process of crushing concrete samples into powder for sampling, this new method is simpler, more accurate and user-friendly. The researchers hope it ...
Internet for billions in 100 countries with no current access and hope for transplant patients worldwide in new World Economic Forum emerging technologies report
2024-06-25
The World Economic Forum, in association with Frontiers, new Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2024, released today (25 June), shows that among technologies emerging globally, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) and High-Altitude Platform Systems (HAPS) have the potential to connect billions worldwide who currently have no internet access.
The report also highlights how advances in genetically engineering animal organs for use in human transplantation gives hope to the millions on waiting lists worldwide. Other technologies in the top ten that that could transform lives and societies ...
A new paradigm in photothermal therapy! DGIST developed “ultrasound-assisted photothermal therapy (ULTRA-PTT)” technology!
2024-06-25
□ Professor Jin-ho Chang’s research team from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at DGIST (President Kun-woo Lee) developed “Ultrasound-assisted photothermal therapy (ULTRA-PTT)” technology that significantly enhances the performance of conventional photothermal therapy. This technology was developed in collaboration with Senior Researcher Hye-min Kim from the Advanced Photonics Research Institute at GIST (President Ki-chul Lim) using the team’s proprietary “ultrasound-induced optical clearing” technology.
□ Phototherapy, using light, ...
Nanowires create elite warriors to enhance T cell therapy
2024-06-25
Adoptive T-cell therapy has revolutionized medicine. A patient’s T-cells — a type of white blood cell that is part of the body’s immune system — are extracted and modified in a lab and then infused back into the body, to seek and destroy infection, or cancer cells.
Now Georgia Tech bioengineer Ankur Singh and his research team have developed a method to improve this pioneering immunotherapy.
Their solution involves using nanowires to deliver therapeutic ...
Plant-sourced nitrate proves positive to human health
2024-06-25
Plant-sourced nitrate proves positive to human health
New research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has found that nitrate from plant sources is associated with a lower risk of mortality while nitrate from other sources such as animal-based foods, processed meat and tap water, is linked to a higher risk of mortality.
Nitrate, a compound found in vegetables, meat, and drinking water, has been the subject of debate due to its potential impact on health. Emerging evidence suggests that dietary nitrate may play a role in preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD), dementia, and ...
DGIST-POSTECH joint research team developed next-generation impact-resistant stretchable electronic component
2024-06-25
□ Professor Kyung-In Jang’s research team from the Department of Robotics and Mechatronics Engineering at DGIST (President Kunwoo Lee) has succeeded in developing a highly stable stretchable electronic device, which overcomes the mechanical limitations of conventional inorganic materials and enhances their stretchability and durability. In collaboration with Professor Taeho Park’s team from the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH (President Seong-Keun Kim), the research team has developed a stretchable hybrid polymer and applied it to electronic devices, enabling them to operate stably even under deformation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Scientists identify safe havens we must preserve to prevent ‘the sixth great extinction of life on Earth’Conserving biodiversity hotspots which cover just 1.22% of the Earth’s terrestrial surface could stop extinctions in their tracks and protect the planet for future generations