(Press-News.org) Trying to figure out whether someone has Alzheimer’s disease usually involves a battery of assessments—interviews, brain imaging, blood and cerebrospinal fluid tests. But, by then, it’s probably already too late: memories have started slipping away, long established personality traits have begun subtly shifting. If caught early, new pioneering treatments can slow the disease’s remorseless progression, but there’s no surefire way to predict who will develop the dementia associated with Alzheimer’s.
Now, Boston University researchers say they have designed a promising new artificial intelligence computer program, or model, that could one day help change that—just by analyzing a patient’s speech.
Their model can predict, with an accuracy rate of 78.5 percent, whether someone with mild cognitive impairment is likely to remain stable over the next six years—or fall into the dementia associated with Alzheimer’s disease. While allowing clinicians to peer into the future and make earlier diagnoses, the researchers say their work could also help make cognitive impairment screening more accessible by automating parts of the process—no expensive lab tests, imaging exams, or even office visits required. The model is powered by machine learning, a subset of AI where computer scientists teach a program to independently analyze data.
“We wanted to predict what would happen in the next six years—and we found we can reasonably make that prediction with relatively good confidence and accuracy,” says Ioannis (Yannis) Paschalidis, director of the BU Rafik B. Hariri Institute for Computing and Computational Science & Engineering. “It shows the power of AI.” The multidisciplinary team of engineers, neurobiologists, and computer and data scientists published their findings in Alzheimer’s & Dementia, the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
“We hope, as everyone does, that there will be more and more Alzheimer’s treatments made available,” says Paschalidis, a BU College of Engineering Distinguished Professor of Engineering and founding member of the Faculty of Computing & Data Sciences. “If you can predict what will happen, you have more of an opportunity and time window to intervene with drugs, and at least try to maintain the stability of the condition and prevent the transition to more severe forms of dementia.”
Calculating the Probability of Alzheimer’s Disease
To train and build their new model, the researchers turned to data from one of the nation’s oldest and longest-running studies—the BU-led Framingham Heart Study. Although the Framingham study is focused on cardiovascular health, participants showing signs of cognitive decline undergo regular neuropsychological tests and interviews, producing a wealth of longitudinal information on their cognitive well-being.
Paschalidis and his colleagues were given audio recordings of 166 initial interviews with people, between ages 63 and 97, diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment—76 who would remain stable for the next six years and 90 whose cognitive function would progressively decline. They then used a combination of speech recognition tools—similar to the programs powering your smart speaker—and machine learning to train a model to spot connections between speech, demographics, diagnosis, and disease progression. After training it on a subset of the study population, they tested its predictive prowess on the rest of the participants.
“We combine the information we extract from the audio recordings with some very basic demographics—age, gender, and so on—and we get the final score,” says Paschalidis. “You can think of the score as the likelihood, the probability, that someone will remain stable or transition to dementia. It had significant predictive ability.”
Rather than using acoustic features of speech, like enunciation or speed, the model is just pulling from the content of the interview—the words spoken, how they’re structured. And Paschalidis says the information they put into the machine learning program is rough around the edges: the recordings, for example, are messy—low-quality and filled with background noise. “It’s a very casual recording,” he says. “And still, with this dirty data, the model is able to make something out of it.”
That’s important, because the project was partly about testing AI’s ability to make the process of dementia diagnosis more efficient and automated, with little human involvement. In the future, the researchers say, models like theirs could be used to bring care to patients who aren’t near medical centers or to provide routine monitoring through interaction with an at-home app, drastically increasing the number of people who get screened. According to Alzheimer’s Disease International, the majority of people with dementia worldwide never receive a formal diagnosis, leaving them shut off from treatment and care.
Rhoda Au, a coauthor on the paper, says AI has the power to create “equal opportunity science and healthcare.” The study builds on the same team’s previous work, where they found AI could accurately detect cognitive impairment using voice recordings.
“Technology can overcome the bias of work that can only be done by those with resources, or care that has relied on specialized expertise that is not available to everyone,” says Au, a BU Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine professor of anatomy and neurobiology. For her, one of the most exciting findings was “that a method for cognitive assessment that has the potential to be maximally inclusive—possibly independent of age, sex/gender, education, language, culture, income, geography—could serve as a potential screening tool for detecting and monitoring symptoms related to Alzheimer’s disease.”
A Dementia Diagnosis from Home
In future research, Paschalidis would like to explore using data not just from formal clinician-patient interviews—with their scripted questions and predictable back-and-forth—but also from more natural, everyday conversations. He’s already looking ahead to a project on if AI can help diagnose dementia via a smartphone app, as well as expanding the current study beyond speech analysis—the Framingham tests also include patient drawings and data on daily life patterns—to boost the model’s predictive accuracy.
“Digital is the new blood,” says Au. “You can collect it, analyze it for what is known today, store it, and reanalyze it for whatever new emerges tomorrow.”
This research was funded, in part, by the National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and the BU Rajen Kilachand Fund for Integrated Life Science and Engineering.
Republishers are kindly reminded to uphold journalistic integrity by providing proper crediting, including a direct link back to the original source URL.
END
New AI program from BU researchers could predict likelihood of Alzheimer’s disease
By analyzing speech patterns, machine learning model can say with a high degree of accuracy whether someone with mild cognitive impairment will develop Alzheimer’s-associated dementia within six years
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Telltale greenhouse gases could signal alien activity
2024-06-25
If aliens modified a planet in their solar system to make it warmer, we’d be able to tell. A new UC Riverside study identifies the artificial greenhouse gases that would be giveaways of a terraformed planet.
A terraformed planet has been artificially made hospitable for life. The gases described in the study would be detectable even at relatively low concentrations in the atmospheres of planets outside our solar system using existing technology. This could include the James Webb Space Telescope, or a future European-led space telescope concept.
And ...
New study unveils formation secrets of tiny rare earth elements
2024-06-25
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin’s School of Natural Sciences have revealed a novel route to the formation of bastnäsite, a crucial mineral for the extraction of rare earth elements (REEs). Their work offers promise in one day making the extraction of these REEs more efficient.
The study – published today in the journal Nanoscale – uncovers for first time how fluocerite, a rare mineral, quickly forms and transforms into bastnäsite. The occurrence and origin of fluocerite in natural deposits was not fully understood, ...
DOE awards Sandia small business program and local veteran
2024-06-25
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — The Department of Energy has once again awarded Sandia National Laboratories for its work helping small businesses. One of those businesses, owned by a disabled veteran, was also awarded for its extraordinary work.
DOE Mentor of the Year
Sandia’s small business Mentor-Protégé Program has been named as DOE Mentor of the year, an award it has received for three consecutive years.
Now in its fifth year, the program has mentored five protégés from around the country. More than 150 volunteer mentors and support personnel help these small and disadvantaged businesses grow, succeed and navigate doing business ...
Family, friends can be more effective health role models than celebrities
2024-06-25
PULLMAN, Wash. – Your mom might be a better health influencer than Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson.
Adults in a study who said they looked to a person they knew as role model for good health—such as a friend, relative or healthcare provider—rather than a celebrity, had greater motivation to reach their health goals. The women participants were also more likely than men to choose a personal role model rather than a celebrity. And the person most often named was their own mother.
“We know that parents have a huge influence on shaping people’s health trajectories throughout their life just ...
Australia’s giant lizards help save sheep from being eaten alive
2024-06-25
Giant lizards called heath goannas could save Australian sheep farmers millions of dollars a year by keeping blowfly numbers down - and must be prioritised in conservation schemes to boost native wildlife, say researchers.
A study led by the University of Cambridge has found that heath goannas - a species of giant, scavenging lizard - act as natural clean-up crews by clearing maggot-ridden animal carcasses from the landscape.
This reduces the emergence of blowflies, which attack sheep by laying eggs on their backsides that hatch into flesh-eating maggots. The disease, known as ‘fly strike’, costs the Australian sheep farming industry an estimated $280 million a year.
This ...
New tipping point discovered beneath the Antarctic ice sheet
2024-06-25
This process is currently not included in models that predict sea level rise, so the new results could offer a more accurate picture of how the world will change with global warming and how much coastal areas will need to adapt.
Carried out by scientists at the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), the findings are published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
“We have identified the possibility of a new tipping-point in Antarctic ice sheet melting,” says Alex Bradley, an ice dynamics researcher ...
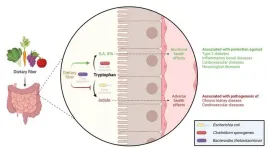
Dietary fibers make our gut bacteria behave healthy
2024-06-25
We get healthy dietary fibres from consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. But why are the fibres so good for us? A team of researchers has discovered that dietary fibres play a crucial role in determining the balance between the production of healthy and harmful substances by influencing the behaviour of bacteria in the colon.
Dietary fibres benefit our health, and scientists from DTU National Food Institute and the Department of Nutrition, Exercise and Sports at the University of Copenhagen have now uncovered an essential part of why this is the case. Different types of bacteria inside our colon compete to utilize an essential amino acid called tryptophan. This competition ...
Study links gut microbiome changes to increased risk of type 2 diabetes
2024-06-25
The largest and most ethnically and geographically comprehensive investigation to date of the gut microbiome of people with type 2 diabetes (T2D), prediabetes, and healthy glucose status has found that specific viruses and genetic variants within bacteria correspond with changes in gut microbiome function and T2D risk. Results of the study—which represents a collaboration across Brigham and Women’s Hospital (a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system), the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health—are published in Nature Medicine.
"The microbiome is highly variable across different geographic ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers present new evidence for how heat is transported below the sun’s surface
2024-06-25
Abu Dhabi, UAE, June 25, 2024: A team of solar physicists at NYU Abu Dhabi’s Center for Astrophysics and Space Science (CASS), led by Research Scientist Chris S. Hanson, Ph.D., has revealed the interior structure of the sun’s supergranules, a flow structure that transports heat from the sun’s hidden interior to its surface. The researchers’ analysis of the supergranules presents a challenge to the current understanding of solar convection.
The sun generates energy in its core through nuclear fusion; that energy is then transported to ...
Gene variant may underlie diabetes disparities: study
2024-06-25
A genetic variation common in people of African ancestry is associated with an increased risk of complications from diabetes, including diabetic retinopathy, according to a report published June 25 in the journal Nature Medicine.
The investigators found that the diagnosis of diabetes and treatment needed to prevent diabetes complications may be delayed in people who carry the variant, G6PDdef, because it is associated with reduced levels of HbA1c, a widely used clinical marker of blood glucose levels.
Testing for genetic variations that cause G6PD ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] New AI program from BU researchers could predict likelihood of Alzheimer’s diseaseBy analyzing speech patterns, machine learning model can say with a high degree of accuracy whether someone with mild cognitive impairment will develop Alzheimer’s-associated dementia within six years