(Press-News.org) This process is currently not included in models that predict sea level rise, so the new results could offer a more accurate picture of how the world will change with global warming and how much coastal areas will need to adapt.
Carried out by scientists at the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), the findings are published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
“We have identified the possibility of a new tipping-point in Antarctic ice sheet melting,” says Alex Bradley, an ice dynamics researcher at BAS and lead author of the new paper. “This means our projections of sea level rise might be significant underestimates.”
The research focuses on a region beneath an ice sheet called the grounding zone, which is where the ground-based ice meets the sea. Over time, such land-based ice moves into the surrounding ocean and eventually melts – a process that takes place around the coast of Antarctica and Greenland and is a major contributor to sea level rise.
The new study models how seawater can seep between the land and the ice sheet that rests on it, and how this affects the localised melting of the ice, lubricating the bed and influencing the speed at which it could slide towards the sea. And it looks at how this process accelerates with warming water.
“Ice sheets are very sensitive to melting in their grounding zones. We find that grounding zone melting displays a ‘tipping point like’ behaviour, where a very small change in ocean temperature can cause a very big increase in grounding zone melting, which would lead to a very big change in flow of the ice above it,” Bradley says.
This happens because warm water melting in the grounding zone of the ice sheet opens new cavities that allow further ingress of warm water, which causes more melting and bigger cavities, and so on. The tipping point comes because a small increase in the water temperature can have a very big impact on the amount of melting.
Ice melt in this way, which is currently not accounted for in the models used by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and others, could explain why ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland seem to be shrinking faster than expected, Bradley says. Including the results of the new work in such models could give more reliable estimates.
“This is missing physics, which isn't in our ice sheet models. They don't have the ability to simulate melting beneath grounded ice, which we think is happening. We're working on putting that into our models now,” he adds.
Ends
END
New tipping point discovered beneath the Antarctic ice sheet
Warm water that seeps underneath can melt ice in way not yet included in models
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dietary fibers make our gut bacteria behave healthy
2024-06-25
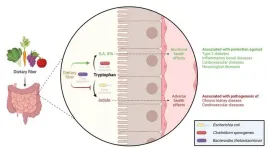
We get healthy dietary fibres from consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. But why are the fibres so good for us? A team of researchers has discovered that dietary fibres play a crucial role in determining the balance between the production of healthy and harmful substances by influencing the behaviour of bacteria in the colon.
Dietary fibres benefit our health, and scientists from DTU National Food Institute and the Department of Nutrition, Exercise and Sports at the University of Copenhagen have now uncovered an essential part of why this is the case. Different types of bacteria inside our colon compete to utilize an essential amino acid called tryptophan. This competition ...
Study links gut microbiome changes to increased risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-06-25
The largest and most ethnically and geographically comprehensive investigation to date of the gut microbiome of people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), prediabetes, and healthy glucose status has found that specific viruses and genetic variants within bacteria correspond with changes in gut microbiome function and T2D risk. Results of the study—which represents a collaboration across Brigham and Women’s Hospital (a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system), the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health—are published in Nature Medicine.
"The microbiome is highly variable across different geographic ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers present new evidence for how heat is transported below the sun’s surface
2024-06-25
Abu Dhabi, UAE, June 25, 2024: A team of solar physicists at NYU Abu Dhabi’s Center for Astrophysics and Space Science (CASS), led by Research Scientist Chris S. Hanson, Ph.D., has revealed the interior structure of the sun’s supergranules, a flow structure that transports heat from the sun’s hidden interior to its surface. The researchers’ analysis of the supergranules presents a challenge to the current understanding of solar convection.
The sun generates energy in its core through nuclear fusion; that energy is then transported to ...
Gene variant may underlie diabetes disparities: study
2024-06-25
A genetic variation common in people of African ancestry is associated with an increased risk of complications from diabetes, including diabetic retinopathy, according to a report published June 25 in the journal Nature Medicine.
The investigators found that the diagnosis of diabetes and treatment needed to prevent diabetes complications may be delayed in people who carry the variant, G6PDdef, because it is associated with reduced levels of HbA1c, a widely used clinical marker of blood glucose levels.
Testing for genetic variations that cause G6PD ...
Scientists identify safe havens we must preserve to prevent ‘the sixth great extinction of life on Earth’
2024-06-25
In a groundbreaking new article, a coalition of conservationists and researchers have shown how we can protect Earth’s remaining biodiversity by conserving just a tiny percentage of the planet’s surface. This affordable, achievable plan would make it possible for us to preserve the most threatened species from extinction, safeguarding Earth’s wildlife for the future.
“Most species on Earth are rare, meaning that species either have very narrow ranges or they occur at very low densities ...
FRONTIERS opens new call for science journalism in residency program
2024-06-25
Today, the FRONTIERS Science Journalism Initiative opens the second call for applications for its science journalism in residency programme. The application period will remain open until the 25th of September 2024, at 17:00 CEST.
Funded by the European Research Council (ERC), this initiative offers science journalists the opportunity to develop independent journalism while spending three to five months in a host research institution, located in an EU Member State or a country associated with the EU’s Horizon Europe Programme. The residency ...
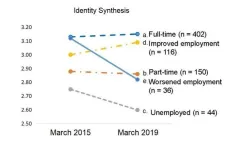
Beyond work: Employment affects identity in late 20-somethings
2024-06-25
Osaka, Japan — For people in their late 20s, “Your job doesn’t define you” is likely an unconvincing cliché.
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have unveiled critical insights into the intricate relationships between employment status, identity development and life satisfaction among Japanese individuals in late emerging adulthood, or their late 20s, highlighting the importance of stable employment during this pivotal life stage.
Their findings were published in the Journal of Youth and Adolescence on May 15.
Identity reflects a sense of self and is closely ...
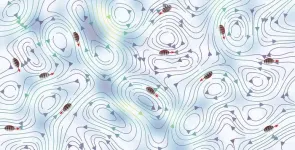
Model shows how plankton survive in a turbulent world
2024-06-25
How do particles move in turbulent fluids? The answer to this question can be found in a new model presented in a thesis from the University of Gothenburg. The model could help speed up the development of new drugs.
When you stir a glass of water, it is easy to think that any particles in the water will end up in chaos and move completely randomly. But this is not always the case. For example, the so-called active micro-swimmers can move through flow on their own. Navid Mousavi, a PhD student at the University of Gothenburg, has created a model including various hydrodynamic factors to study how these particles handle and even ...
Study: Teacher perceptions of chronically absent young students may add to the challenges of missing school
2024-06-25
Washington, June 25, 2024—A new study finds that early elementary school teachers report feeling less close to chronically absent students and view them less positively, even when those students do not cause trouble in the classroom. This “cooling down” in the relationship between teachers and their chronically absent students may exacerbate the academic challenges these children face.
The study—by Michael A. Gottfried and Phil H. Kim at the University of Pennsylvania, and Tina Fletcher at the ...
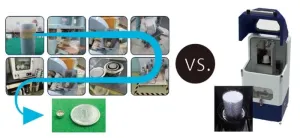
All-in-one method measures CO2 in concrete
2024-06-25
A new device can measure carbon dioxide captured in concrete more simply and in a third of the time of current methods. Researchers at the University of Tokyo worked with engineers in industry to create the boxlike device called the concrete thermal gravimetry and gas analyzer. The device heats concrete samples to almost 1,000 degrees Celsius, causing the CO2 within to be released so it can be measured. Compared to the current technique, which involves a time-consuming and complicated process of crushing concrete samples into powder for sampling, this new method is simpler, more accurate and user-friendly. The researchers hope it ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] New tipping point discovered beneath the Antarctic ice sheetWarm water that seeps underneath can melt ice in way not yet included in models