(Press-News.org) If aliens modified a planet in their solar system to make it warmer, we’d be able to tell. A new UC Riverside study identifies the artificial greenhouse gases that would be giveaways of a terraformed planet.
A terraformed planet has been artificially made hospitable for life. The gases described in the study would be detectable even at relatively low concentrations in the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system using existing technology. This could include the James Webb Space Telescope, or a future European-led space telescope concept.
And while such pollutant gases must be controlled on Earth to prevent harmful climate effects, there are reasons they might be used intentionally on an exoplanet.
“For us, these gases are bad because we don’t want to increase warming. But they’d be good for a civilization that perhaps wanted to forestall an impending ice age or terraform an otherwise-uninhabitable planet in their system, as humans have proposed for Mars,” said UCR astrobiologist and lead study author Edward Schwieterman.
Since these gases are not known to occur in significant quantities in nature, they must be manufactured. Finding them, therefore, would be a sign of intelligent, technology-using life forms. Such signs are called technosignatures.
The five gases proposed by the researchers are used on Earth in industrial applications such as making computer chips. They include fluorinated versions of methane, ethane, and propane, along with gases made of nitrogen and fluorine or sulfur and fluorine. A new Astrophysical Journal paper details their merits as terraforming gases.
One advantage is that they are incredibly effective greenhouse gases. Sulfur hexafluoride, for example, has 23,500 times the warming power of carbon dioxide. A relatively small amount could heat a freezing planet to the point where liquid water could persist on its surface.
Another advantage of the proposed gases — at least from an alien point of view — is that they are exceptionally long-lived and would persist in an Earth-like atmosphere for up to 50,000 years. “They wouldn’t need to be replenished too often for a hospitable climate to be maintained,” Schwieterman said.
Others have proposed refrigerant chemicals, like CFCs, as technosignature gases because they are almost exclusively artificial and visible in Earth’s atmosphere. However, CFCs may not be advantageous because they destroy the ozone layer, unlike the fully fluorinated gases discussed in the new paper, which are chemically inert.
“If another civilization had an oxygen-rich atmosphere, they’d also have an ozone layer they’d want to protect,” Schwieterman said. “CFCs would be broken apart in the ozone layer even as they catalyzed its destruction.”
As they’re more easily broken apart, CFCs are also short-lived, making them harder to detect.
Finally, the fluorinated gases have to absorb infrared radiation to have an impact on the climate. That absorption produces a corresponding infrared signature that could be detectable with space-based telescopes. With current or planned technology, scientists could detect these chemicals in certain nearby exoplanetary systems.
“With an atmosphere like Earth’s, only one out of every million molecules could be one of these gases, and it would be potentially detectable,” Schwieterman said. “That gas concentration would also be sufficient to modify the climate.”
To arrive at this calculation, the researchers simulated a planet in the TRAPPIST-1 system, about 40 light-years away from Earth. They chose this system, which contains seven known rocky planets, because it is one of the most studied planetary systems aside from our own. It is also a realistic target for existing space-based telescopes to examine.
The group also considered the European LIFE mission’s ability to detect the fluorinated gases. The LIFE mission would be able to directly image planets using infrared light, allowing it to target more exoplanets than the Webb telescope, which looks at planets as they pass in front of their stars.
This work was done in collaboration with Daniel Angerhausen at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology/PlanetS, and with researchers at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, the Blue Marble Space Institute of Science, and Paris University.
While the researchers cannot quantify the likelihood of finding these gases in the near future, they are confident that — if they are present — it is entirely possible to detect them during currently planned missions to characterize planetary atmospheres.
“You wouldn’t need extra effort to look for these technosignatures, if your telescope is already characterizing the planet for other reasons,” said Schwieterman. “And it would be jaw-droppingly amazing to find them.”
Other members of the research team echo not only enthusiasm for the potential of finding signs of intelligent life, but also for how much closer current technology has brought us to that goal.
“Our thought experiment shows how powerful our next-generation telescopes will be. We are the first generation in history that has the technology to systematically look for life and intelligence in our galactic neighborhood,” added Angerhausen.
END
Telltale greenhouse gases could signal alien activity
Detecting intelligent life that’s light years away
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study unveils formation secrets of tiny rare earth elements
2024-06-25
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin’s School of Natural Sciences have revealed a novel route to the formation of bastnäsite, a crucial mineral for the extraction of rare earth elements (REEs). Their work offers promise in one day making the extraction of these REEs more efficient.
The study – published today in the journal Nanoscale – uncovers for first time how fluocerite, a rare mineral, quickly forms and transforms into bastnäsite. The occurrence and origin of fluocerite in natural deposits was not fully understood, ...
DOE awards Sandia small business program and local veteran
2024-06-25
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — The Department of Energy has once again awarded Sandia National Laboratories for its work helping small businesses. One of those businesses, owned by a disabled veteran, was also awarded for its extraordinary work.
DOE Mentor of the Year
Sandia’s small business Mentor-Protégé Program has been named as DOE Mentor of the year, an award it has received for three consecutive years.
Now in its fifth year, the program has mentored five protégés from around the country. More than 150 volunteer mentors and support personnel help these small and disadvantaged businesses grow, succeed and navigate doing business ...
Family, friends can be more effective health role models than celebrities
2024-06-25
PULLMAN, Wash. – Your mom might be a better health influencer than Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson.
Adults in a study who said they looked to a person they knew as role model for good health—such as a friend, relative or healthcare provider—rather than a celebrity, had greater motivation to reach their health goals. The women participants were also more likely than men to choose a personal role model rather than a celebrity. And the person most often named was their own mother.
“We know that parents have a huge influence on shaping people’s health trajectories throughout their life just ...
Australia’s giant lizards help save sheep from being eaten alive
2024-06-25
Giant lizards called heath goannas could save Australian sheep farmers millions of dollars a year by keeping blowfly numbers down - and must be prioritised in conservation schemes to boost native wildlife, say researchers.
A study led by the University of Cambridge has found that heath goannas - a species of giant, scavenging lizard - act as natural clean-up crews by clearing maggot-ridden animal carcasses from the landscape.
This reduces the emergence of blowflies, which attack sheep by laying eggs on their backsides that hatch into flesh-eating maggots. The disease, known as ‘fly strike’, costs the Australian sheep farming industry an estimated $280 million a year.
This ...
New tipping point discovered beneath the Antarctic ice sheet
2024-06-25
This process is currently not included in models that predict sea level rise, so the new results could offer a more accurate picture of how the world will change with global warming and how much coastal areas will need to adapt.
Carried out by scientists at the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), the findings are published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
“We have identified the possibility of a new tipping-point in Antarctic ice sheet melting,” says Alex Bradley, an ice dynamics researcher ...
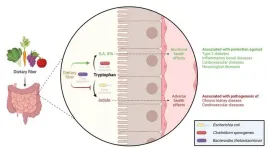
Dietary fibers make our gut bacteria behave healthy
2024-06-25
We get healthy dietary fibres from consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. But why are the fibres so good for us? A team of researchers has discovered that dietary fibres play a crucial role in determining the balance between the production of healthy and harmful substances by influencing the behaviour of bacteria in the colon.
Dietary fibres benefit our health, and scientists from DTU National Food Institute and the Department of Nutrition, Exercise and Sports at the University of Copenhagen have now uncovered an essential part of why this is the case. Different types of bacteria inside our colon compete to utilize an essential amino acid called tryptophan. This competition ...
Study links gut microbiome changes to increased risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-06-25
The largest and most ethnically and geographically comprehensive investigation to date of the gut microbiome of people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), prediabetes, and healthy glucose status has found that specific viruses and genetic variants within bacteria correspond with changes in gut microbiome function and T2D risk. Results of the study—which represents a collaboration across Brigham and Women’s Hospital (a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system), the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health—are published in Nature Medicine.
"The microbiome is highly variable across different geographic ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers present new evidence for how heat is transported below the sun’s surface
2024-06-25
Abu Dhabi, UAE, June 25, 2024: A team of solar physicists at NYU Abu Dhabi’s Center for Astrophysics and Space Science (CASS), led by Research Scientist Chris S. Hanson, Ph.D., has revealed the interior structure of the sun’s supergranules, a flow structure that transports heat from the sun’s hidden interior to its surface. The researchers’ analysis of the supergranules presents a challenge to the current understanding of solar convection.
The sun generates energy in its core through nuclear fusion; that energy is then transported to ...
Gene variant may underlie diabetes disparities: study
2024-06-25
A genetic variation common in people of African ancestry is associated with an increased risk of complications from diabetes, including diabetic retinopathy, according to a report published June 25 in the journal Nature Medicine.
The investigators found that the diagnosis of diabetes and treatment needed to prevent diabetes complications may be delayed in people who carry the variant, G6PDdef, because it is associated with reduced levels of HbA1c, a widely used clinical marker of blood glucose levels.
Testing for genetic variations that cause G6PD ...
Scientists identify safe havens we must preserve to prevent ‘the sixth great extinction of life on Earth’
2024-06-25
In a groundbreaking new article, a coalition of conservationists and researchers have shown how we can protect Earth’s remaining biodiversity by conserving just a tiny percentage of the planet’s surface. This affordable, achievable plan would make it possible for us to preserve the most threatened species from extinction, safeguarding Earth’s wildlife for the future.
“Most species on Earth are rare, meaning that species either have very narrow ranges or they occur at very low densities ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] Telltale greenhouse gases could signal alien activityDetecting intelligent life that’s light years away